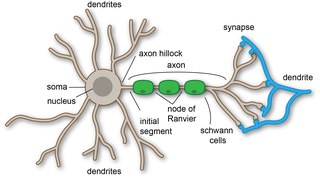
Dendrites, also dendrons, are branched protoplasmic extensions of a nerve cell that propagate the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body, or soma, of the neuron from which the dendrites project. Electrical stimulation is transmitted onto dendrites by upstream neurons via synapses which are located at various points throughout the dendritic tree.

A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via synapses - specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells.
Computational neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience which employs mathematical models, computer simulations, theoretical analysis and abstractions of the brain to understand the principles that govern the development, structure, physiology and cognitive abilities of the nervous system.
An inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) is a kind of synaptic potential that makes a postsynaptic neuron less likely to generate an action potential. IPSP were first investigated in motorneurons by David P. C. Lloyd, John Eccles and Rodolfo Llinás in the 1950s and 1960s. The opposite of an inhibitory postsynaptic potential is an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP), which is a synaptic potential that makes a postsynaptic neuron more likely to generate an action potential. IPSPs can take place at all chemical synapses, which use the secretion of neurotransmitters to create cell to cell signalling. Inhibitory presynaptic neurons release neurotransmitters that then bind to the postsynaptic receptors; this induces a change in the permeability of the postsynaptic neuronal membrane to particular ions. An electric current that changes the postsynaptic membrane potential to create a more negative postsynaptic potential is generated, i.e. the postsynaptic membrane potential becomes more negative than the resting membrane potential, and this is called hyperpolarisation. To generate an action potential, the postsynaptic membrane must depolarize—the membrane potential must reach a voltage threshold more positive than the resting membrane potential. Therefore, hyperpolarisation of the postsynaptic membrane makes it less likely for depolarisation to sufficiently occur to generate an action potential in the postsynaptic neurone.

Pyramidal cells, or pyramidal neurons, are a type of multipolar neuron found in areas of the brain including the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. Pyramidal neurons are the primary excitation units of the mammalian prefrontal cortex and the corticospinal tract. Pyramidal neurons are also one of two cell types where the characteristic sign, Negri bodies, are found in post-mortem rabies infection. Pyramidal neurons were first discovered and studied by Santiago Ramón y Cajal. Since then, studies on pyramidal neurons have focused on topics ranging from neuroplasticity to cognition.
Synaptogenesis is the formation of synapses between neurons in the nervous system. Although it occurs throughout a healthy person's lifespan, an explosion of synapse formation occurs during early brain development, known as exuberant synaptogenesis. Synaptogenesis is particularly important during an individual's critical period, during which there is a certain degree of synaptic pruning due to competition for neural growth factors by neurons and synapses. Processes that are not used, or inhibited during their critical period will fail to develop normally later on in life.

Neuronal noise or neural noise refers to the random intrinsic electrical fluctuations within neuronal networks. These fluctuations are not associated with encoding a response to internal or external stimuli and can be from one to two orders of magnitude. Most noise commonly occurs below a voltage-threshold that is needed for an action potential to occur, but sometimes it can be present in the form of an action potential; for example, stochastic oscillations in pacemaker neurons in suprachiasmatic nucleus are partially responsible for the organization of circadian rhythms.

The basal ganglia form a major brain system in all species of vertebrates, but in primates there are special features that justify a separate consideration. As in other vertebrates, the primate basal ganglia can be divided into striatal, pallidal, nigral, and subthalamic components. In primates, however, there are two pallidal subdivisions called the external globus pallidus (GPe) and internal globus pallidus (GPi). Also in primates, the dorsal striatum is divided by a large tract called the internal capsule into two masses named the caudate nucleus and the putamen—in most other species no such division exists, and only the striatum as a whole is recognized. Beyond this, there is a complex circuitry of connections between the striatum and cortex that is specific to primates. This complexity reflects the difference in functioning of different cortical areas in the primate brain.

Classical cable theory uses mathematical models to calculate the electric current along passive neurites, particularly the dendrites that receive synaptic inputs at different sites and times. Estimates are made by modeling dendrites and axons as cylinders composed of segments with capacitances and resistances combined in parallel. The capacitance of a neuronal fiber comes about because electrostatic forces are acting through the very thin lipid bilayer. The resistance in series along the fiber is due to the axoplasm's significant resistance to movement of electric charge.
Neural backpropagation is the phenomenon in which, after the action potential of a neuron creates a voltage spike down the axon, another impulse is generated from the soma and propagates towards the apical portions of the dendritic arbor or dendrites. In addition to active backpropagation of the action potential, there is also passive electrotonic spread. While there is ample evidence to prove the existence of backpropagating action potentials, the function of such action potentials and the extent to which they invade the most distal dendrites remain highly controversial.
In neuroscience and computer science, synaptic weight refers to the strength or amplitude of a connection between two nodes, corresponding in biology to the amount of influence the firing of one neuron has on another. The term is typically used in artificial and biological neural network research.

