
The Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, known as FR Yugoslavia or simply Yugoslavia, was a country in the Balkans that existed from 1992 to 2003, following the breakup of the SFR Yugoslavia. The Federal Republic of Yugoslavia comprised the Republic of Serbia and the Republic of Montenegro. In February 2003, FR Yugoslavia was transformed from a federal republic to a political union officially known as the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro. In 2006, Montenegro seceded from the union, leading to the full independence of Serbia and Montenegro.

Serbia, officially the Republic of Serbia is a country in the Central and Southeast Europe. It is situated in the southern Pannonian Plain and central Balkans, and borders Hungary to the north, Romania to the northeast, Bulgaria to the southeast, North Macedonia to the south, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina to the west, and Montenegro to the southwest; while claiming a border with Albania through the disputed territory of Kosovo. Serbia has a population of roughly 7 million, with Belgrade as its capital and largest city.

The United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK) is the officially mandated mission of the United Nations in Kosovo. The UNMIK describes its mandate as being to "help the United Nations Security Council achieve an overall objective, namely, to ensure conditions for a peaceful and normal life for all inhabitants of Kosovo and advance regional stability in the western Balkans."

Vojvodina is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital Belgrade and the Sava and Danube Rivers. The administrative center, Novi Sad, is the second-largest city in Serbia.

Serbia is a country situated at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the far southern edges of the Pannonian Plain and the central Balkans. It shares borders with Bosnia-Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Hungary, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Romania and Albania through the disputed territory of Kosovo. Serbia is landlocked, though it is able to access the Adriatic Sea through Montenegro and inland Europe and the Black Sea via the Danube.
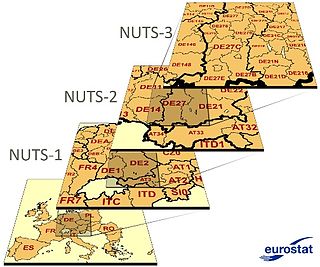
Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics or NUTS is a geocode standard for referencing the subdivisions of countries for statistical purposes. The standard, adopted in 2003, is developed and regulated by the European Union, and thus only covers the member states of the EU in detail. The Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics is instrumental in the European Union's Structural Funds and Cohesion Fund delivery mechanisms and for locating the area where goods and services subject to European public procurement legislation are to be delivered.

Central Serbia, also referred to as Serbia proper, is the region of Serbia lying outside the provinces of Vojvodina to the north and the disputed territory of Kosovo to the south. Central Serbia is a term of convenience, not an administrative division of Serbia as such, and does not have any form of separate administration.

An okrug is one of the first-level administrative divisions of Serbia, corresponding to a "district" in many other countries. The term okrug literally means "encircling", and can also be translated as "county", though it is generally rendered by the Serbian government as "district".

Šumadija is a geographical region in the central part of Serbia. The area used to be heavily covered with forests, hence the name. The city of Kragujevac is the administrative center of the Šumadija District in the Šumadija and Western Serbia statistical region.

The Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS) is a geocode standard for referencing the subdivisions of Ireland for statistical purposes. The standard is developed and regulated by the European Union. The NUTS standard is instrumental in delivering the European Union's Structural Funds. The NUTS code for Ireland is IE and a hierarchy of three levels is established by Eurostat. Below these is a further levels of geographic organisation - the local administrative unit (LAU). In Ireland, the LAUs are electoral divisions.

Serbian culture is a term that encompasses the artistic, culinary, literary, musical, political and social elements that are representative of Serbs and Serbia.
The administrative divisions of Serbia are regulated by the Government of Serbia Enactment of 29 January 1992, and by the Law on Territorial Organization adopted by the National Assembly of Serbia on 29 December 2007.

The municipalities and cities are the second level administrative subdivisions of Serbia. The country is divided into 145 municipalities and 29 cities, forming the basic level of local government.
The political status of Kosovo, also known as the Kosovo question, is the subject of a long-running political and territorial dispute between the Serbian government and the Government of Kosovo, stemming from the breakup of Yugoslavia (1991–92) and the ensuing Kosovo War (1998–99). In 1999 the administration of the province was handed on an interim basis to the United Nations under the terms of UNSCR 1244 which ended the Kosovo conflict of that year. That resolution reaffirmed the sovereignty of Serbia over Kosovo but required the UN administration to promote the establishment of 'substantial autonomy and self-government' for Kosovo pending a 'final settlement' for negotiation between the parties.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Serbia:

There are nearly 70,000 hectares of vineyards in Serbia, producing about 425,000 tons of grapes annually. The majority of Serbian wines are produced in local wineries.

Kosovo unilaterally declared independence from Serbia in 2008, a move which Serbia rejects. Serbia does not recognize Kosovo as an independent state and continues to claim it as the Autonomous Province of Kosovo and Metohija. Initially there were no relations between the two; however, in the following years there has been increased dialogue and cooperation between the two sides.

The Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS) is developed by Eurostat, and employed in Portugal for statistical purposes. The NUTS branch extends from NUTS1, NUTS2 and NUTS3 regions, with the complementary LAU sub-categorization being used to differentiate the local areas, of trans-national importance.

The Šumadija and Western Serbia is one of the five statistical regions of Serbia. It is also a level-2 statistical region according to the Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS). It was formed in 2010. The region has a total population of 2,031,697, according to the 2011 census.
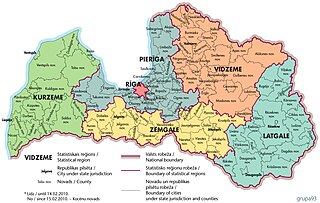
There are six statistical regions in Latvia are Kurzeme, Latgale, Pierīga, Rīga, Vidzeme and Zemgale.



















