
The One Hundred Sixth United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, DC from January 3, 1999, to January 3, 2001, during the last two years of Bill Clinton's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the Twenty-first Census of the United States in 1990. Both chambers had a Republican majority.

The One Hundred Second United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, DC from January 3, 1991, to January 3, 1993, during the last two years of the administration of U.S. President George H. W. Bush.
A congressional subcommittee in the United States Congress is a subdivision of a United States congressional committee that considers specified matters and reports back to the full committee.

Donald Wayne Riegle Jr. is an American politician, author and businessman from Michigan, who served for five terms as a Representative and for three terms as a Senator in the U.S. Congress.

The United States Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation is a standing committee of the United States Senate. It is empowered with legislative oversight of the Coast Guard and Merchant Marine, interstate commerce, communications, the Internet, highways, aviation, rail, shipping, transportation security, oceans, fisheries, climate change, natural disasters, science, sports, tourism, consumer protection, economic development, technology, competitiveness, product safety, insurance, and standards and measurement. The committee also has jurisdiction over coastal zone management, inland waterways, the Panama Canal and other interoceanic canals, and commerce aspects of Continental Shelf lands.
The Committee on Science, Space and Technology is a committee of the United States House of Representatives. It has jurisdiction over non-defense federal scientific research and development. More specifically, the committee has complete jurisdiction over the following federal agencies: NASA, NSF, NIST, and the OSTP. The Committee also has authority over R&D activities at the Department of Energy, the EPA, FAA, NOAA, the DOT, the NWS, the DHS and the U.S. Fire Administration.

The Ninety-eighth United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from January 3, 1983, to January 3, 1985, during the third and fourth years of Ronald Reagan's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1980 U.S. Census. The Republicans controlled the Senate, while the Democrats controlled the House of Representatives.

The Ninety-third United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, DC from January 3, 1973, to January 3, 1975, during the end of Richard Nixon's presidency, and the beginning of Gerald Ford's. This Congress was the first Congress with more than two Senate Presidents, in this case, three. After the resignation of Spiro Agnew, Gerald Ford was appointed under the authority of the newly ratified 25th Amendment. Ford became President the next year and Nelson Rockefeller was appointed in his place. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the Nineteenth Census of the United States in 1970. Both chambers had a Democratic majority.
The U.S. Senate Agriculture Subcommittee on Commodities, Markets and Trade is one of five subcommittees of the U.S. Senate Committee on Agriculture, Nutrition and Forestry.
U.S. Senate Appropriations Subcommittee on Commerce, Justice, Science, and Related Agencies, often referred to colloquially as the CJS Subcommittee is one of twelve subcommittees of the U.S. Senate Committee on Appropriations. It was formerly known as the Subcommittee on Commerce, Justice, State, and the Judiciary during the 108th Congress (2003-2005), but responsibility for the State Department and the federal Judiciary are now handled by separate subcommittees. The United States Senate Committee on Appropriations has joint jurisdiction with the United States House Committee on Appropriations over all appropriations bills in the United States Congress. Each committee has 12 matching subcommittees, each of which is tasked with working on one of the twelve annual regular appropriations bills. This subcommittee has jurisdiction over the budget for the United States Department of Commerce, the United States Department of Justice, and Science policy of the United States.

The Committee on Energy and Commerce is one of the oldest standing committees of the United States House of Representatives. Established in 1795, it has operated continuously—with various name changes and jurisdictional changes—for more than 200 years. The two other House standing committees with such continuous operation are the House Ways and Means Committee and the House Rules Committee. The Committee has served as the principal guide for the House in matters relating to the promotion of commerce and to the public’s health and marketplace interests, with the relatively recent addition of energy considerations among them.
The Science Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics is one of six subcommittees of the United States House Committee on Science and Technology.
The Science Subcommittee on Technology is one of six subcommittees of the United States House Committee on Science and Technology.
The United States House Appropriations Subcommittee on Commerce, Justice, Science, and Related Agencies is a standing committee of the U.S. House subcommittees and is within the United States House Committee on Appropriations. The United States House Committee on Appropriations has joint jurisdiction with the United States Senate Committee on Appropriations over all appropriations bills in the United States Congress. Each committee has 12 matching subcommittees, each of which is tasked with working on one of the twelve annual regular appropriations bills. This subcommittee has jurisdiction over the budgets for the United States Department of Commerce, the United States Department of Justice, and Science policy of the United States.
The Senate Committee on Railroads is a defunct committee of the United States Senate. It succeeded the Committee on the Pacific Railroad on March 12, 1873. The committee reviewed legislation and matters related to railroad transportation on the United States. The committee existed until April 8, 1921, when it was abolished due to inactivity. The committee's role waned after the 50th Congress (1887-89) as other Senate committees acquired legislative jurisdiction over railroad matters. The United States Senate Committee on Interstate Commerce, in particular, focused on regulating railroad rates and assuring safety of railroad passengers and crews. A separate Committee on Pacific Railroads also operated from 1893-1921, investigating the financial status of the Union Pacific Railroad.
The Senate Commerce Subcommittee on Aviation and Space is one of the six subcommittees within the Senate Committee on Commerce, Science and Transportation. The Subcommittee was formerly known as the Senate Commerce Subcommittee on Aviation Operations, Safety and Security.
The Senate Commerce Subcommittee on Communications Technology, Innovation, and the Internet is one of the six subcommittees within the Senate Committee on Commerce, Science and Transportation. It was renamed from the Subcommittee on Science, Technology, and Innovation at the start of the 111th Congress, with its science function transferred to the Subcommittee on Science and Space.
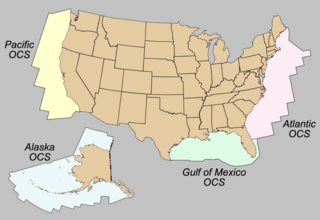
The Outer Continental Shelf (OCS) is a peculiarity of the political geography of the United States. The OCS is the part of the internationally recognized continental shelf of the United States which does not fall under the jurisdictions of the individual U.S. States.






