
Agriculture is the science and art of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in cities. The history of agriculture began thousands of years ago. After gathering wild grains beginning at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers began to plant them around 11,500 years ago. Pigs, sheep and cattle were domesticated over 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. Industrial agriculture based on large-scale monoculture in the twentieth century came to dominate agricultural output, though about 2 billion people still depended on subsistence agriculture into the twenty-first.

The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations, dedicated to providing the world with an objective, scientific view of climate change, its natural, political and economic impacts and risks, and possible response options.

Kiribati, officially the Republic of Kiribati, is a sovereign state in Micronesia in the central Pacific Ocean. The permanent population is just over 110,000 (2015), more than half of whom live on Tarawa Atoll. The state comprises 32 atolls and reef islands and one raised coral island, Banaba. They have a total land area of 800 square kilometres (310 sq mi) and are dispersed over 3.5 million square kilometres. Their spread straddles both the equator and the 180th meridian, although the International Date Line goes round Kiribati and swings far to the east, almost reaching the 150°W meridian. This brings the Line Islands into the same day as the Kiribati Islands. Kiribati's easternmost islands, the southern Line Islands, south of Hawaii, have the most advanced time on Earth: UTC+14 hours.

The Kyoto Protocol is an international treaty which extends the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that (part one) global warming is occurring and (part two) it is extremely likely that human-made CO2 emissions have predominantly caused it. The Kyoto Protocol was adopted in Kyoto, Japan on 11 December 1997 and entered into force on 16 February 2005. There are currently 192 parties (Canada withdrew from the protocol, effective December 2012) to the Protocol.

The San Diego Padres are an American professional baseball team based in San Diego, California. The Padres compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) West division. Founded in 1969, the Padres have won two NL pennants — in 1984 and 1998, losing in the World Series both years. As of 2018, they have had 14 winning seasons in franchise history. The Padres are one of two Major League Baseball teams in California to originate from that state; the Athletics were originally from Philadelphia, and the Dodgers and Giants are originally from two New York City boroughs – Brooklyn and Manhattan, respectively. The Padres are the only major professional sports franchise to be located in San Diego, following the relocation of the Chargers to Los Angeles in 2017. The Padres are the only MLB team that does not share its city with another major league professional sports franchise.

The United Nations member states are the 193 sovereign states that are members of the United Nations (UN) and have equal representation in the UN General Assembly. The UN is the world's largest intergovernmental organization.
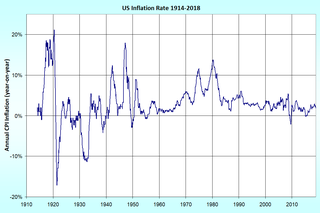
In economics, inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.
When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation reflects a reduction in the purchasing power per unit of money – a loss of real value in the medium of exchange and unit of account within the economy. A chief measure of price inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index, usually the consumer price index, over time. The opposite of inflation is deflation.

Climate change is a change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns when that change lasts for an extended period of time. Climate change can be caused by factors such as biotic processes, variations in solar radiation received by Earth, plate tectonics, and volcanic eruptions.
Daylight saving time (DST), also daylight savings time or daylight time, also summer time, is the practice of advancing clocks during summer months so that evening daylight lasts longer, while sacrificing normal sunrise times. Typically, regions that use daylight saving time adjust clocks forward one hour close to the start of spring and adjust them backward in the autumn to standard time. In effect, DST causes a lost hour of sleep in the spring and an extra hour of sleep in the fall.
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that, together, laid the foundation for classical mechanics. They describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it, and its motion in response to those forces. More precisely, the first law defines the force qualitatively, the second law offers a quantitative measure of the force, and the third asserts that a single isolated force doesn't exist. These three laws have been expressed in several ways, over nearly three centuries, and can be summarised as follows:

Mean sea level (MSL) is an average level of the surface of one or more of Earth's oceans from which heights such as elevation may be measured. MSL is a type of vertical datum – a standardised geodetic datum – that is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is the midpoint between a mean low and mean high tide at a particular location.

