Related Research Articles

In the fields of physical security and information security, access control (AC) is the selective restriction of access to a place or other resource. The act of accessing may mean consuming, entering, or using. Permission to access a resource is called authorization.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an Internet Standard protocol for collecting and organizing information about managed devices on IP networks and for modifying that information to change device behavior. Devices that typically support SNMP include cable modems, routers, switches, servers, workstations, printers, and more.
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) is a networking protocol, operating on port 1812 that provides centralized Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting management for users who connect and use a network service. RADIUS was developed by Livingston Enterprises, Inc. in 1991 as an access server authentication and accounting protocol and later brought into the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standards.
Internet security is a branch of computer security specifically related to not only the Internet, often involving browser security and the World Wide Web, but also network security as it applies to other applications or operating systems as a whole. Its objective is to establish rules and measures to use against attacks over the Internet. The Internet represents an insecure channel for exchanging information, which leads to a high risk of intrusion or fraud, such as phishing, online viruses, trojans, worms and more.
In computing, the term virtual directory has a couple of meanings. It may simply designate a folder which appears in a path but which is not actually a subfolder of the preceding folder in the path. However, this article will discuss the term in the context of directory services and identity management.
Quattor is a generic open-source tool-kit used to install, configure, and manage computers. Quattor was originally developed in the framework of European Data Grid project (2001-2004). Since its first release in 2003, Quattor has been maintained and extended by a volunteer community of users and developers, primarily from the community of grid system administrators. The Quattor tool-kit, like other configuration management systems, reduces the manpower required to maintain a cluster and facilitates reliable change management. However, three unique features make it particularly attractive for managing grid resources:

LAMP is an archetypal model of web service stacks, named as an acronym of the names of its original four open-source components: the Linux operating system, the Apache HTTP Server, the MySQL relational database management system (RDBMS), and the PHP programming language. The LAMP components are largely interchangeable and not limited to the original selection. As a solution stack, LAMP is suitable for building dynamic web sites and web applications.
Database security concerns the use of a broad range of information security controls to protect databases against compromises of their confidentiality, integrity and availability. It involves various types or categories of controls, such as technical, procedural/administrative and physical. Database security is a specialist topic within the broader realms of computer security, information security and risk management.

The Open Grid Forum (OGF) is a community of users, developers, and vendors for standardization of grid computing. It was formed in 2006 in a merger of the Global Grid Forum and the Enterprise Grid Alliance. The OGF models its process on the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), and produces documents with many acronyms such as OGSA, OGSI, and JSDL.
Database administration is the function of managing and maintaining database management systems (DBMS) software. Mainstream DBMS software such as Oracle, IBM DB2 and Microsoft SQL Server need ongoing management. As such, corporations that use DBMS software often hire specialized information technology personnel called Database Administrators or DBAs.
Security Support Provider Interface (SSPI) is a Win32 API used by Microsoft Windows systems to perform a variety of security-related operations such as authentication.
Security patterns can be applied to achieve goals in the area of security. All of the classical design patterns have different instantiations to fulfill some information security goal: such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Additionally, one can create a new design pattern to specifically achieve some security goal.
The INFN Grid project was an initiative of the Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN) —Italy's National Institute for Nuclear Physics—for grid computing. It was intended to develop and deploy grid middleware services to allow INFN's users to transparently and securely share the computing and storage resources together with applications and technical facilities for scientific collaborations.
Eucalyptus is a paid and open-source computer software for building Amazon Web Services (AWS)-compatible private and hybrid cloud computing environments, originally developed by the company Eucalyptus Systems. Eucalyptus is an acronym for Elastic Utility Computing Architecture for Linking Your Programs To Useful Systems. Eucalyptus enables pooling compute, storage, and network resources that can be dynamically scaled up or down as application workloads change. Mårten Mickos was the CEO of Eucalyptus. In September 2014, Eucalyptus was acquired by Hewlett-Packard and then maintained by DXC Technology. After DXC stopped developing the product in late 2017, AppScale Systems forked the code and started supporting Eucalyptus customers.

gLite is a middleware computer software project for grid computing used by the CERN LHC experiments and other scientific domains. It was implemented by collaborative efforts of more than 80 people in 12 different academic and industrial research centers in Europe. gLite provides a framework for building applications tapping into distributed computing and storage resources across the Internet. The gLite services were adopted by more than 250 computing centres and used by more than 15000 researchers in Europe and around the world.

The ARDA Metadata Grid Application (AMGA) is a general purpose metadata catalogue and part of the European Middleware Initiative middleware distribution. It was originally developed by the EGEE project as part of its gLite middleware, when it became clear that many Grid applications needed metadata information on files and to organize a work-flow. AMGA is now developed and supported by the European Middleware Initiative.
Identity assurance in the context of federated identity management is the ability for a party to determine, with some level of certainty, that an electronic credential representing an entity with which it interacts to effect a transaction, can be trusted to actually belong to the entity.
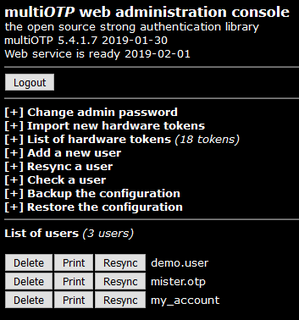
multiOTP is an open source PHP class, a command line tool and a web interface that can be used to provide an operating system independent strong authentication system. multiOTP is OATH certified since version 4.1.0 and is developed under the LGPL license. Starting with version 4.3.2.5, multiOTP open source is also available as a virtual appliance - as a standard OVA file, a customized OVA file with open-vm-tools, and also as an Hyper-V downloadable file.
IBM API Management is an API Management platform for use in the API Economy. IBM API Management enables users to create, assemble, manage, secure and socialize web application programming interfaces (APIs).