
Developmental psychology is the scientific study of how and why human beings change over the course of their life. Originally concerned with infants and children, the field has expanded to include adolescence, adult development, aging, and the entire lifespan. Developmental psychologists aim to explain how thinking, feeling, and behaviors change throughout life. This field examines change across three major dimensions: physical development, cognitive development, and socioemotional development. Within these three dimensions are a broad range of topics including motor skills, executive functions, moral understanding, language acquisition, social change, personality, emotional development, self-concept, and identity formation.

Jean Piaget was a Swiss psychologist known for his work on child development. Piaget's theory of cognitive development and epistemological view are together called "genetic epistemology".
Psychology is an academic and applied discipline involving the scientific study of human mental functions and behavior. Occasionally, in addition or opposition to employing the scientific method, it also relies on symbolic interpretation and critical analysis, although these traditions have tended to be less pronounced than in other social sciences, such as sociology. Psychologists study phenomena such as perception, cognition, emotion, personality, behavior, and interpersonal relationships. Some, especially depth psychologists, also study the unconscious mind.
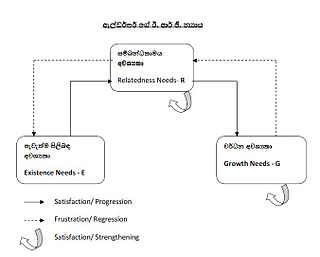
ERG theory is a theory in psychology proposed by Clayton Alderfer.
Cognitive development is a field of study in neuroscience and psychology focusing on a child's development in terms of information processing, conceptual resources, perceptual skill, language learning, and other aspects of the developed adult brain and cognitive psychology. Qualitative differences between how a child processes its waking experience and how an adult processes his/her waking experience are acknowledged. Cognitive development is defined in adult terms as the emergence of ability to consciously cognize and consciously understand and articulate their understanding. From an adult point of view, cognitive development can also be called intellectual development.

Development theory is a collection of theories about how desirable change in society is best achieved. Such theories draw on a variety of social science disciplines and approaches. In this article, multiple theories are discussed, as are recent developments with regard to these theories. Depending on which theory that is being looked at, there are different explanations to the process of development and their inequalities
James W. Fowler III was an American theologian who was Professor of Theology and Human Development at Emory University. He was director of both the Center for Research on Faith and Moral Development and the Center for Ethics until he retired in 2005. He was a minister in the United Methodist Church.
Self-actualization is a term that has been used in various psychology theories, often in different ways. The term was originally introduced by the organismic theorist Kurt Goldstein for the motive to realize one's full potential. In Goldstein's view, it is the organism's master motive, the only real motive: "the tendency to actualize itself as fully as possible is the basic drive ... the drive of self-actualization". Carl Rogers similarly wrote of "the curative force in psychotherapy – man's tendency to actualize himself, to become his potentialities ... to express and activate all the capacities of the organism". The concept was brought most fully to prominence in Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory as the final level of psychological development that can be achieved when all basic and mental needs are essentially fulfilled and the "actualization" of the full personal potential takes place, although he adapted this viewpoint later on in life, and saw it more flexibly.
Ego integrity was the term given by Erik Erikson to the last of his eight stages of psychosocial development, and used by him to represent 'a post-narcissistic love of the human ego—as an experience which conveys some world order and spiritual sense, no matter how dearly paid for'.
The model of hierarchical complexity is a framework for scoring how complex a behavior is, such as verbal reasoning or other cognitive tasks. It quantifies the order of hierarchical complexity of a task based on mathematical principles of how the information is organized, in terms of information science. This model has been developed by Michael Commons and others since the 1980s.
Positive adult development is a subfield of developmental psychology that studies positive development during adulthood. It is one of four major forms of adult developmental study that can be identified, according to Michael Commons; the other three forms are directionless change, stasis, and decline. Commons divided positive adult developmental processes into at least six areas of study: hierarchical complexity, knowledge, experience, expertise, wisdom, and spirituality.
Organismic theories in psychology are a family of holistic psychological theories which tend to stress the organization, unity, and integration of human beings expressed through each individual's inherent growth or developmental tendency. The idea of an explicitly "organismic theory" dates at least back to the publication of Kurt Goldstein's The organism: A holistic approach to biology derived from pathological data in man in 1934. Organismic theories and the "organic" metaphor were inspired by organicist approaches in biology. The most direct influence from inside psychology comes from gestalt psychology. This approach is often contrasted with mechanistic and reductionist perspectives in psychology.
Infant cognitive development is the study of how psychological processes involved in thinking and knowing develop in young children. Information is acquired in a number of ways including through sight, sound, touch, taste, smell and language, all of which require processing by our cognitive system.
Neo-Piagetian theories of cognitive development criticize and build upon Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development.






