
Naval Submarine Base New London is the United States Navy's primary East Coast submarine base, also known as the "Home of the Submarine Force". It is located in Groton, Connecticut.

The Mare Island Naval Shipyard (MINSY) was the first United States Navy base established on the Pacific Ocean. It is located 25 miles northeast of San Francisco in Vallejo, California. The Napa River goes through the Mare Island Strait and separates the peninsula shipyard from the main portion of the city of Vallejo. MINSY made a name for itself as the premier US West Coast submarine port as well as serving as the controlling force in San Francisco Bay Area shipbuilding efforts during World War II. The base closed in 1996 and has gone through several redevelopment phases. It was registered as a California Historical Landmark in 1960, and parts of it were declared a National Historic Landmark District in 1975.

USS Jimmy Carter (SSN-23) is the third and final Seawolf-class, nuclear-powered, fast-attack submarine in the United States Navy. She is named for Jimmy Carter, the 39th President of the United States and the only president to have qualified in submarines, having served as an officer for communications, sonar, electronics, weapons, and supply while on board USS Pomfret. Jimmy Carter is one of the few ships of the United States Navy and the third submarine to be named for a living person, and the only submarine to be named for a living president.

USS Nautilus (SSN-571) was the world's first operational nuclear-powered submarine and the first submarine to complete a submerged transit of the North Pole on 3 August 1958.

USS Marlin (SST-2), originally USS T-2 (SST-2), was a T-1-class training submarine in commission from 1953 to 1973. She was the second submarine of the United States Navy to be named for the marlin, a large game fish. Except for the first 25 early development pre-WWI subs, she was one of the smallest operational submarines ever built for the U.S. Navy.

The Balao class was a successful design of United States Navy submarine used during World War II, and with 120 units completed, the largest class of submarines in the United States Navy. An improvement on the earlier Gato class, the boats had slight internal differences. The most significant improvement was the use of thicker, higher yield strength steel in the pressure hull skins and frames, which increased their test depth to 400 feet (120 m). Tang actually achieved a depth of 612 ft (187 m) during a test dive,
and exceeded that test depth when taking on water in the forward torpedo room while evading a destroyer.

The New York Shipbuilding Corporation was an American shipbuilding company that operated from 1899 to 1968, ultimately completing more than 500 vessels for the U.S. Navy, the United States Merchant Marine, the United States Coast Guard, and other maritime concerns. At its peak during World War II, NYSB was the largest and most productive shipyard in the world. Its best-known vessels include the destroyer USS Reuben James (DD-245), the cruiser USS Indianapolis (CA-35), the aircraft carrier USS Kitty Hawk (CV-63), the nuclear-powered cargo ship NS Savannah, and a quartet of cargo-passenger liners nicknamed the Four Aces.
A nuclear submarine is a submarine powered by a nuclear reactor. The performance advantages of nuclear submarines over "conventional" submarines are considerable. Nuclear propulsion, being completely independent of air, frees the submarine from the need to surface frequently, as is necessary for conventional submarines. The large amount of power generated by a nuclear reactor allows nuclear submarines to operate at high speed for long periods of time; and the long interval between refuelings grants a range virtually unlimited, making the only limits on voyage times being imposed by such factors as the need to restock food or other consumables.

USS Cavalla (SS/SSK/AGSS-244), a Gato-class submarine, was a ship of the United States Navy named for a salt water fish, best known for sinking the Japanese aircraft carrier Shōkaku, a veteran of the Pearl Harbor attack.

USS Cutlass (SS-478), a Tench-class submarine, was the only ship of the United States Navy to be named for the cutlassfish, a long, thin fish found widely along the coasts of the United States and in the West Indies. Her keel was laid down by the Portsmouth Navy Yard on 10 July 1944. She was launched on 5 November 1944 sponsored by Mrs. R. E. Kintner, and commissioned on 17 March 1945 with Commander Herbert L. Jukes in command.

USS Bremerton (SSN-698), a Los Angeles-class submarine, is the second vessel of the United States Navy to be named for Bremerton, Washington. The contract to build her was awarded to the Electric Boat Division of General Dynamics Corporation in Groton, Connecticut on 24 January 1972 and her keel was laid down on 8 May 1976. She was launched on 22 July 1978 sponsored by Mrs. Helen Jackson, wife of Henry M. Jackson, and commissioned on 28 March 1981 with Captain Thomas H. Anderson in command.
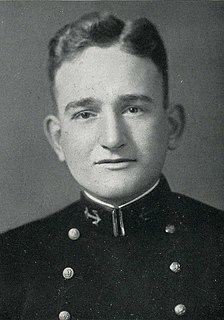
George William Grider was a United States Navy Captain, an attorney, and a Democratic U.S. Representative from Tennessee from 1965 to 1967.

The United States' S-class submarines, often simply called S-boats, were the first class of submarines with a significant number built to United States Navy designs. Others of this class were built to contractor designs.

Battleship Memorial Park is a military history park and museum located on the western shore of Mobile Bay in Mobile, Alabama. It has a collection of notable aircraft and museum ships including the South Dakota-class battleship USS Alabama and Gato-class submarine USS Drum. USS Alabama and USS Drum are both National Historic Landmarks; the park as a whole was listed on the Alabama Register of Landmarks and Heritage prior to that time, on October 28, 1977.

The K-class submarines were a class of eight submarines of the United States Navy, serving between 1914 and 1923, including World War I. They were designed by Electric Boat and were built by other yards under subcontracts. K-1, K-2, K-5, and K-6 were built by Fore River Shipyard in Quincy, Massachusetts, K-3, K-7, and K-8 by Union Iron Works in San Francisco, and K-4 by Seattle Construction and Drydock Company in Seattle, Washington. All were decommissioned in 1923 and scrapped in 1931 to comply with the limits of the London Naval Treaty.

USS Greenlet (ASR-10) was a Chanticleer-class submarine rescue ship in the United States Navy.

The 5"/25 caliber gun entered service as the standard heavy anti-aircraft (AA) gun for United States Washington Naval Treaty cruisers commissioned in the 1920s and 1930s. The goal of the 5"/25 design was to produce a heavy AA gun that was light enough to be rapidly trained manually. The gun was also mounted on pre-World War II battleships and aircraft carriers until replaced by the standard dual-purpose 5"/38 caliber gun, which was derived from the 5"/25 and was similar except for the barrel length. Guns removed from battleships were probably converted for submarine use by late 1943, while a purpose-built variant for submarines was available in mid-1944, and was widely used by them. United States naval gun terminology indicates the gun fired a projectile 5 inches (127 mm) in diameter, and the barrel was 25 calibers long.















