
In astronomy, a double planet is a binary system where both objects are of planetary mass. The term is not recognized by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) and is therefore not an official classification. At its 2006 General Assembly, the International Astronomical Union considered a proposal that Pluto and Charon be reclassified as a double planet, but the proposal was abandoned in favor of the current definition of planet. In promotional materials advertising the SMART-1 mission and pre-dating the IAU planet definition, the European Space Agency once referred to the Earth–Moon system as a double planet.
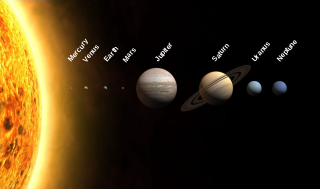
The Solar System is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it, either directly or indirectly. Of the objects that orbit the Sun directly, the largest are the eight planets, with the remainder being smaller objects, such as the five dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies. Of the objects that orbit the Sun indirectly—the moons—two are larger than the smallest planet, Mercury.

Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass one-thousandth that of the Sun, but two-and-a-half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined. Jupiter has been known to astronomers since antiquity. It is named after the Roman god Jupiter. When viewed from Earth, Jupiter can be bright enough for its reflected light to cast shadows, and is on average the third-brightest natural object in the night sky after the Moon and Venus.

A natural satellite or moon is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet or minor planet.

In astronomy, an extraterrestrial sky is a view of outer space from the surface of an astronomical body other than Earth.
A Journey in Other Worlds: A Romance of the Future is a science fiction novel by John Jacob Astor IV, published in 1894.
Many parts of the outer Solar System have been considered for possible future colonization. Most of the larger moons of the outer planets contain water ice, liquid water, and organic compounds that might be useful for sustaining human life.

Buck Rogers XXVC is a game setting created by TSR, Inc. in the late 1980s. Products based on this setting include novels, graphic novels, a role-playing game (RPG), board game, and video games. The setting was active from 1988 until 1995.

The planet Jupiter, the largest planet in the solar system, is a popular backdrop for science fiction stories and films. Early works of science fiction used Jupiter itself as a location for stories, but modern science has shown that the planet has no solid surface one could land on and that its atmosphere, temperature, high gravity and intense radiation is hostile to human life. As a result, the Jovian system as a whole, including both the space around Jupiter and its very extensive system of moons, is a more common setting for science fiction.
Titan is the largest moon of Saturn. It has a substantial atmosphere and is the most Earth-like satellite in the Solar System, making it a popular science fiction setting. Science fiction set on Titan can be roughly divided into the pre- and post-Pioneer eras, with a division set by the flyby of Saturn by the Pioneer 11 space probe on April 5, 1973, which showed that Titan's surface was too cold to sustain (Earthlike) life. Somewhat later, the arrival of Cassini–Huygens mission in 2004 with the Huygens probe's landing in 2005 showed the presence of hydrocarbon lakes on Titan, leading to further changes in its depiction in science fiction.
The Grand Tour is a series of novels written by American science fiction author Ben Bova.

The formation and evolution of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.

Jupiter's extensive system of natural satellites – in particular the four large Galilean moons – has been a common science fiction setting.

Several of Saturn's natural satellites have figured prominently in works of science fiction.
In astronomy, an inner moon or inner natural satellite is a natural satellite following a prograde, low-inclination orbit inwards of the large satellites of the parent planet. They are generally thought to have been formed in situ at the same time as the coalescence of the original planet. Neptune's moons are an exception, as they are likely reaggregates of the pieces of the original bodies, which were disrupted after the capture of the large moon Triton. Inner satellites are distinguished from other regular satellites by their proximity to the parent planet, their short orbital periods, their low mass, small size, and irregular shapes.

The magnetosphere of Jupiter is the cavity created in the solar wind by the planet's magnetic field. Extending up to seven million kilometers in the Sun's direction and almost to the orbit of Saturn in the opposite direction, Jupiter's magnetosphere is the largest and most powerful of any planetary magnetosphere in the Solar System, and by volume the largest known continuous structure in the Solar System after the heliosphere. Wider and flatter than the Earth's magnetosphere, Jupiter's is stronger by an order of magnitude, while its magnetic moment is roughly 18,000 times larger. The existence of Jupiter's magnetic field was first inferred from observations of radio emissions at the end of the 1950s and was directly observed by the Pioneer 10 spacecraft in 1973.

The exploration of Jupiter has been conducted via close observations by automated spacecraft. It began with the arrival of Pioneer 10 into the Jovian system in 1973, and, as of 2016, has continued with eight further spacecraft missions. All of these missions were undertaken by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), and all but two have been flybys that take detailed observations without the probe landing or entering orbit. These probes make Jupiter the most visited of the Solar System's outer planets as all missions to the outer Solar System have used Jupiter flybys to reduce fuel requirements and travel time. On 5 July 2016, spacecraft Juno arrived and entered the planet's orbit—the second craft ever to do so. Sending a craft to Jupiter entails many technical difficulties, especially due to the probes' large fuel requirements and the effects of the planet's harsh radiation environment.

Discovery and exploration of the Solar System is observation, visitation, and increase in knowledge and understanding of Earth's "cosmic neighborhood". This includes the Sun, Earth and the Moon, the major planets Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, their satellites, as well as smaller bodies including comets, asteroids, and dust.
The Solar System — our Sun’s system of planets, moons, and smaller debris — is humankind’s cosmic backyard. Small by factors of millions compared to interstellar distances, the spaces between the planets are daunting, but technologically surmountable

Raja yogas are Shubha ('auspicious') yogas that give success and a grand rise in career or business, and a greater degree of financial prosperity particularly during the dasha of the planets that give rise to Raja yogas. However, these results get adversely modified by the presence of other Ashubha ('inauspicious') Arista yogas. Basically, the Yoga or Raja yoga-causing planets during the course of their respective dashas confer their most auspicious results if they happen to own the lagna-bhava or the Suta-bhava or the Bhagyasthana ; the person remains healthy, wealthy, happy and successful enjoying yoga and Raja yoga results in case the lagna, the 3rd, the 6th, the 8th, the 9th and the 12th houses counted from the lagna are also not occupied by any planet, and the kendras (quadrants) are occupied only by benefic planets.

Gardens of the Sun is a 2009 science fiction novel by Paul J. McAuley. It was initially published by Gollancz on November 19, 2009 as a sequel to the 2008 novel The Quiet War.


























