Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories and Nunavut. This area covers about 48 per cent of Canada's total land area, but has less than 0.5 per cent of Canada's population.

The Beaufort Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of the Northwest Territories, the Yukon, and Alaska, and west of Canada's Arctic islands. The sea is named after Sir Francis Beaufort, a hydrographer. The Mackenzie River, the longest in Canada, empties into the Canadian part of the Beaufort Sea west of Tuktoyaktuk, which is one of the few permanent settlements on the sea's shores.
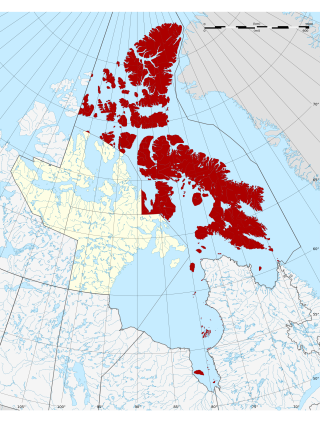
The Qikiqtaaluk Region, Qikiqtani Region or the Baffin Region is the easternmost, northernmost, and southernmost administrative region of Nunavut, Canada. Qikiqtaaluk is the traditional Inuktitut name for Baffin Island. Although the Qikiqtaaluk Region is the most commonly used name in official contexts, several notable public organizations, including Statistics Canada prior to the 2021 Canadian census, use the older term Baffin Region.

Devon Island is an island in Canada and the largest uninhabited island in the world. It is located in Baffin Bay, Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is one of the largest members of the Arctic Archipelago, the second-largest of the Queen Elizabeth Islands, Canada's sixth-largest island, and the 27th-largest island in the world. It has an area of 55,247 km2 (21,331 sq mi). The bedrock is Precambrian gneiss and Paleozoic siltstones and shales. The highest point is the Devon Ice Cap at 1,920 m (6,300 ft) which is part of the Arctic Cordillera. Devon Island contains several small mountain ranges, such as the Treuter Mountains, Haddington Range and the Cunningham Mountains. The notable similarity of its surface to that of Mars has attracted interest from scientists.
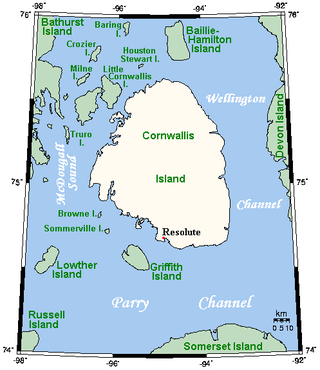
Cornwallis Island is one of the Queen Elizabeth Islands, part of the Arctic Archipelago, in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut in the Canadian Arctic. It lies to the west of Devon Island, the largest uninhabited island in the world, and at its greatest length is about 113 km (70 mi). At 6,995 km2 (2,701 sq mi) in size, it is the 96th largest island in the world, and Canada's 21st largest island. Cornwallis Island is separated by the Wellington Channel from Devon Island, and by the Parry Channel from Somerset Island to the south. Northwest of Cornwallis Island lies Little Cornwallis Island, the biggest of a group of small islands at the north end of McDougall Sound, which separates Cornwallis Island from nearby Bathurst Island.

Cambridge Bay is a hamlet located on Victoria Island in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is the largest settlement on Victoria Island. Cambridge Bay is named for Prince Adolphus, Duke of Cambridge, while the traditional Inuinnaqtun name for the area is Ikaluktutiak or Iqaluktuuttiaq meaning "good fishing place".

The Arctic char or Arctic charr is a cold-water fish in the family Salmonidae, native to alpine lakes, as well as Arctic and subarctic coastal waters in the Holarctic.

Ovayok Territorial Park is a park situated 15 km (9.3 mi) east of Cambridge Bay, in the Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut, Canada. The park is relatively small and covers an area of approximately 16 km2 (6.2 sq mi). The park can be accessed by vehicle from the community as a gravel road runs directly to it.

Lake Hazen is a freshwater lake in the northern part of Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, Canada, north of the Arctic Circle. It is the largest lake north of the Arctic Circle by volume. By surface area it is third largest, after Lake Taymyr in Russia and Lake Inari in Finland.
The Burnside River is a river in the Canadian territory of Nunavut. It has its headwaters at Contwoyto Lake, flows across the Precambrian Shield's Contwoyto Plateau, flows through isolated and rugged tundra, into Lake Kathawachaga, and through the Wilberforce Hills region. Before emptying into Bathurst Inlet on the Arctic Ocean, the Mara River empties into the Burnside River. The river has an island, Nadlak, historically notable for Inuit use of caribou antlers as hut roof infrastructures.

Chantrey Inlet (Tariunnuaq) is a bay on the Arctic coast of Canada. It marks the southeast "corner" where the generally east–west coast turns sharply north. To the west is the Adelaide Peninsula and to the east is mainland. King William Island shelters it to the northwest. To the west the Simpson Strait separates King William Island from the Adelaide Peninsula. Its mouth is marked by Point Ogle on the west and Cape Britannia on the east. West of Point Ogle is Barrow Bay, Starvation Cove and Point Richardson. The Back River enters from the south. Near its mouth is a weather station on the Hayes River. Montreal Island is contained within the Inlet. It is 160 km (100 mi) long and 80 km (50 mi) wide at its mouth.

Tahiryuaq, formerly Ferguson Lake, is located on southern Victoria Island in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, in northern Canada. It drains westward into Iqaluktuuq which is a segment of the Ekalluk River, 8.0 km (5 mi) from the northeastern side of Wellington Bay (Ekaloktok), on Dease Strait, Arctic Ocean Ferguson Lake was the namesake of Constable Ferguson, a Royal Canadian Mounted Police member, but is now known by the original name of Tahiryuaq

Copper Inuit, also known as Inuinnait and Kitlinermiut, are a Canadian Inuit group who live north of the tree line, in what is now the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut and in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories. Most of them historically lived in the area around Coronation Gulf, on Victoria Island, and southern Banks Island.

Kuunajuk formerly Ellice River, for Edward Ellice, Jr., is a waterway in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada. It rises close to the Back River between Lake Beechey and Pelly Lake, and flows northward into the Queen Maud Gulf. Its mouth opens between Campbell Bay and Gernon Bay. The land between the river and Sherman Inlet is generally flat and marshy. Muskox and barren-ground caribou frequent the area.

The Inuvialuit Settlement Region, abbreviated as ISR, located in Canada's western Arctic, was designated in 1984 in the Inuvialuit Final Agreement by the Government of Canada for the Inuvialuit people. It spans 90,650 km2 (35,000 sq mi) of land, mostly above the tree line, and includes several subregions: the Beaufort Sea, the Mackenzie River delta, the northern portion of Yukon, and the northwest portion of the Northwest Territories. The ISR includes both Crown Lands and Inuvialuit Private Lands.
Creswell Bay is an Arctic waterway in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is an arm of western Prince Regent Inlet in eastern Somerset Island. Its northeastern landmark, Fury Point, is approximately 100 km (62 mi) west of Baffin Island.
The Ekalluk River is a river in the Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in central through southeastern Victoria Island. Its source is Tahiryuaq, and it flows west to Wellington Bay and east to Albert Edward Bay. Nearby lakes include Keyhole Lake, Kitigaq, and Surrey Lake. The closest community is Cambridge Bay.

Sylvia Grinnell Territorial Park is a Canadian territorial park on Baffin Island in the province of Nunavut.

Stanwell-Fletcher Lake is the largest lake on Somerset Island, the tenth-largest island of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The lake, along with most of Somerset Island, is located within the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the Canadian territory of Nunavut.