
An administrative division, unit, entity, area or region, also referred to as a subnational entity, constituent unit, or country subdivision, is a portion of a country or other region delineated for the purpose of administration. Administrative divisions are granted a certain degree of autonomy and are usually required to manage themselves through their own local governments. Countries are divided up into these smaller units to make managing their land and the affairs of their people easier. A country may be divided into provinces, which, in turn, may be divided in whole or in part into municipalities.

The United Mexican States is a federal republic composed of 31 states and the capital, Mexico City, an autonomous entity.

A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions of municipalities, school district, or political district.

The administrative geography of the United Kingdom is complex, multi-layered and non-uniform. The United Kingdom, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe, consists of England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales. For local government in the United Kingdom, England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales each have their own system of administrative and geographic demarcation. Consequently, there is "no common stratum of administrative unit encompassing the United Kingdom".

In Nigeria, a state is a federated political entity that shares sovereignty with the federal government. There are 36 states bound together by a federal agreement. The Federal Capital Territory is not a state and under the direct control of the federal government. The states are further divided into a total of 774 Local Government Areas. Under the Nigerian Constitution, states have the power to ratify constitutional amendments.
A legislative council is the legislature, or one of the legislative chambers, of a nation, colony, or subnational division such as a province or state; or, in the United States, a council within a legislature which supervises nonpartisan legislative support staff. A member of a legislative council is commonly referred to as an MLC.
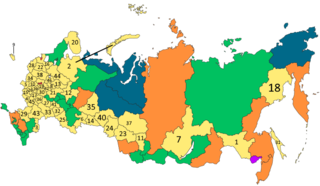
An Oblast is a type of federal subject of the Russian Federation.

A krai is a type of federal subject of Russia. The country is divided into 85 federal subjects, of which nine are krais. Oblasts, another type of federal subject, are legally identical to krais and the difference between a political entity with the name "krai" or "oblast" is purely traditional, similar to the commonwealths in the United States; both are constituent entities equivalent in legal status in Russia with representation in the Federation Council. During the Soviet era, the autonomous oblasts could be subordinated to republics or krais, but not to oblasts.

The regions of Ghana constitute the first level of subnational government administration within the Republic of Ghana. There are currently sixteen regions, further divided for administrative purposes into 216 local districts.
A state government is the government of a country subdivision in a federal form of government, which shares political power with the federal or national government. A state government may have some level of political autonomy, or be subject to the direct control of the federal government. This relationship may be defined by a constitution.
Supranational or supra-national may refer to:
A raion is a type of administrative unit of several post-Soviet states. The term is from the French "rayon", which is both a type of a subnational entity and a division of a city, and is commonly translated in English as "district".
A central government is the government that holds absolute supremacy over a unitary state. Its equivalent in a federation is the federal government, which may have distinct powers at various levels authorized or delegated to it by its federated states, though the adjective 'central' is sometimes also used to describe it.
Banner is a type of administrative division, and may more specifically refer to:
The Swiss Confederation comprises the 26 cantons of Switzerland.
The administrative divisions of India are subnational administrative units of India; they compose a nested hierarchy of country subdivisions. Indian states and territories frequently use different local titles for the same level of subdivision.

The Kallikratis Programme is the common name of Greek law 3852/2010, a major administrative reform in Greece. It brought upon the second major reform of the country's administrative divisions after the 1997 Kapodistrias reform.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.








