In architecture, a lunette is a half-moon shaped space, either filled with recessed masonry or void. A lunette is formed when a horizontal cornice transects a round-headed arch at the level of the imposts, where the arch springs. If a door is set within a round-headed arch, the space within the arch above the door, masonry or glass, is a lunette. If the door is a major access, and the lunette above is massive and deeply set, it may be called a tympanum.
Prefabrication is the practice of assembling components of a structure in a factory or other manufacturing site, and transporting complete assemblies or sub-assemblies to the construction site where the structure is to be located. The term is used to distinguish this process from the more conventional construction practice of transporting the basic materials to the construction site where all assembly is carried out.
Gladiators 2000 is a children's game show and spin-off of American Gladiators. It was hosted by Ryan Seacrest and Maria Sansone. Season 5 American Gladiators grand champion Peggy Odita served as head referee. It premiered on September 17, 1994 and ran until May 11, 1996. It was often partnered with its parent show in syndication, although some markets ran it independently. Like AG, the series was produced by Four Point Entertainment, and distributed by Samuel Goldwyn Television. In response to NBC's 2008 revival of American Gladiators, the show was brought back in syndicated reruns for the 2008-2009 television season.
In video gaming, the HUD or status bar is the method by which information is visually relayed to the player as part of a game's user interface. It takes its name from the head-up displays used in modern aircraft.

The trunk, boot, dickie or compartment of a car is the vehicle's main storage compartment.

A window shutter is a solid and stable window covering usually consisting of a frame of vertical stiles and horizontal rails. Set within this frame can be louvers, solid panels, fabric, glass and almost any other item that can be mounted within a frame. Shutters may be employed for a variety of reasons, including controlling the amount of sunlight that enters a room, to provide privacy, security, to protect against weather or unwanted intrusion or damage and to enhance the aesthetics of a building.
This page is a glossary of architecture.

Flashing refers to thin pieces of impervious material installed to prevent the passage of water into a structure from a joint or as part of a weather resistant barrier (WRB) system. In modern buildings, flashing is intended to decrease water penetration at objects such as chimneys, vent pipes, walls, windows and door openings to make buildings more durable and to reduce indoor mold problems. Metal flashing materials include lead, aluminium, copper, stainless steel, zinc alloy, and other materials.
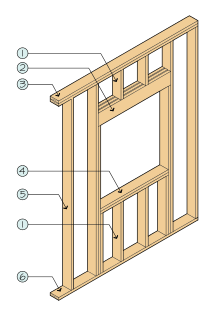
A wall stud is a vertical framing member in a building's wall of smaller cross section than a post. They are a fundamental element in frame building.

The Sims 3 is the third major title in the life simulation video game developed by Maxis and published by Electronic Arts. It is the sequel to The Sims 2. It was announced that it was in development for PlayStation 3 and Wii in November 2006, and later announced for OS X and Microsoft Windows. It was first released on June 2, 2009 simultaneously for OS X and Microsoft Windows – both versions on the same disc. Smartphone versions were also released on June 2, 2009. Console versions were released for PlayStation 3, Xbox 360, and Nintendo DS in October 2010 and a month later for the Wii. The Windows Phone version was made available on the Windows Phone Store on October 15, 2010. A Nintendo 3DS version, released on March 27, 2011, was one of its launch titles.

A house plan is a set of construction or working drawings that define all the construction specifications of a residential house such as dimensions, materials, layouts, installation methods and techniques.

Norman Park State School is a heritage-listed state school at 68-88 Agnew Street, Norman Park, City of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. It was designed by Department of Public Works (Queensland) and built in 1900. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 7 April 2017.

A locker is a small, usually narrow storage compartment. They are commonly found in dedicated cabinets, very often in large numbers, in various public places such as locker rooms, workplaces, middle and high schools, transport hub and the like. They vary in size, purpose, construction, and security.

The Suntop Homes, also known under the early name of The Ardmore Experiment, were quadruple residences located in Ardmore, Pennsylvania, and based largely upon the 1935 conceptual Broadacre City model of the minimum houses. The design was commissioned by Otto Tod Mallery of the Tod Company in 1938 in an attempt to set a new standard for the entry-level housing market in the United States and to increase single-family dwelling density in the suburbs. In cooperation with Frank Lloyd Wright, the Tod Company secured a patent for the unique design, intending to sell development rights for Suntops across the country.

Kura are traditional Japanese storehouses. They are commonly durable buildings built from timber, stone or clay used to safely store valuable commodities.

Kerala architecture is a kind of architectural style that is mostly found in Indian state of Kerala. Kerala's style of architecture is unique in India, in its striking contrast to Dravidian architecture which is normally practiced in other parts of South India. The architecture of Kerala has been influenced by Dravidian and Indian Vedic architectural science over two millennia. The Tantrasamuchaya, Thachu-Shastra, Manushyalaya-Chandrika and Silparatna are important architectural sciences, which have had a strong impact in Kerala Architecture style. The Manushyalaya-Chandrika, a work devoted to domestic architecture is one such science which has its strong roots in Kerala.

Millwork building materials are historically any woodmill-produced products for building construction. Stock profiled and patterned millwork building components fabricated by milling at a planing mill can usually be installed with minimal alteration. Today, millwork also encompasses items that are made using alternatives to wood, including synthetics, plastics, and wood-adhesive composites.

The Edificio del Seguro Médico in El Vedado was built between 1955 and 1958, designed as a mixed use building for apartments and offices for the headquarters of the National Medical Insurance Company, it is considered to be one of the best commercial buildings in Havana of the 50s and of the best modernist buildings overall including the FOCSA Building by Ernesto Gómez Sampera (1921–2004) and Martín Domínguez Esteban (1897-1970). The latter designed the Radiocentro CMQ Building. In regards to Edificio del Seguro Médico an architect from the Universidad de Oriente, Santiago de Cuba, Carlos Alberto Odio Soto made the following observation:
"Within the modern heritage architecture of the 50s, there is the Medical Insurance Building, work designed by the architect Antonio Quintana in 1955. This work was praised even before its inauguration by the prestigious Professor Pedro Martínez Inclán on the occasion of the delivery of the First Prize to the Project where he proposed that Quintana, when he managed to carry out his project, could blazon of having endowed Havana, according to the famous sentence of Paul Valery, "of a building that speaks." At the national level, Quintana received the recognition of the main specialized publications that circulated in the country at that time: Architecture, Space, Cuba Album, etc .; at the same time is diffused internationally through the book Latin American Architecture since 1945, published by the Museum of Modern Art in New York, and the Exhibition of Modern Cuban Architecture held in the city itself by the Architectural League. Almost at the end of the 50s, he receives two distinctions: in 1959 the Gold Medal Award of the National College of Architects and the condition of best commercial work of this period."