
Helium-3 is a light, stable isotope of helium with two protons and one neutron. Other than protium, helium-3 is the only stable isotope of any element with more protons than neutrons. Helium-3 was discovered in 1939.

Tritium or hydrogen-3 is a rare and radioactive isotope of hydrogen. The nucleus of tritium contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of the common isotope hydrogen-1 (protium) contains just one proton, and that of hydrogen-2 (deuterium) contains one proton and one neutron.
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:

The Joint European Torus, or JET, is an operational magnetically confined plasma physics experiment, located at Culham Centre for Fusion Energy in Oxfordshire, UK. Based on a tokamak design, the fusion research facility is a joint European project with a main purpose of opening the way to future nuclear fusion grid energy. It was the largest machine in production when the JET design began.
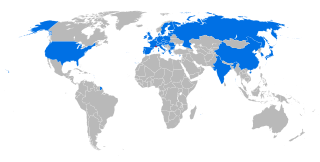
ITER is an international nuclear fusion research and engineering megaproject aimed at replicating the fusion processes of the Sun to create energy on earth. Upon completion of construction and first plasma, planned for late 2025, it will be the world's largest magnetic confinement plasma physics experiment and the largest experimental tokamak nuclear fusion reactor, which is being built next to the Cadarache facility in southern France. ITER will be the largest of more than 100 fusion reactors built since the 1950s, with ten times the plasma volume of any other tokamak operating today.
Breeding is sexual reproduction that produces offspring, usually animals or plants. It can only occur between a male and a female animal or plant.

Tritium radioluminescence is the use of gaseous tritium, a radioactive isotope of hydrogen, to create visible light. Tritium emits electrons through beta decay and, when they interact with a phosphor material, light is emitted through the process of phosphorescence. The overall process of using a radioactive material to excite a phosphor and ultimately generate light is called radioluminescence. As tritium illumination requires no electrical energy, it has found wide use in applications such as emergency exit signs, illumination of wristwatches, and portable yet very reliable sources of low intensity light which won't degrade human night vision. Gun sights for night use and small lights used mostly by military personnel fall under the latter application.
A transformation language is a computer language designed to transform some input text in a certain formal language into a modified output text that meets some specific goal.

The Tokamak Fusion Test Reactor (TFTR) was an experimental tokamak built at Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) circa 1980 and entering service in 1982. TFTR was designed with the explicit goal of reaching scientific breakeven, the point where the heat being released from the fusion reactions in the plasma is equal or greater than the heating being supplied to the plasma by external devices to warm it up.
Grand Gulf Nuclear Station is a nuclear power station with one operational GE BWR reactor. It lies on a 2,100 acres (850 ha) site near Port Gibson, Mississippi. The site is wooded and contains two lakes. The plant has a 520-foot natural draft cooling tower.

Hydrogen (1H) has three naturally occurring isotopes, sometimes denoted 1H, 2H, and 3H. The first two of these are stable, while 3H has a half-life of 12.32 years. There are also heavier isotopes, which are all synthetic and have a half-life less than one zeptosecond. Of these, 5H is the most stable, and 7H is the least.

Radioluminescence is the phenomenon by which light is produced in a material by bombardment with ionizing radiation such as alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma rays. Radioluminescence is used as a low level light source for night illumination of instruments or signage. Radioluminescent paint used to be used for clock hands and instrument dials, enabling them to be read in the dark. Radioluminescence is also sometimes seen around high-power radiation sources, such as nuclear reactors and radioisotopes.
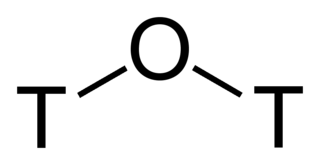
Tritiated water is a radioactive form of water in which the usual protium atoms are replaced with tritium. In its pure form it may be called tritium oxide (T2O or 3H2O) or super-heavy water. Pure T2O is corrosive due to self-radiolysis. Diluted, tritiated water is mainly H2O plus some HTO (3HOH). It is also used as a tracer for water transport studies in life-science research. Furthermore, since it naturally occurs in minute quantities, it can be used to determine the age of various water-based liquids, such as vintage wines.

Tritium Calcio 1908 is an Italian association football club located in Trezzo sull'Adda, Lombardy, currently playing in Serie D.

The Yardymly meteorite is an iron meteorite that fell in Yardymli Rayon, Azerbaijan on November 24, 1959. The remains were discovered in the nearby village of Aroos. With five individual specimens, the total weight of the meteorite is estimated at 150.29 kilograms (331.3 lb). The meteorite is kept in the Institute of Geology of Azerbaijan National Academy of Sciences. According to the director of Şamaxı Astrophysical Observatory Eyub Guliyev, the Yardymli meteorite may originate from the shower of Perseids.
Tritium is a simple scripting language for efficiently transforming structured data like HTML, XML, and JSON. It is similar in purpose to XSLT but has a syntax influenced by jQuery, Sass, and CSS versus XSLT’s XML based syntax.
The Chinese Fusion Engineering Test Reactor (CFETR) is a proposed tokamak fusion reactor which harnesses the power of a magnetic field via the use of magnetic field coils in order to confine plasma and generate energy. Presently, tokamak devices are leading candidates for the construction of a viable and practical thermonuclear fusion reactor. These reactors may be used to generate sustainable energy whilst ensuring a low environmental impact and a smaller carbon footprint than fossil fuel-based power plants.









