
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of French domination over most of continental Europe. The wars stemmed from the unresolved disputes associated with the French Revolution and the French Revolutionary Wars consisting of the War of the First Coalition (1792–1797) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). The Napoleonic Wars are often described as five conflicts, each termed after the coalition that fought Napoleon: the Third Coalition (1803–1806), the Fourth (1806–1807), the Fifth (1809), the Sixth (1813–1814), and the Seventh (1815) plus the Peninsular War (1807–1814) and the French invasion of Russia (1812).

The Peninsular War (1807–1814) was the military conflict fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Spain, Portugal, and the United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars. In Spain, it is considered to overlap with the Spanish War of Independence. The war started when the French and Spanish armies invaded and occupied Portugal in 1807 by transiting through Spain, and it escalated in 1808 after Napoleonic France occupied Spain, which had been its ally. Napoleon Bonaparte forced the abdications of Ferdinand VII and his father Charles IV and then installed his brother Joseph Bonaparte on the Spanish throne and promulgated the Bayonne Constitution. Most Spaniards rejected French rule and fought a bloody war to oust them. The war on the peninsula lasted until the Sixth Coalition defeated Napoleon in 1814, and is regarded as one of the first wars of national liberation. It is also significant for the emergence of large-scale guerrilla warfare.

At the Battle of Vitoria a British, Portuguese and Spanish army under the Marquess of Wellington broke the French army under King Joseph Bonaparte and Marshal Jean-Baptiste Jourdan near Vitoria in Spain, eventually leading to victory in the Peninsular War.

The Battle of Assaye was a major battle of the Second Anglo-Maratha War fought between the Maratha Empire and the British East India Company. It occurred on 23 September 1803 near Assaye in western India. An outnumbered Indian and British force, under the command of Major General Arthur Wellesley, defeated a combined Maratha army of Daulatrao Scindia and the Bhonsle Raja of Berar. The battle was Wellesley's first major victory and the one he later described as his finest accomplishment on the battlefield, even more so than his more famous victories in the Peninsular War, and his defeat of Napoleon Bonaparte at the Battle of Waterloo.

The Battle of Corunna, in Spain known as Battle of Elviña, took place on 16 January 1809, when a French corps under Marshal of the Empire Jean de Dieu Soult attacked a British army under Lieutenant-General Sir John Moore. The battle took place amidst the Peninsular War, which was a part of the wider Napoleonic Wars. It was a result of a French campaign, led by Napoleon, which had defeated the Spanish armies and caused the British army to withdraw to the coast following an unsuccessful attempt by Moore to attack Soult's corps and divert the French army.

The Battle of Talavera was fought just outside the town of Talavera de la Reina, Spain some 120 kilometres (75 mi) southwest of Madrid, during the Peninsular War. At Talavera, an Anglo-Spanish army under Sir Arthur Wellesley combined with a Spanish army under General Cuesta in operations against French-occupied Madrid. The French army withdrew at night after several of its attacks had been repulsed.

Death to the French is a 1932 novel of the Peninsular War during the Napoleonic Wars, written by C. S. Forester, the author of the Horatio Hornblower novels. It was also published in the United States under the title Rifleman Dodd.
The Battle of Valmaseda took place on 5 November 1808, during Lieutenant-General Blake's retreat from superior French armies in northern Spain. Reinforced by veteran regular infantry from General La Romana's Division of the North, Blake's force suddenly turned on its pursuers and ambushed General Victor's errant vanguard under Général de division Villatte.

The two Battles of the Bruch(Spanish: Batallas del Bruch; Catalan: Batalles del Bruc) were engagements fought successively between French columns commanded by Brigadier General François de Schwarz and General of Division Joseph Chabran, and a body of Catalan volunteers and mercenaries led by General Antoni Franch i Estalella and Joan de la Creu Baiget, during the Peninsular War. The result of these battles and actions fought at El Bruc, near Barcelona, Catalonia, between 6–14 June 1808 was a Spanish victory.
The Battle of Tamames was lost by part of Marshal Michel Ney's French army under General of Division Jean Marchand in the Peninsular War. The French, advancing out of Salamanca, were met and defeated in battle by a Spanish army on 18 October 1809.

The Pride and the Passion is a 1957 Napoleonic-era war film in Technicolor and VistaVision from United Artists, produced and directed by Stanley Kramer, and starring Cary Grant, Frank Sinatra and Sophia Loren. The film co-stars Theodore Bikel and Jay Novello.