Biological neuron models, also known as a spiking neuron models, are mathematical descriptions of the properties of certain cells in the nervous system that generate sharp electrical potentials across their cell membrane, roughly one millisecond in duration, called action potentials or spikes. Since spikes are transmitted along the axon and synapses from the sending neuron to many other neurons, spiking neurons are considered to be a major information processing unit of the nervous system. Spiking neuron models can be divided into different categories: the most detailed mathematical models are biophysical neuron models that describe the membrane voltage as a function of the input current and the activation of ion channels. Mathematically simpler are integrate-and-fire models that describe the membrane voltage as a function of the input current and predict the spike times without a description of the biophysical processes that shape the time course of an action potential. Even more abstract models only predict output spikes as a function of the stimulation where the stimulation can occur through sensory input or pharmacologically. This article provides a short overview of different spiking neuron models and links, whenever possible to experimental phenomena. It includes deterministic and probabilistic models.
In mammals, the Bötzinger complex (BötC) is a group of neurons located in the rostral ventrolateral medulla, and ventral respiratory column. In the medulla, this group is located caudally to the facial nucleus and ventral to nucleus ambiguus.
The Mauthner cells are a pair of big and easily identifiable neurons located in the rhombomere 4 of the hindbrain in fish and amphibians that are responsible for a very fast escape reflex. The cells are also notable for their unusual use of both chemical and electrical synapses.

In neurophysiology, a dendritic spike refers to an action potential generated in the dendrite of a neuron. Dendrites are branched extensions of a neuron. They receive electrical signals emitted from projecting neurons and transfer these signals to the cell body, or soma. Dendritic signaling has traditionally been viewed as a passive mode of electrical signaling. Unlike its axon counterpart which can generate signals through action potentials, dendrites were believed to only have the ability to propagate electrical signals by physical means: changes in conductance, length, cross sectional area, etc. However, the existence of dendritic spikes was proposed and demonstrated by W. Alden Spencer, Eric Kandel, Rodolfo Llinás and coworkers in the 1960s and a large body of evidence now makes it clear that dendrites are active neuronal structures. Dendrites contain voltage-gated ion channels giving them the ability to generate action potentials. Dendritic spikes have been recorded in numerous types of neurons in the brain and are thought to have great implications in neuronal communication, memory, and learning. They are one of the major factors in long-term potentiation.

Retrograde tracing is a research method used in neuroscience to trace neural connections from their point of termination to their source. Retrograde tracing techniques allow for detailed assessment of neuronal connections between a target population of neurons and their inputs throughout the nervous system. These techniques allow the "mapping" of connections between neurons in a particular structure and the target neurons in the brain. The opposite technique is anterograde tracing, which is used to trace neural connections from their source to their point of termination. Both the anterograde and retrograde tracing techniques are based on the visualization of axonal transport.
Gordon Murray Shepherd was an American neuroscientist who carried out basic experimental and computational research on how neurons are organized into microcircuits to carry out the functional operations of the nervous system. Using the olfactory system as a model that spans multiple levels of space, time and disciplines, his studies have ranged from molecular to behavioral, recognized by an annual lecture at Yale University on "integrative neuroscience". At the time of his death, he was professor of neuroscience emeritus at the Yale School of Medicine. He graduated from Iowa State University with a BA, Harvard Medical School with a MD, and the University of Oxford with a DPhill.
Compartmental modelling of dendrites deals with multi-compartment modelling of the dendrites, to make the understanding of the electrical behavior of complex dendrites easier. Basically, compartmental modelling of dendrites is a very helpful tool to develop new biological neuron models. Dendrites are very important because they occupy the most membrane area in many of the neurons and give the neuron an ability to connect to thousands of other cells. Originally the dendrites were thought to have constant conductance and current but now it has been understood that they may have active Voltage-gated ion channels, which influences the firing properties of the neuron and also the response of neuron to synaptic inputs. Many mathematical models have been developed to understand the electric behavior of the dendrites. Dendrites tend to be very branchy and complex, so the compartmental approach to understand the electrical behavior of the dendrites makes it very useful.
Dendrodendritic synapses are connections between the dendrites of two different neurons. This is in contrast to the more common axodendritic synapse (chemical synapse) where the axon sends signals and the dendrite receives them. Dendrodendritic synapses are activated in a similar fashion to axodendritic synapses in respects to using a chemical synapse. An incoming action potential permits the release of neurotransmitters to propagate the signal to the post synaptic cell. There is evidence that these synapses are bi-directional, in that either dendrite can signal at that synapse. Ordinarily, one of the dendrites will display inhibitory effects while the other will display excitatory effects. The actual signaling mechanism utilizes Na+ and Ca2+ pumps in a similar manner to those found in axodendritic synapses.
Arnold Bernard Scheibel was an American neuroscientist, professor of psychiatry and neuroanatomy, and the former director of the Brain Research Institute at the University of California, Los Angeles. He is well known for his research regarding the anatomy of the spinal cord, brain stem, and cerebral cortex. He introduced the concept of modular organization in the nervous system. His Golgi studies of human brain tissue extended the knowledge about the nature of neuronal changes in senile brain disease and in schizophrenia. He demonstrated the correlations between human cognitive activity and structural change, and also emphasized the role of plasticity in the living reactive brain."








