
The kilogram or kilogramme is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI). Until 20 May 2019, it remains defined by a platinum alloy cylinder, the International Prototype Kilogram, manufactured in 1889, and carefully stored in Saint-Cloud, a suburb of Paris. After 20 May, it will be defined in terms of fundamental physical constants.

The Metre Convention, also known as the Treaty of the Metre, is an international treaty that was signed in Paris on 20 May 1875 by representatives of 17 nations. The treaty created the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM), an intergovernmental organization under the authority of the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) and the supervision of the International Committee for Weights and Measures (CIPM), that coordinates international metrology and the development of the metric system.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is a physical sciences laboratory, and a non-regulatory agency of the United States Department of Commerce. Its mission is to promote innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into laboratory programs that include nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. The American AI initiative has called NIST to lead the development of appropriate technical standards for reliable, robust, trustworthy, secure, portable, and interoperable AI systems.

The International System of Units is the modern form of the metric system, and is the most widely used system of measurement. It comprises a coherent system of units of measurement built on seven base units, which are the ampere, kelvin, second, metre, kilogram, candela, mole, and a set of twenty prefixes to the unit names and unit symbols that may be used when specifying multiples and fractions of the units. The system also specifies names for 22 derived units, such as lumen and watt, for other common physical quantities.
United States customary units are a system of measurements commonly used in the United States. The United States customary system developed from English units which were in use in the British Empire before the U.S. became an independent country. However, the United Kingdom's system of measures was overhauled in 1824 to create the imperial system, changing the definitions of some units. Therefore, while many U.S. units are essentially similar to their Imperial counterparts, there are significant differences between the systems.

The metric system is an internationally recognised decimalised system of measurement. It is in widespread use, and where it is adopted, it is the only or most common system of weights and measures. It is now known as the International System of Units (SI). It is used to measure everyday things such as the mass of a sack of flour, the height of a person, the speed of a car, and the volume of fuel in its tank. It is also used in science, industry and trade.

Metrology is the science of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to standardise units in France, when a length standard taken from a natural source was proposed. This led to the creation of the decimal-based metric system in 1795, establishing a set of standards for other types of measurements. Several other countries adopted the metric system between 1795 and 1875; to ensure conformity between the countries, the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM) was established by the Metre Convention. This has evolved into the International System of Units (SI) as a result of a resolution at the 11th Conference Generale des Poids et Mesures (CGPM) in 1960.
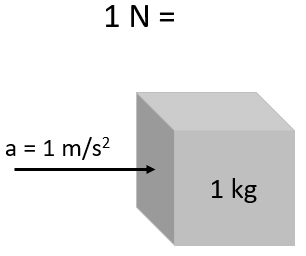
The newton is the International System of Units (SI) derived unit of force. It is named after Isaac Newton in recognition of his work on classical mechanics, specifically Newton's second law of motion.

The avoirdupois system is a measurement system of weights which uses pounds and ounces as units. It was first commonly used in the 13th century and was updated in 1959.

The stone or stone weight is an English and imperial unit of weight now equal to 14 pounds (6.35029318 kg).

Deadweight tonnage or tons deadweight (TDW) is a measure of how much weight a ship can carry, not its weight, empty or in any degree of load. DWT is the sum of the weights of cargo, fuel, fresh water, ballast water, provisions, passengers, and crew.
In the United Kingdom, the retail prices index or retail price index (RPI) is a measure of inflation published monthly by the Office for National Statistics. It measures the change in the cost of a representative sample of retail goods and services.

Pera Museum is an art museum in the Tepebaşı quarter of the Beyoğlu (Pera) district in Istanbul, Turkey, located at Meşrutiyet Avenue No. 65 It has a particular focus on Orientalism in 19th-century art.
The National Conference on Weights and Measures (NCWM) is a not-for-profit corporation dedicated to developing the United States technical standards for weights and measures in commerce. The organization's official mission is to advance a healthy business and consumer climate through the development and implementation of uniform and equitable weights and measures standards using a consensus building process.
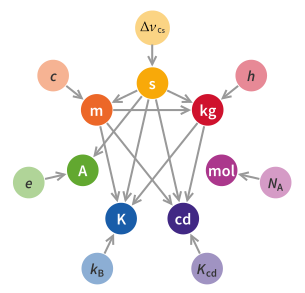
A redefinition of SI base units is scheduled to come into force on 20 May 2019. The kilogram, ampere, kelvin, and mole will then be defined by setting exact numerical values for the Planck constant, the elementary electric charge, the Boltzmann constant, and the Avogadro constant, respectively. The second, metre and candela are already defined by physical constants, subject to correction to their present definitions. The new definitions aim to improve the SI without changing the size of any units, thus ensuring continuity with existing measurements. In November 2018, the 26th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) unanimously approved these changes, which the International Committee for Weights and Measures (CIPM) had proposed earlier that year.

The metric system was developed during the French Revolution to replace the various measures previously used in France. The metre is the unit of length in the metric system and was originally based on the dimensions of the earth, as far as it could be measured at the time. The litre, is the unit of volume and was defined as one thousandth of a cubic metre. The metric unit of mass is the kilogram and it was defined as the mass of one litre of water. The metric system was, in the words of French philosopher Marquis de Condorcet, "for all people for all time".