Agustina Raimunda Maria Saragossa i Domènech or Agustina of Aragón was a Spanish heroine who defended Spain during the Peninsular War, first as a civilian and later as a professional officer in the Spanish Army. Known as "the Spanish Joan of Arc," she has been the subject of much folklore, mythology, and artwork, including sketches by Francisco Goya and the poetry of Lord Byron.

The siege of Cádiz was a siege of the large Spanish naval base of Cádiz by a French army from 5 February 1810 to 24 August 1812 during the Peninsular War. Following the occupation of Seville, Cádiz became the Spanish seat of power, and was targeted by 70,000 French troops under the command of the Marshals Claude Victor and Nicolas Jean-de-Dieu Soult for one of the most important sieges of the war. Defending the city were 2,000 Spanish troops who, as the siege progressed, received aid from 10,000 Spanish reinforcements as well as British and Portuguese troops.

In the Siege of Almeida, Portugal, the French corps of Marshal Michel Ney captured the border fortress from Brigadier General William Cox's Portuguese garrison. This action was fought in the summer of 1810 during the Peninsular War portion of the Napoleonic Wars. Almeida is located in eastern Portugal, near the border with Spain.

At the siege of Burgos, from 19 September to 21 October 1812, the Anglo-Portuguese Army led by General Arthur Wellesley, Marquess of Wellington tried to capture the castle of Burgos from its French garrison under the command of General of Brigade Jean-Louis Dubreton. The French repulsed every attempt to seize the fortress, resulting in Wellington's withdrawal. The siege took place during the Peninsular War, part of the Napoleonic Wars. Burgos is located about 210 kilometres (130 mi) north of Madrid.
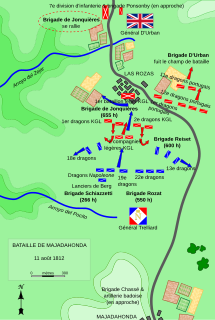
The Battle of Majadahonda saw an Imperial French cavalry division led by Anne-François-Charles Trelliard attack two brigades of cavalry under Benjamin d'Urban and forming the advance guard of Arthur Wellesley, Earl of Wellington's army. Trelliard's leading brigade routed d'Urban's Portuguese horsemen and overran three British cannons. King's German Legion (KGL) cavalry led by Eberhardt Otto George von Bock intervened to halt the Imperial French horsemen, but were finally compelled to withdraw when Trelliard committed his second and third brigades to the contest. The Imperial French cavalry was unable to cope with a KGL infantry battalion defending a village and they withdrew at the approach of additional British cavalry and infantry. This Peninsular War action was fought near Majadahonda, which is located 16 kilometres (9.9 mi) northwest of Madrid.

The First Battle of Valencia was an attack on the Spanish city of Valencia on 26 June 1808, early in the Peninsular War. Marshal Moncey's French Imperial troops failed to take the city by storm and retreated upon Madrid, leaving much of eastern Spain unconquered and beyond the reach of Napoleon.

The second siege of Badajoz saw an Anglo-Portuguese Army, first led by William Carr Beresford and later commanded by Arthur Wellesley, the Viscount Wellington, besiege a French garrison under Armand Philippon at Badajoz, Spain. After failing to force a surrender, Wellington withdrew his army when the French mounted a successful relief effort by combining the armies of Marshals Nicolas Soult and Auguste Marmont. The action was fought during the Peninsular War, part of the Napoleonic Wars. Badajoz is located 6 kilometres (4 mi) from the Portuguese border on the Guadiana River in western Spain.

Guerrilla warfare in the Peninsular War refers to the armed civilian actions carried out by non-regular troops against Napoleon's Grande Armée in Spain and Portugal during the Peninsular War. These armed men were a constant source of drain and harassment to the French army, as described by a Prussian officer fighting for the French: "Wherever we arrived, they disappeared, whenever we left, they arrived — they were everywhere and nowhere, they had no tangible center which could be attacked." The Peninsular War was significant in that it was the first to see a large-scale use of guerrilla warfare in European history and as a result of the guerrillas, Napoleon's troops were not only defeated in the Peninsular War, but tied down on the Iberian peninsula, unable to conduct military operations elsewhere on the European Continent. The strain the guerrillas caused on the French troops led Napoleon to dub the conflict the "Spanish Ulcer."

The Cavalry Regiment El Rey is the oldest cavalry regiment in the Spanish Army, distinguishing itself on several occasions during the Peninsular War. They are best known for their charge at the Battle of Talavera where they dealt the decisive blow against General Jean François Leval's German Division.


















