
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is therapy using ionizing radiation, generally as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radiation therapy may be curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor. Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology.
A radiation oncologist is a specialist physician who uses ionizing radiation in the treatment of cancer. Radiation oncology is one of the three primary specialties, the other two being surgical and medical oncology, involved in the treatment of cancer. Radiation can be given as a curative modality, either alone or in combination with surgery and/or chemotherapy. It may also be used palliatively, to relieve symptoms in patients with incurable cancers. A radiation oncologist may also use radiation to treat some benign diseases, including benign tumors. In some countries, radiotherapy and chemotherapy are controlled by a single oncologist who is a "clinical oncologist". Radiation oncologists work closely with other physicians such as surgical oncologists, interventional radiologists, internal medicine subspecialists, and medical oncologists, as well as medical physicists and technicians as part of the multi-disciplinary cancer team.. Radiation oncologists undergo four years of oncology specific training whereas oncologists who deliver chemotherapy have two years of additional training in cancer care during fellowship after internal medicine residency in the United States.
A radiation therapist, therapeutic radiographer or radiotherapist is an allied health professional who works in the field of radiation oncology. Radiation therapists plan and administer radiation treatments to cancer patients in most Western countries including the United Kingdom, Australia, most European countries, and Canada, where the minimum education requirement is often a baccalaureate degree or postgraduate degrees in radiation therapy. Radiation therapists can also prescribe medications and radiation, interpret tests results, perform follow ups, reviews, and provide consultations to cancer patients in the United Kingdom and Ontario, Canada .
In the United States, radiation therapists have a lower educational requirement and often require postgraduate education and certification in order to plan treatments.
Surgical oncology is the branch of surgery applied to oncology; it focuses on the surgical management of tumors, especially cancerous tumors.

Chandler Park is an American physician, medical journalist, and clinical researcher. Park contributes regularly as an expert physician for popular newspapers and magazines such as Newsweek, Reader's Digest, U.S. News & World Report, The Exponent-Telegram, College of St. Scholastica, and Medscape. He writes medical news for Doximity an online medical social network that includes over 1,000,000 clinicians. Park is a clinical professor that teaches at the University of Louisville School of Medicine
M. Krishnan Nair is a leading oncologist working in India. He is the founding director of the Regional Cancer Centre, Thiruvananthapuram, a director of the S.U.T. Institute of Oncology, and Trivandrum Cancer Center(TCC), part of SUT ROYAL HOSPITAL in Thiruvananthapuram(Trivandrum) and a professor at the Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences & Research in Kochi. He received the Padma Shri award from the President of India.

