Thiouracil may refer to:
| This set index page lists chemical compounds articles associated with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Thiouracil may refer to:
| This set index page lists chemical compounds articles associated with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid, is an endocrine gland in the neck, consisting of two lobes connected by an isthmus. It is found at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones, namely the two thyroid hormones (thyroxine/T4 and triiodothyronine/T3) and calcitonin. The thyroid hormones primarily influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis, but they also have many other effects, including effects on development. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis.
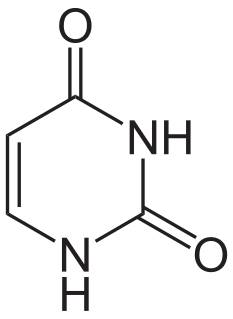
Uracil is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of RNA that are represented by the letters A, G, C and U. The others are adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine. Uracil is a demethylated form of thymine.
Phenylthiocarbamide (PTC), also known as phenylthiourea (PTU), is an organosulfur thiourea containing a phenyl ring.
ATC code H03Thyroid therapy is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the WHO for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup H03 is part of the anatomical group H Systemic hormonal preparations, excluding sex hormones and insulins.

Propylthiouracil (PTU) is a medication used to treat hyperthyroidism. This includes hyperthyroidism due to Graves' disease and toxic multinodular goiter. In a thyrotoxic crisis it is generally more effective than methimazole. Otherwise it is typically only used when methimazole, surgery, and radioactive iodine is not possible. It is taken by mouth.

Thyroid peroxidase, also called thyroperoxidase (TPO) or iodide peroxidase, is an enzyme expressed mainly in the thyroid where it is secreted into colloid. Thyroid peroxidase oxidizes iodide ions to form iodine atoms for addition onto tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin for the production of thyroxine (T4) or triiodothyronine (T3), the thyroid hormones. In humans, thyroperoxidase is encoded by the TPO gene.

Aminoallyl nucleotide is a nucleotide with a modified base containing an allylamine. They are used in post-labeling of nucleic acids by fluorescence detection in microarray. They are reactive with N-Hydroxysuccinimide ester group which helps attach a fluorescent dye to the primary amino group on the nucleotide. These nucleotides are known as 5-(3-aminoallyl)-nucleotides since the aminoallyl group is usually attached to carbon 5 of the pyrimidine ring of uracil or cytosine. The primary amine group in the aminoallyl moiety is aliphatic and thus more reactive compared to the amine groups that are directly attached to the rings (aromatic) of the bases. Common names of aminoallyl nucleosides are initially abbreviated with aa- or AA- to indicate aminoallyl. The 5-carbon sugar is indicated with or without the lowercase "d" indicating deoxyribose if included or ribose if not. Finally the nitrogenous base and number of phosphates are indicated.

A taste receptor is a type of receptor which facilitates the sensation of taste. These receptors are of four types. When food or other substances enter the mouth, molecules interact with saliva and are bound to taste receptors in the oral cavity and other locations. Molecules which give a sensation of taste are considered "sapid".

2-Thiouracil is a specific molecule consisting of a sulfated uracil.

Taste receptor type 2 member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAS2R1 gene.
Serum sickness–like reactions (SSLRs) refer to adverse reactions that have symptoms similar to those of serum sickness but in which immune complexes are not found.
The molecular formula C4H4N2OS may refer to:

Leonidas D. Marinelli, was born in Argentina and died in Hinsdale, DuPage County, Illinois was an American radiologist, health physicist and inventor.

Amphenone B, or simply amphenone, also known as 3,3-bis(p-aminophenyl)butan-2-one, is an inhibitor of steroid hormone and thyroid hormone biosynthesis which was never marketed but has been used as a tool in scientific research to study corticosteroids and the adrenal glands. It acts as competitive inhibitor of 11β-hydroxylase, 17α-hydroxylase, 17,20-lyase, 21-hydroxylase, and 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, as well as of cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme, thereby inhibiting the production of steroid hormones including glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens. In addition, amphenone B inhibits the production of thyroxine by a thiouracil-like mechanism, specifically via inhibition of organic binding of iodine and uptake of iodide by the thyroid gland.

4-Thiouracil is a heterocyclic organic compound having a pyrimidine skeleton. It is a derivative of the nucleobase uracil with a sulfur instead of oxygen in position 4.