
Debt is when something, usually money, is owed by one party, the borrower or debtor, to a second party, the lender or creditor. Debt is a deferred payment, or series of payments, that is owed in the future, which is what differentiates it from an immediate purchase. The debt may be owed by sovereign state or country, local government, company, or an individual. Commercial debt is generally subject to contractual terms regarding the amount and timing of repayments of principal and interest. Loans, bonds, notes, and mortgages are all types of debt. The term can also be used metaphorically to cover moral obligations and other interactions not based on economic value. For example, in Western cultures, a person who has been helped by a second person is sometimes said to owe a "debt of gratitude" to the second person.

In finance, a loan is the lending of money by one or more individuals, organizations, or other entities to other individuals, organizations etc. The recipient incurs a debt, and is usually liable to pay interest on that debt until it is repaid, and also to repay the principal amount borrowed.

A student loan is a type of loan designed to help students pay for post-secondary education and the associated fees, such as tuition, books and supplies, and living expenses. It may differ from other types of loans in the fact that the interest rate may be substantially lower and the repayment schedule may be deferred while the student is still in school. It also differs in many countries in the strict laws regulating renegotiating and bankruptcy. This article highlights the differences of the student loan system in several major countries.
Refinancing is the replacement of an existing debt obligation with another debt obligation under different terms. The terms and conditions of refinancing may vary widely by country, province, or state, based on several economic factors such as inherent risk, projected risk, political stability of a nation, currency stability, banking regulations, borrower's credit worthiness, and credit rating of a nation. In many industrialized nations, a common form of refinancing is for a place of primary residency mortgage.

In economics, consumer debt is the amount owed by consumers, as opposed to that of businesses or governments. In macroeconomic terms, it is debt which is used to fund consumption rather than investment. It includes debts incurred on purchase of goods that are consumable and/or do not appreciate.
A hire purchase (HP), known as installment plan in North America, is an arrangement whereby a customer agrees to a contract to acquire an asset by paying an initial installment and repays the balance of the price of the asset plus interest over a period of time. Other analogous practices are described as closed-end leasing or rent to own.

A financial transaction is an agreement, or communication, carried out between a buyer and a seller to exchange an asset for payment.
The Federal Home Loan Banks are 11 U.S. government-sponsored banks that provide reliable liquidity to member financial institutions to support housing finance and community investment. With their members, the FHLBanks represents the largest collective source of home mortgage and community credit in the United States.
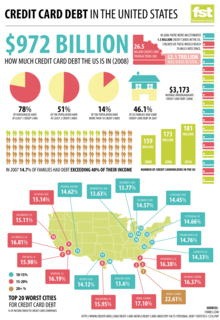
Credit card debt is an example of unsecured consumer debt, accessed through credit cards.

Citibank Limited is a licensed bank incorporated in Hong Kong.

Credit is the trust which allows one party to provide money or resources to another party wherein the second party does not reimburse the first party immediately, but promises either to repay or return those resources at a later date. In other words, credit is a method of making reciprocity formal, legally enforceable, and extensible to a large group of unrelated people.
The debt-snowball method is a debt reduction strategy, whereby one who owes on more than one account pays off the accounts starting with the smallest balances first, while paying the minimum payment on larger debts. Once the smallest debt is paid off, one proceeds to the next slightly larger small debt above that, so on and so forth, gradually proceeding to the larger ones later. This method is sometimes contrasted with the debt stacking method, also called the "debt avalanche method", where one pays off accounts on the highest interest rate first.
Payment protection insurance (PPI), also known as credit insurance, credit protection insurance, or loan repayment insurance, is an insurance product that enables consumers to ensure repayment of credit if the borrower dies, becomes ill or disabled, loses a job, or faces other circumstances that may prevent them from earning income to service the debt. It is not to be confused with income protection insurance, which is not specific to a debt but covers any income. PPI was widely sold by banks and other credit providers as an add-on to the loan or overdraft product.
Project finance is the long-term financing of infrastructure and industrial projects based upon the projected cash flows of the project rather than the balance sheets of its sponsors. Usually, a project financing structure involves a number of equity investors, known as 'sponsors', a 'syndicate' of banks or other lending institutions that provide loans to the operation. They are most commonly non-recourse loans, which are secured by the project assets and paid entirely from project cash flow, rather than from the general assets or creditworthiness of the project sponsors, a decision in part supported by financial modeling. The financing is typically secured by all of the project assets, including the revenue-producing contracts. Project lenders are given a lien on all of these assets and are able to assume control of a project if the project company has difficulties complying with the loan terms.
A cashback reward program is an incentive program operated by credit card companies where a percentage of the amount spent is paid back to the card holder. Many credit card issuers, particularly those in the United Kingdom and United States, run programs to encourage use of the card where the card holder is given points, frequent flyer miles or a monetary amount. This last benefit, a monetary amount, is usually known as cashback or cash back reward.
Student loans are a form of financial aid used to help students access higher education. Student loan debt in the United States has been growing rapidly since 2006, rising to nearly $1.4 trillion by late 2016, roughly 7.5% GDP. Approximately 43 million people have student loans, with an average balance of $30,000. Average student loan debt reached $39,400 in 2017, an increase of 6% over 2016. Americans owe more than $1.48 trillion, which is roughly $620 billion more than the overall credit card debt in the country. Loans usually must be repaid, in contrast to other forms of financial aid such as scholarships, which never have to be repaid, and grants, which rarely have to be repaid. Research indicates the increased usage of student loans has been a significant factor in college cost increases.

A credit card is a payment card issued to users (cardholders) to enable the cardholder to pay a merchant for goods and services based on the cardholder's promise to the card issuer to pay them for the amounts plus the other agreed charges. The card issuer creates a revolving account and grants a line of credit to the cardholder, from which the cardholder can borrow money for payment to a merchant or as a cash advance. In other words, credit cards combine payment services with extensions of credit. Complex fee structures in the credit card industry may limit customers' ability to comparison shop, helping to ensure that the industry is not price-competitive and helping to maximize industry profits. Due to concerns about this, many legislatures have regulated credit card fees.
A rebate card is a debit card that provides funds promised by a business as a rebate. They are often offered to those who make a specific purchase, or for loyalty to a company by accumulating a certain amount of money or number of points worth of purchases from a particular company.
Securitization is the financial practice of pooling various types of contractual debt such as residential mortgages, commercial mortgages, auto loans or credit card debt obligations and selling their related cash flows to third party investors as securities, which may be described as bonds, pass-through securities, or collateralized debt obligations (CDOs). Investors are repaid from the principal and interest cash flows collected from the underlying debt and redistributed through the capital structure of the new financing. Securities backed by mortgage receivables are called mortgage-backed securities (MBS), while those backed by other types of receivables are asset-backed securities (ABS).
FreedomPay was founded in 2000 and is currently located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. In early 2000, FreedomPay launched mobile payment "proof of concepts" with enterprises such as McDonald's, Bank of America and Visa. Later in 2004, FreedomPay delivered a closed loop payment system for stored value and voucher systems to the markets in the food service industry.






