This article does not cite any sources .(May 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
The Super 1750 Clone was a 512 kB RAM expansion unit designed as a tiny, but compatible, third-party replacement for Commodore's then out-of-production CBM 1750 REU. Manufactured by Chip Level Designs, the Super 1750 Clone was sold by Software Support International.

Random-access memory is a form of computer data storage that stores data and machine code currently being used. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read or written in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory. In contrast, with other direct-access data storage media such as hard disks, CD-RWs, DVD-RWs and the older magnetic tapes and drum memory, the time required to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their physical locations on the recording medium, due to mechanical limitations such as media rotation speeds and arm movement.

Commodore International was an American home computer and electronics manufacturer founded by Jack Tramiel. Commodore International (CI), along with its subsidiary Commodore Business Machines (CBM), participated in the development of the home–personal computer industry in the 1970s and 1980s. The company developed and marketed the world's best-selling desktop computer, the Commodore 64 (1982), and released its Amiga computer line in July 1985. With quarterly sales ending 1983 of $49 million, Commodore was one of the world's largest personal computer manufacturers.
Commodore's RAM Expansion Unit (REU) range of external RAM add-ons for their Commodore 64/128 home computers was announced at the same time as the C128. The REUs came in three models, initially the 1700 and 1750, and later the 1764.
- Used the same MOS 8726 REC (RAM Expansion Controller) chip as the Commodore REUs.
- Worked on the C128 and the C64.
- Rather than 16 chips of 256K×1-bit DRAMs, it used four 256K×4-bit DRAMs (in ZIP packages). This gave several advantages over Commodore's original REUs:
- Less power consumption, so did not require the C64 to be upgraded with a heavy-duty power supply to use it.
- Much smaller; the plastic case was the same type used by the Epyx FastLoad cartridge.

MOS Technology, Inc., also known as CSG , was a semiconductor design and fabrication company based in Norristown, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is most famous for its 6502 microprocessor and various designs for Commodore International's range of home computers.
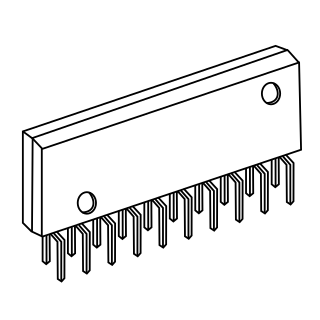
The zig-zag in-line package or ZIP is a packaging technology for integrated circuits. It was intended as a replacement for dual in-line packaging. A ZIP is an integrated circuit encapsulated in a slab of plastic with 20 or 40 pins, measuring about 3 mm x 30 mm x 10 mm. The package's pins protrude in two rows from one of the long edges. The two rows are staggered by 1.27 mm (0.05"), giving them a zig-zag appearance, and allowing them to be spaced more closely than a rectangular grid would allow. The pins are inserted into holes in a printed circuit board, with the packages standing at right-angles to the board, allowing them to be placed closer together than DIPs of the same size. ZIPs have now been superseded by surface-mount packages such as the thin small-outline packages (TSOPs) but they are still in use.

A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The primary function of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a result, power supplies are sometimes referred to as electric power converters. Some power supplies are separate standalone pieces of equipment, while others are built into the load appliances that they power. Examples of the latter include power supplies found in desktop computers and consumer electronics devices. Other functions that power supplies may perform include limiting the current drawn by the load to safe levels, shutting off the current in the event of an electrical fault, power conditioning to prevent electronic noise or voltage surges on the input from reaching the load, power-factor correction, and storing energy so it can continue to power the load in the event of a temporary interruption in the source power.