The European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) is a unique pan-European non-profit clinical cancer research organisation established in 1962 operating as an international association under Belgium law. It develops, conducts, coordinates and stimulates high-quality translational and clinical trial research to improve the survival and quality of life of cancer patients. This is achieved through the development of new drugs and other innovative approaches, and the testing of more effective therapeutic strategies, using currently approved drugs, surgery and/or radiotherapy in clinical trials conducted under the auspices of a vast network of clinical cancer researchers supported by 220 staff members based in Brussels. EORTC has the expertise to conduct large and complex trials especially specific populations such as the older patient and rare tumours.
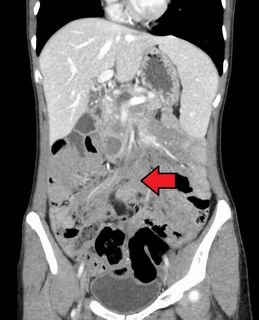
Aggressive fibromatosis is a rare condition marked by the presence of desmoid tumors. Desmoid tumors can arise in virtually any part of the body, and are tumors that arise from cells called fibroblasts, which are found throughout the body and provide structural support, protection to the vital organs, and play a critical role in wound healing. These tumors tend to occur in women in their thirties, but can occur in anyone at any age. They can be either relatively slow-growing or malignant. However, aggressive fibromatosis is locally aggressive. When they are aggressive they can cause life-threatening problems or even death when they compress vital organs such as intestines, kidney, lungs, blood vessels, nerves etc. Most cases are sporadic, but some are associated with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). Approximately 10% of individuals with Gardner's syndrome, a type of FAP with extracolonic features, have desmoid tumors.
Image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) is the process of frequent two and three-dimensional imaging, during a course of radiation treatment, used to direct radiation therapy utilizing the imaging coordinates of the actual radiation treatment plan. The patient is localized in the treatment room in the same position as planned from the reference imaging dataset. An example of IGRT would include localization of a cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) dataset with the planning computed tomography (CT) dataset from planning. IGRT would also include matching planar kilovoltage (kV) radiographs or megavoltage (MV) images with digital reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) from the planning CT. These two methods comprise the bulk of IGRT strategies currently employed circa 2013.
Breast cancer management takes different approaches depending on physical and biological characteristics of the disease, as well as the age, over-all health and personal preferences of the patient. Treatment types can be classified into local therapy and systemic treatment. Local therapy is most efficacious in early stage breast cancer, while systemic therapy is generally justified in advanced and metastatic disease, or in diseases with specific phenotypes.
A chemosensitivity assay is a laboratory test that measures the number of tumor cells that are killed by chemotherapy. The test is done after the tumor cells are removed from the body. A chemosensitivity assay may help in choosing the best drug or drugs for the cancer being treated.
Stereotactic radiation therapy, also called stereotactic external-beam radiation therapy and stereotaxic radiation therapy, is a type of external radiation therapy that uses special equipment to position the patient and precisely deliver radiation to a tumor. The total dose of radiation is divided into several smaller doses given over several days. Stereotactic radiation therapy is used to treat brain tumors and other brain disorders. It is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer, such as lung cancer.
What differentiates Stereotactic from conventional radiotherapy is the precision with which it is delivered. There are multiple systems available, some of which use specially designed frames which physically attach to the patient's skull while newer more advanced techniques use thermoplastic masks and highly accurate imaging systems to locate the patient. The end result is the delivery of high doses of radiation with sub-millimetre accuracy.

Hyperthermia therapy is a type of medical treatment in which body tissue is exposed to higher temperatures in an effort to treat cancer.
Plaque radiotherapy is a type of radiation therapy used to treat eye tumors. A thin piece of metal with radioactive seeds placed on one side is sewn onto the outside wall of the eye with the seeds aimed at the tumor. It is removed at the end of treatment, which usually lasts for several days.
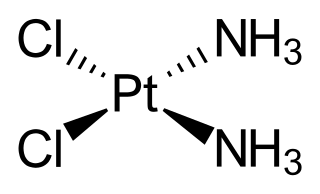
A radiosensitizer is an agent that makes tumor cells more sensitive to radiation therapy. It is sometimes also known as a radiation sensitizer or radio-enhancer.

Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an oncologist. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (ónkos), meaning "tumor", "volume" or "mass" and the word λόγος (logos), meaning "study".
Cancer can be treated by surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy and synthetic lethality. The choice of therapy depends upon the location and grade of the tumor and the stage of the disease, as well as the general state of the patient. A number of experimental cancer treatments are also under development. Under current estimates, two in five people will have cancer at some point in their lifetime.

Seattle Cancer Care Alliance (SCCA) is a cancer treatment and research center in Seattle, Washington. Established in 1998, this nonprofit provides clinical oncology care for patients treated at its three partner organizations: Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle Children's and UW Medicine. Together, these four institutions form the Fred Hutch/University of Washington Cancer Consortium.
Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University is a nonprofit cancer research and patient care center based in Atlanta, Georgia. Winship Cancer Institute is the only National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Center in Georgia.
Oncocare Cancer Treatment Centre is a cancer treatment clinic in Harare. Founded in 2016, Oncocare offers radiation treatment, chemotherapy and treatment support, and has a specialist cancer retail pharmacy. Its equipment includes the only digital linear accelerator in Zimbabwe. Oncocare is the only private medical institution in the country exclusively treating cancer.










