
The Latin American Integration Association / Asociación Latinoamericana de Integración / Associação Latino-Americana de Integração is an international and regional scope organization. It was created on 12 August 1980 by the 1980 Montevideo Treaty, replacing the Latin American Free Trade Association (LAFTA/ALALC). Currently, it has 13 member countries, and any of the Latin American States may apply for accession.

Jamaica has diplomatic relations with most nations and is a member of the United Nations and the Organization of American States. Jamaica chairs the Working Group on smaller Economies.

Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage, transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic beverages. The word is also used to refer to a period of time during which such bans are enforced.

The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) was established in 1964 as a permanent intergovernmental body.

The prohibition of drugs through sumptuary legislation or religious law is a common means of attempting to prevent the recreational use of certain intoxicating substances.

A trade agreement is a wide-ranging taxes, tariff and trade treaty that often includes investment guarantees. When two or more countries agree on terms that helps them trade with each other. The most common trade agreements are of the preferential and free trade types are concluded in order to reduce tariffs, quotas and other trade restrictions on items traded between the signatories.
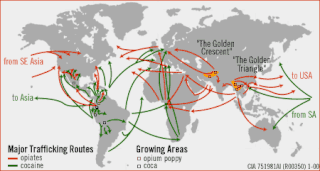
The illegal drug trade or drug trafficking is a global black market dedicated to the cultivation, manufacture, distribution and sale of drugs that are subject to drug prohibition laws. Most jurisdictions prohibit trade, except under license, of many types of drugs through the use of drug prohibition laws.
The Generalized System of Preferences, or GSP, is a preferential tariff system which provides tarriff reduction on various products. The concept of gsp is very different from the concept of mfn .MFN status provides equal treeatment in the case of tarriff being imposed by a nation but in case of gsp differential tarriff could be imposed by a nation on various country whether it is a developed country or a developing country. Both the rules comes under the purview of wto.

Rum-running, or bootlegging, is the illegal business of transporting (smuggling) alcoholic beverages where such transportation is forbidden by law. Smuggling usually takes place to circumvent taxation or prohibition laws within a particular jurisdiction. The term rum-running is more commonly applied to smuggling over water; bootlegging is applied to smuggling over land.
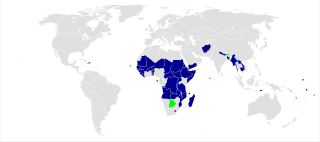
Everything but Arms (EBA) is an initiative of the European Union under which all imports to the EU from the Least Developed Countries are duty-free and quota-free, with the exception of armaments. EBA entered into force on 5 March 2001. There were transitional arrangements for bananas, sugar and rice until January 2006, July 2009 and September 2009 respectively. The EBA is part of the EU Generalized System of Preferences (GSP).

A preferential trade area is a trading bloc that gives preferential access to certain products from the participating countries. This is done by reducing tariffs but not by abolishing them completely. A PTA can be established through a trade pact. It is the first stage of economic integration. The line between a PTA and a free trade area (FTA) may be blurred, as almost any PTA has a main goal of becoming a FTA in accordance with the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade.
The Linder hypothesis is an economics conjecture about international trade patterns: The more similar the demand structures of countries, the more they will trade with one another. Further, international trade will still occur between two countries having identical preferences and factor endowments.
The Agreement on Trade-Related Investment Measures (TRIMs) are rules that are applicable to the domestic regulations a country applies to foreign investors, often as part of an industrial policy. The agreement, concluded in 1994, was negotiated under the WTO's predecessor, the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), and came into force in 1995. The agreement was agreed upon by all members of the World Trade Organization. Trade-Related Investment Measures is one of the four principal legal agreements of the WTO trade treaty.
A drug policy is the policy, usually of a government, regarding the control and regulation of drugs considered dangerous, particularly those that are addictive. Governments try to combat drug addiction with policies that address both the demand and supply of drugs, as well as policies that mitigate the harms of drug abuse, and for medical treatment. Demand reduction measures include prohibition, fines for drug offenses, incarceration for persons convicted for drug offenses, treatment, awareness campaigns, community social services, and support for families. Supply side reduction involves measures such as enacting foreign policy aimed at eradicating the international cultivation of plants used to make drugs and interception of drug trafficking. Policies that help mitigate drug abuse include needle exchange and drug substitution programs, and free facilities for testing a drug's purity.
The 1923 Alberta prohibition plebiscite, held on November 5, 1923, was a province-wide plebiscite held in Alberta, Canada, to allow alcoholic beverages, triggered by an affirmative vote in the Legislative Assembly of Alberta, based on the presentation of a 56,000-name petition in accordance with the requirements of the Citizens Referendum Law, initiative law, in force at the time. Prohibition was defeated by nearly 58 percent (58%) of the vote.
The Global System of Trade Preferences among Developing Countries (GSTP) is a preferential trade agreement signed on 13 April 1988 with the aim of increasing trade between developing countries in the framework of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development. Its entry into force was on 19 April 1989 and its notification to the WTO on 25 September 1989.
The service model generally describes an approach whereby labour unions aim to satisfy members' demands for resolving grievances and securing benefits through methods other than direct grassroots-oriented pressure on employers. It is often contrasted to the organising model, and to rank and file organization.

Since the end of apartheid foreign trade in South Africa has increased, following the lifting of several sanctions and boycotts which were imposed as a means of ending apartheid.







