
The president of the Philippines is the head of state, head of government and chief executive of the Philippines. The president leads the executive branch of the Philippine government and is the commander-in-chief of the Armed Forces of the Philippines.
The Congress of the Philippines is the legislature of the national government of the Philippines. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, although colloquially the term "Congress" commonly refers to just the latter, and an upper body, the Senate. The House of Representatives meets in the Batasang Pambansa in Quezon City while the Senate meets in the GSIS Building in Pasay.

The House of Representatives of the Philippines is the lower house of Congress, the bicameral legislature of the Philippines, with the Senate of the Philippines as the upper house. The lower house is usually called Congress, although the term collectively refers to both houses.

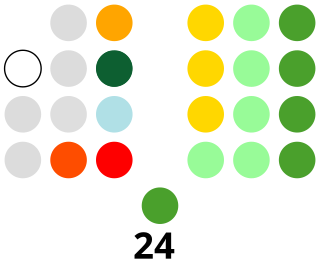
The Senate of the Philippines is the upper house of Congress of the bicameral legislature of the Philippines with the House of Representatives as the lower house. The Senate is composed of 24 senators who are elected at-large under plurality-at-large voting.

The prime minister of the Philippines was the official designation of the head of the government of the Philippines from 1978 until the People Power Revolution in 1986. During martial law and the fourth republic, the prime minister served as the head the Armed Forces of the Philippines. A limited version of this office, officially known as the President of the Council of Government, existed temporarily in 1899 during the First Philippine Republic.
The legislative districts of Aurora are the representations of the province of Aurora in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province is currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through its lone congressional district.

The legislative districts of Quezon are the representations of the province of Quezon and the highly urbanized city of Lucena in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province and the city are currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through their first, second, third, and fourth congressional districts.

The inauguration of the president of the Republic of the Philippines is a ceremony marking the commencement of the six-year term of a president of the Philippines, who is both head of state and head of government. The inauguration is performed on June 30, as mandated by the 1987 Constitution. Under the older 1935 Constitution, the date was December 30, which is also Rizal Day; the last inauguration held on the older date was Ferdinand Marcos' second one on December 30, 1969. The most recent public presidential inauguration ceremony was that of President Bongbong Marcos, who began his six-year term in office on Thursday, June 30, 2022.

The Batasang Pambansa Complex, or simply the Batasan, is the seat of the House of Representatives of the Philippines. It is located along the Batasan Road in Batasan Hills, Quezon City.

The National Museum of Fine Arts, formerly known as the National Art Gallery, is an art museum in Manila, Philippines. It is located on Padre Burgos Avenue across from the National Museum of Anthropology in the eastern side of Rizal Park. The museum, owned and operated by the National Museum of the Philippines, was founded in 1998 and houses a collection of paintings and sculptures by classical Filipino artists such as Juan Luna, Félix Resurrección Hidalgo and Guillermo Tolentino.
The Philippine presidential line of succession defines who becomes or acts as president upon the incapacity, death, resignation, or removal from office of a sitting president or a president-elect.

The 2015 State of the Nation Address was the sixth and last State of the Nation Address delivered by President Benigno Aquino III.

The 2016 State of the Nation Address was the first State of the Nation Address delivered by President Rodrigo Duterte.

The 2020 State of the Nation Address was the fifth State of the Nation Address delivered by President Rodrigo Duterte.

The 2021 State of the Nation Address was the sixth and final State of the Nation Address delivered by President Rodrigo Duterte.

The 2022 State of the Nation Address was the first State of the Nation Address that was delivered by President Bongbong Marcos on July 25, 2022 at the Batasang Pambansa Complex.

The 2023 State of the Nation Address was the second State of the Nation Address that was delivered by President Bongbong Marcos on July 24, 2023, at the Batasang Pambansa Complex.



















