This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
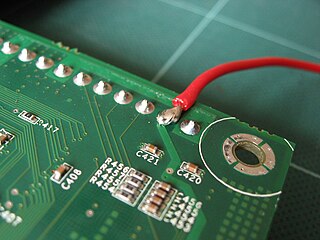
Solder is a fusible metal alloy used to create a permanent bond between metal workpieces. The word solder comes from the Middle English word soudur, via Old French solduree and soulder, from the Latin solidare, meaning "to make solid". In fact, solder must first be melted in order to adhere to and connect the pieces together after cooling, which requires that an alloy suitable for use as solder have a lower melting point than the pieces being joined. The solder should also be resistant to oxidative and corrosive effects that would degrade the joint over time. Solder used in making electrical connections also needs to have favorable electrical characteristics.
Tin(IV) chloride, also known as tin tetrachloride or stannic chloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula SnCl4.
It is a colourless hygroscopic liquid, which fumes on contact with air. It is used as a precursor to other tin compounds. It was first discovered by Andreas Libavius (1550–1616) and was known as spiritus fumans libavii.

Organotin compounds or stannanes are chemical compounds based on tin with hydrocarbon substituents. Organotin chemistry is part of the wider field of organometallic chemistry. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide ((C2H5)2SnI2), discovered by Edward Frankland in 1849. The area grew rapidly in the 1900s, especially after the discovery of the Grignard reagents, which are useful for producing Sn-C bonds. The area remains rich with many applications in industry and continuing activity in the research laboratory.

Tin(II) chloride, also known as stannous chloride, is a white crystalline solid with the formula SnCl2. It forms a stable dihydrate, but aqueous solutions tend to undergo hydrolysis, particularly if hot. SnCl2 is widely used as a reducing agent (in acid solution), and in electrolytic baths for tin-plating. Tin(II) chloride should not be confused with the other chloride of tin; tin(IV) chloride or stannic chloride (SnCl4).

Tin(II) oxide is a compound with the formula SnO. It is composed of tin and oxygen where tin has the oxidation state of +2. There are two forms, a stable blue-black form and a metastable red form.

Tin(IV) Oxide, also known as stannic oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula SnO2. The mineral form of SnO2 is called cassiterite, and this is the main ore of tin. With many other names, this oxide of tin is an important material in tin chemistry. It is a colourless, diamagnetic, amphoteric solid.
Fluoride volatility is the tendency of highly fluorinated molecules to vaporize at comparatively low temperatures. Heptafluorides, hexafluorides and pentafluorides have much lower boiling points than the lower-valence fluorides. Most difluorides and trifluorides have high boiling points, while most tetrafluorides and monofluorides fall in between. The term "fluoride volatility" is jargon used particularly in the context of separation of radionuclides.

Tin(II) sulfate (SnSO4) is a chemical compound. It is a white solid that can absorb enough moisture from the air to become fully dissolved, forming an aqueous solution; this property is known as deliquescence. It can be prepared by a displacement reaction between metallic tin and copper(II) sulfate:
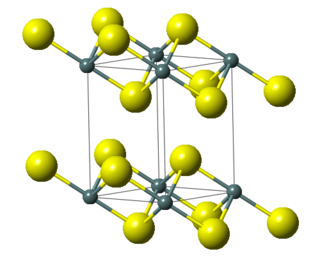
Tin(IV) sulfide is a compound with the formula SnS
2. The compound crystallizes in the cadmium iodide motif, with the Sn(IV) situated in "octahedral holes' defined by six sulfide centers. It occurs naturally as the rare mineral berndtite. It is useful as semiconductor material with band gap 2.2 eV.
Vanadium(IV) fluoride (VF4) is an inorganic compound of vanadium and fluorine. It is paramagnetic yellow-brown solid that is very hygroscopic. Unlike the corresponding vanadium tetrachloride, the tetrafluoride is not volatile because it adopts a polymeric structure. It decomposes before melting.
Tin(II) bromide is a chemical compound of tin and bromine with a chemical formula of SnBr2. Tin is in the +2 oxidation state. The stability of tin compounds in this oxidation state is attributed to the inert pair effect.

Dental amalgam is a liquid mercury and metal alloy mixture used in dentistry to fill cavities caused by tooth decay. Low-copper amalgam commonly consists of mercury (50%), silver (~22–32%), tin (~14%), copper (~8%) and other trace metals.
Tin(II) sulfide is a chemical compound of tin and sulfur. The chemical formula is SnS. Its natural occurrence concerns herzenbergite (α-SnS), a rare mineral. At elevated temperatures above 905K, SnS undergoes a second order phase transition to β-SnS (space group: cmcm, No. 63). in recent years, it has become evident that a new polymorph of SnS exist based upon the cubic crystal system, π-SnS (space group: P213, No. 198).
Fluorophosphate glass is a class of optical glasses composed of metaphosphates and fluorides of various metals. It is a variant of phosphate glasses. Fluorophosphate glasses are very unusual in nature. Fluorophosphate glasses have ultra-low theoritical loss of 0.001 dB/km, longer fluorescent lifetime of rare earths, lower coefficient of thermal expansion of ~13×10−6/°C.

Palladium(II,IV) fluoride, also known as palladium trifluoride, is a chemical compound of palladium and fluorine. It has the empirical formula PdF3, but is better described as the mixed-valence compound palladium(II) hexafluoropalladate(IV), PdII[PdIVF6] and is often written as Pd[PdF6] or Pd2F6.
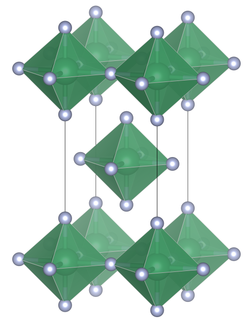
Niobium(IV) fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula NbF4; it is a nonvolatile black solid. It absorbs vapor strongly. It turns into NbO2F in moist air. NbF4 reacts with water to form a brown solution and a brown precipitate whose components are unknown. It is stable between 275 °C and 325 °C when heated in a vacuum. However, it disproportionates at 350 °C rapidly to form niobium(V) fluoride and niobium(III) fluoride:










