This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
In astronomy, a variable star designation is a unique identifier given to variable stars. It uses a variation on the Bayer designation format, with an identifying label preceding the Latin genitive of the name of the constellation in which the star lies. See List of constellations for a list of constellations and the genitive forms of their names. The identifying label can be one or two Latin letters or a V plus a number. Examples are R Coronae Borealis, YZ Ceti, V603 Aquilae.
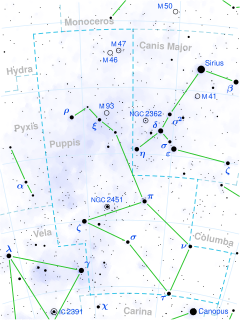
Zeta Puppis, also named Naos, is a star in the constellation of Puppis.

Upsilon Sagittarii is a spectroscopic binary star system in the constellation Sagittarius. Upsilon Sagittarii is the prototypical hydrogen-deficient binary (HdB), and one of only four such systems known. The unusual spectrum of hydrogen-deficient binaries has made stellar classification of Upsilon Sagittarii difficult.
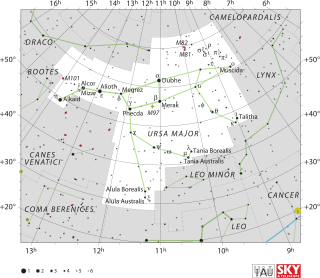
Tau Ursae Majoris (τ UMa) is the Bayer designation for a binary star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. It is visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 4.66. With an annual parallax shift of 25.82 mas, it is located about 126 light years from the Sun. At that distance, the visual magnitude is diminished by an extinction factor of 0.19 due to interstellar dust.

Pi Puppis, Latinized from π Puppis, also named Ahadi, is the second-brightest star in the southern constellation of Puppis. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 2.733, so it can be viewed with the naked eye at night. Parallax measurements yield an estimated distance of roughly 810 light-years from the Earth. This is a double star with a magnitude 6.86 companion at an angular separation of 0.72 arcsecond and a position angle of 148° from the brighter primary.

L2 Puppis (also known as HD 56096) is a giant star in the constellation of Puppis and is located between the bright stars Canopus and Sirius. It is a semi-regular pulsating star.

RS Puppis is a Cepheid variable star around 6,000 ly away in the constellation of Puppis. It is one of the brightest known Cepheids in the Milky Way galaxy and has one of the longest periods for this class of star at 41.5 days.

k Puppis is a Bayer designation given to an optical double star in the constellation Puppis, the two components being k1 Puppis and k2 Puppis.
An Am star or metallic-line star is a type of chemically peculiar star of spectral type A whose spectrum has strong and often variable absorption lines of metals such as zinc, strontium, zirconium, and barium, and deficiencies of others, such as calcium and scandium. The original definition of an Am star was one in which the star shows "an apparent surface underabundance of Ca and/or an apparent overabundance of the Fe group and heavier elements".

Collinder 135, known sometimes as the Pi Puppis Cluster, is an open cluster in Puppis constellation.

Rho Puppis, also named Tureis, is a star in the southern constellation of Puppis. With an average apparent visual magnitude of 2.78, it is the third-brightest member of this generally faint constellation. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, Rho Puppis is located at a distance of 63.5 light-years from the Sun. It is the prototype of the ρ Puppis class of evolved Am stars.

Omicron Puppis (ο Puppis) is candidate binary star system in the southern constellation of Puppis. It is visible to the naked eye, having a combined apparent visual magnitude of +4.48. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 2.30 mas as seen from Earth, it is located roughly 1,400 light years from the Sun.

NS Puppis is an irregular variable star in the constellation Puppis. Its apparent magnitude varies between 4.4 and 4.5.

NV Puppis, also known as υ1 Puppis, is a class B2V star in the constellation Puppis. Its apparent magnitude is 4.67 and it is approximately 800 light years away based on parallax.

KQ Puppis is a spectroscopic binary variable star in the constellation Puppis. A red supergiant star and a hot main sequence star orbit each other every 9,742 days. Its apparent magnitude varies between 4.82 and 5.17.
NW Puppis, also known as υ2 Puppis, is a star in the constellation Puppis. Located around 760 light-years distant, it shines with a luminosity approximately 1108 times that of the Sun and has a surface temperature of 15000 K. Anamarija Stankov ruled this star out as a Beta Cephei variable.
The Bayer designation L Puppis is shared by two stars in the constellation Puppis:
The Bayer designations h Puppis and H Puppis are distinct. They can refer to three stars in the constellation Puppis:








