This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
A document type definition (DTD) is a set of markup declarations that define a document type for a SGML-family markup language.

Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for creating web pages and web applications. With Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and JavaScript, it forms a triad of cornerstone technologies for the World Wide Web.
In computing, a namespace is a set of symbols that are used to organize objects of various kinds, so that these objects may be referred to by name. In Java, a namespace ensures that all the identifiers within it must have unique names so that they can be easily identified. In order to manage the namespace Java provides the mechanism of creating Java packages. Prominent examples include:
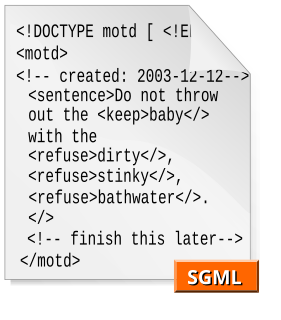
The Standard Generalized Markup Language is a standard for defining generalized markup languages for documents. ISO 8879 Annex A.1 defines generalized markup:-
Generalized markup is based on two postulates:
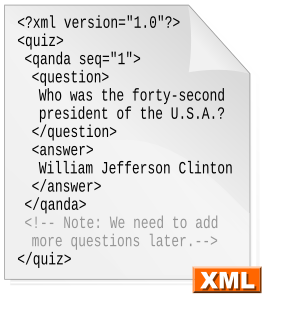
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. The W3C's XML 1.0 Specification and several other related specifications—all of them free open standards—define XML.
In computing, the Java API for XML Processing, or JAXP, one of the Java XML Application programming interfaces (API)s, provides the capability of validating and parsing XML documents. It has three basic parsing interfaces:
DocBook is a semantic markup language for technical documentation. It was originally intended for writing technical documents related to computer hardware and software but it can be used for any other sort of documentation.
XPointer is a system for addressing components of XML-based Internet media. It is divided among four specifications: a "framework" that forms the basis for identifying XML fragments, a positional element addressing scheme, a scheme for namespaces, and a scheme for XPath-based addressing. XPointer Framework is a W3C recommendation since March 2003.

The Meta-Object Facility (MOF) is an Object Management Group (OMG) standard for model-driven engineering. Its purpose is to provide a type system for entities in the CORBA architecture and a set of interfaces through which those types can be created and manipulated. The official reference page may be found at OMG's website.
XSD, a recommendation of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), specifies how to formally describe the elements in an Extensible Markup Language (XML) document. It can be used by programmers to verify each piece of item content in a document. They can check if it adheres to the description of the element it is placed in.
In computing, RELAX NG is a schema language for XML—a RELAX NG schema specifies a pattern for the structure and content of an XML document. A RELAX NG schema is itself an XML document but RELAX NG also offers a popular compact, non-XML syntax. Compared to other XML schema languages RELAX NG is considered relatively simple.
An XML schema is a description of a type of XML document, typically expressed in terms of constraints on the structure and content of documents of that type, above and beyond the basic syntactical constraints imposed by XML itself. These constraints are generally expressed using some combination of grammatical rules governing the order of elements, Boolean predicates that the content must satisfy, data types governing the content of elements and attributes, and more specialized rules such as uniqueness and referential integrity constraints.
The Darwin Information Typing Architecture or Document Information Typing Architecture (DITA) is an XML data model for authoring and publishing. It is an open standard that is defined and maintained by the OASIS DITA Technical Committee.
ISO/IEC 11179 is an international standard for representing metadata for an organization in a metadata registry.
XMLBeans is a Java-to-XML binding framework which is part of the Apache Software Foundation XML project.
The Internationalization Tag Set (ITS) is a set of attributes and elements designed to provide internationalization and localization support in XML documents.
Petri Net Markup Language (PNML) is an interchange format aimed at enabling Petri net tools to exchange Petri net models. PNML is an XML-based syntax for high-level Petri nets, which is being designed as a standard interchange format for Petri net tools.
It will end up being the second part of the ISO standard ISO/IEC 15909.
PNML grammar is publicly available on its reference site.
Extensible Hypertext Markup Language (XHTML) is part of the family of XML markup languages. It mirrors or extends versions of the widely used Hypertext Markup Language (HTML), the language in which Web pages are formulated.
A well-formed document in XML is a document that "adheres to the syntax rules specified by the XML 1.0 specification in that it must satisfy both physical and logical structures".