Social change involves alteration of the social order of a society. It may include changes in social institutions, social behaviours or social relations.
Central European Time (CET), used in most parts of Europe and a few North African countries, is a standard time which is 1 hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The time offset from UTC can be written as UTC+01:00. The same standard time, UTC+01:00, is also known as Middle European Time and under other names like Berlin Time, Warsaw Time and Romance Standard Time (RST), Paris Time or Rome Time.
The Billboard charts tabulate the relative weekly popularity of songs and albums in the United States and elsewhere. The results are published in Billboard magazine. Billboard biz, the online extension of the Billboard charts, provides additional weekly charts. There are also Year End charts. The charts may be dedicated to specific genre such as R&B, country or rock, or they may cover all genres. The charts can be ranked according to sales, streams or airplay, and for main song charts such as the Hot 100 song chart, all three pools of data are used to compile the charts. For the Billboard 200 album chart, streams and track sales are included in addition to album sales.

Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, and volume in response to a change in temperature.

The effects of global warming are the environmental and social changes caused by human emissions of greenhouse gases. There is a scientific consensus that climate change is occurring, and that human activities are the primary driver. Many impacts of climate change have already been observed, including glacier retreat, changes in the timing of seasonal events, and changes in agricultural productivity.
Anthropogenic forcing has likely contributed to some of the observed changes, including sea level rise, changes in climate extremes, declines in Arctic sea ice extent and glacier retreat.

Global warming is a long-term rise in the average temperature of the Earth's climate system, an aspect of climate change shown by temperature measurements and by multiple effects of the warming. The term commonly refers to the mainly human-caused observed warming since pre-industrial times and its projected continuation, though there were also much earlier periods of global warming. In the modern context the terms global warming and climate change are commonly used interchangeably, but climate change includes both global warming and its effects, such as changes to precipitation and impacts that differ by region. Many of the observed warming changes since the 1950s are unprecedented in the instrumental temperature record, and in historical and paleoclimate proxy records of climate change over thousands to millions of years.

Climate change denial, or global warming denial, is part of the global warming controversy. It involves denial, dismissal, or unwarranted doubt that contradicts the scientific opinion on climate change, including the extent to which it is caused by humans, its impacts on nature and human society, or the potential of adaptation to global warming by human actions. Some deniers endorse the term, while others prefer the term climate change skepticism. Several scientists have noted that "skepticism" is an inaccurate description for those who deny anthropogenic global warming. In effect, the two terms form a continuous, overlapping range of views, and generally have the same characteristics: both reject, to a greater or lesser extent, the scientific consensus on climate change. Climate change denial can also be implicit, when individuals or social groups accept the science but fail to come to terms with it or to translate their acceptance into action. Several social science studies have analyzed these positions as forms of denialism and pseudoscience.

In biology, a hermaphrodite is an organism that has complete or partial reproductive organs and produces gametes normally associated with both male and female sexes. Many taxonomic groups of animals do not have separate sexes. In these groups, hermaphroditism is a normal condition, enabling a form of sexual reproduction in which either partner can act as the "female" or "male." For example, the great majority of tunicates, pulmonate snails, opisthobranch snails, earthworms and slugs are hermaphrodites. Hermaphroditism is also found in some fish species and to a lesser degree in other vertebrates. Most plants are also hermaphrodites.
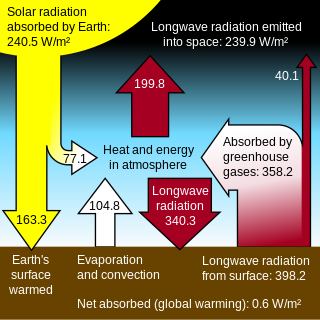
A greenhouse gas is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range. Greenhouse gases cause the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and ozone. Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface would be about −18 °C (0 °F), rather than the present average of 15 °C (59 °F). The atmospheres of Venus, Mars and Titan also contain greenhouse gases.




















