
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the power of a signal. It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is a circuit that has a power gain greater than one.

A non-disclosure agreement (NDA), also known as a confidentiality agreement (CA), confidential disclosure agreement (CDA), proprietary information agreement (PIA) or secrecy agreement (SA), is a legal contract between at least two parties that outlines confidential material, knowledge, or information that the parties wish to share with one another for certain purposes, but wish to restrict access to or by third parties. The most common forms of these are in doctor–patient confidentiality, attorney–client privilege, priest–penitent privilege, and bank–client confidentiality agreements.

A superheterodyne receiver, often shortened to superhet, is a type of radio receiver that uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original carrier frequency. It was invented by US engineer Edwin Armstrong in 1918 during World War I. Virtually all modern radio receivers use the superheterodyne principle.
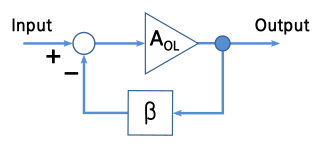
A Negative-feedback amplifier is an electronic amplifier that subtracts a fraction of its output from its input, so that negative feedback opposes the original signal. The applied negative feedback can improve its performance and reduces sensitivity to parameter variations due to manufacturing or environment. Because of these advantages, many amplifiers and control systems use negative feedback.

Negative feedback occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other disturbances.

A guitar amplifier is an electronic device or system that strengthens the weak electrical signal from a pickup on an electric guitar, bass guitar, or acoustic guitar so that it can produce sound through one or more loudspeakers, which are typically housed in a wooden cabinet. A guitar amplifier may be a standalone wood or metal cabinet that contains only the power amplifier circuits, requiring the use of a separate speaker cabinet–or it may be a "combo" amplifier, which contains both the amplifier and one or more speakers in a wooden cabinet. There is a wide range of sizes and power ratings for guitar amplifiers, from small, lightweight "practice amplifiers" with a single 6" speaker and a 10 watt amp to heavy combo amps with four 10” or four 12" speakers and a powerful 100 watt amplifier, which are loud enough to use in a nightclub or bar performance.

A differential amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that amplifies the difference between two input voltages but suppresses any voltage common to the two inputs. It is an analog circuit with two inputs
and
and one output
in which the output is ideally proportional to the difference between the two voltages

A buffer amplifier is one that provides electrical impedance transformation from one circuit to another, with the aim of preventing the signal source from being affected by whatever currents that the load may produce. The signal is 'buffered from' load currents. Two main types of buffer exist: the voltage buffer and the current buffer.
The magnetic amplifier is an electromagnetic device for amplifying electrical signals. The magnetic amplifier was invented early in the 20th century, and was used as an alternative to vacuum tube amplifiers where robustness and high current capacity were required. World War II Germany perfected this type of amplifier, and it was used in the V-2 rocket. The magnetic amplifier was most prominent in power control and low-frequency signal applications from 1947 to about 1957, when the transistor began to supplant it. The magnetic amplifier has now been largely superseded by the transistor-based amplifier, except in a few safety critical, high-reliability or extremely demanding applications. Combinations of transistor and mag-amp techniques are still used.

Marshall Amplification is an English company that designs and manufactures music amplifiers, speaker cabinets, brands personal headphones and earphones, and, having acquired Natal Drums, drums and bongos. It was founded by drum shop owner and drummer Jim Marshall, and is now based in Bletchley, Milton Keynes, Buckinghamshire.
Unilateral hearing loss (UHL) is a type of hearing impairment where there is normal hearing in one ear and impaired hearing in the other ear.
United Western Recorders was a two-building recording studio complex in Hollywood, which became one of the most successful independent recording studios of the 1960s. The complex merged neighboring studios United Recording Corp. on 6050 Sunset Boulevard and Western Studio on 6000 Sunset Boulevard.

Unconscionability is a doctrine in contract law that describes terms that are so extremely unjust, or overwhelmingly one-sided in favor of the party who has the superior bargaining power, that they are contrary to good conscience. Typically, an unconscionable contract is held to be unenforceable because no reasonable or informed person would otherwise agree to it. The perpetrator of the conduct is not allowed to benefit, because the consideration offered is lacking, or is so obviously inadequate, that to enforce the contract would be unfair to the party seeking to escape the contract.

Offer and acceptance analysis is a traditional approach in contract law. The offer and acceptance formula, developed in the 19th century, identifies a moment of formation when the parties are of one mind. This classical approach to contract formation has been modified by developments in the law of estoppel, misleading conduct, misrepresentation and unjust enrichment.
In contract law, a mistake is an erroneous belief, at contracting, that certain facts are true. It can be argued as a defense, and if raised successfully can lead to the agreement in question being found void ab initio or voidable, or alternatively an equitable remedy may be provided by the courts. Common law has identified three different types of mistake in contract: the 'unilateral mistake', the 'mutual mistake' and the 'common mistake'. The distinction between the 'common mistake' and the 'mutual mistake' is important.

In electronics, a current divider is a simple linear circuit that produces an output current (IX) that is a fraction of its input current (IT). Current division refers to the splitting of current between the branches of the divider. The currents in the various branches of such a circuit will always divide in such a way as to minimize the total energy expended.
Attila was the name of a band featuring a young Billy Joel. Joel was a member of a band called The Hassles; he and the drummer, Jon Small, broke away from the Hassles and formed Attila in 1969. The instrumentation was organ and drums, with Joel also handling the bass lines with a keyboard, similar to the Doors' Ray Manzarek. Their creative partnership ended in 1970 when Joel ran off with Small's wife, Elizabeth, although this did not end their collaborations, as Small produced Joel's Концерт video as well as the Live at Shea Stadium performance.

The one and a half syndrome is a rare weakness in eye movement affecting both eyes, in which one cannot move laterally at all, and the other can move in only one lateral direction. More formally, it is characterized by "a conjugate horizontal gaze palsy in one direction and an internuclear ophthalmoplegia in the other". The most common manifestation of this unusual syndrome is limitation of horizontal eye movement to abduction of one eye with no horizontal movement of the other eye. Nystagmus is also present when the eye on the opposite side of the lesion is abducted. Convergence is classically spared as cranial nerve III and its nucleus is spared bilaterally.
Scots contract law governs the rules of contract in Scotland.











