Related Research Articles

Franklin Delano Roosevelt, commonly known by his initials FDR, was an American politician and statesman who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. He was a member of the Democratic Party and is the only U.S. president to have served more than two terms in office. During his third and fourth terms he was preoccupied with World War II.

The 1944 United States presidential election was the 40th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 7, 1944. The election took place during World War II, which ended the following year. Incumbent Democratic President Franklin D. Roosevelt defeated Republican Thomas E. Dewey to win an unprecedented fourth term. It was also the fifth presidential election in which both major party candidates were registered in the same home state; the others have been in 1860, 1904, 1920, 1940, and 2016.
The New Deal coalition was an American political coalition that supported the Democratic Party beginning in 1932. The coalition is named after President Franklin D. Roosevelt's New Deal programs, and the follow-up Democratic presidents. It was composed of voting blocs who supported them. The coalition included labor unions, blue-collar workers, racial and religious minorities, liberal white Southerners, and intellectuals. Besides voters the coalition included powerful interest groups: Democratic Party organizations in most states, city machines, labor unions, some third parties, universities, and foundations. It was largely opposed by the Republican Party, the business community, and rich Protestants. In creating his coalition, Roosevelt was at first eager to include liberal Republicans and some radical third parties, even if it meant downplaying the "Democratic" name. By the 1940s, the Republican and third-party allies had mostly been defeated. In 1948, the Democratic Party stood alone and survived the splits that created two splinter parties.

Kenneth Lauren Burns is an American filmmaker known for his documentary films and television series, many of which chronicle American history and culture. His work is often produced in association with WETA-TV and/or the National Endowment for the Humanities and distributed by PBS.

Henry Steele Commager was an American historian. As one of the most active and prolific liberal intellectuals of his time, with 40 books and 700 essays and reviews, he helped define modern liberalism in the United States.

Samuel Eliot Morison was an American historian noted for his works of maritime history and American history that were both authoritative and popular. He received his Ph.D. from Harvard University in 1912, and taught history at the university for 40 years. He won Pulitzer Prizes for Admiral of the Ocean Sea (1942), a biography of Christopher Columbus, and John Paul Jones: A Sailor's Biography (1959). In 1942, he was commissioned to write a history of United States naval operations in World War II, which was published in 15 volumes between 1947 and 1962. Morison wrote the popular Oxford History of the American People (1965), and co-authored the classic textbook The Growth of the American Republic (1930) with Henry Steele Commager.
The Bureau of Prohibition was the United States federal law enforcement agency formed to enforce the National Prohibition Act of 1919, commonly known as the Volstead Act, which enforced the 18th Amendment to the United States Constitution regarding the prohibition of the manufacture, sale, and transportation of alcoholic beverages. When it was first established in 1920, it was a unit of the Bureau of Internal Revenue. On April 1, 1927, it became an independent entity within the Department of the Treasury, changing its name from the Prohibition Unit to the Bureau of Prohibition. In 1930, it became part of the Department of Justice. By 1933, with the repeal of Prohibition imminent, it was briefly absorbed into the FBI, or "Bureau of Investigation" as it was then called, and became the Bureau's "Alcohol Beverage Unit," though, for practical purposes it continued to operate as a separate agency. Very shortly after that, once repeal became a reality, and the only federal laws regarding alcoholic beverages being their taxation, it was switched back to Treasury, where it was renamed the Alcohol Tax Unit.

Geoffrey Champion Ward is an American editor, author, historian and writer of scripts for American history documentaries for public television. He is the author or co-author of 19 books, including 10 companion books to the documentaries he has written. He is the winner of seven Emmy Awards.
The Second New Deal is a term used by historians to characterize the second stage, 1935–36, of the New Deal programs of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The most famous laws included the Emergency Relief Appropriation Act, the Banking Act, the Wagner National Labor Relations Act, the Public Utility Holding Companies Act, the Social Security Act, and the Wealth Tax Act.

Before, during and after his presidential terms and continuing today, there has been criticism of Franklin D. Roosevelt (1882–1945). His critics have questioned not only his policies and positions, but also accused him of trying to centralize power in his own hands by controlling both the government and the Democratic Party. Many denounced his breaking of a long-standing tradition by running for a third term in 1940.
The Francis Parkman Prize, named after Francis Parkman, is awarded by the Society of American Historians for the best book in American history each year. Its purpose is to promote literary distinction in historical writing. The Society of American Historians is an affiliate of the American Historical Association.

Margaret Lynch Suckley was a sixth cousin, intimate friend, and confidante of US President Franklin D. Roosevelt, as well as an archivist for the first American presidential library. She was one of four women at the Little White House with Roosevelt in Warm Springs, Georgia, when he died of a cerebral hemorrhage in 1945.

Walter Parker Stacy was a chief justice of the North Carolina Supreme Court from 1925 until his death in 1951. He is the longest-serving chief justice in North Carolina history.

Prohibition is a 2011 American television documentary miniseries directed by Ken Burns and Lynn Novick with narration by Peter Coyote. The series originally aired on PBS between October 2, 2011 and October 4, 2011. It was funded in part by the National Endowment for the Humanities. It draws heavily from the 2010 book Last Call: The Rise and Fall of Prohibition by Daniel Okrent.

The Roosevelts: An Intimate History is a 2014 American documentary television miniseries directed and produced by Ken Burns. It covers the lives and times of the three most prominent members of the Roosevelt family, Theodore Roosevelt, a Republican and the 26th President of the United States; Franklin D. Roosevelt, a Democrat, the 32nd President of the United States, and fifth cousin of Theodore; and Eleanor Roosevelt, the longest-serving First Lady of the United States, a niece of Theodore, and wife of Franklin. As a result of the influence of Theodore and Franklin as Presidents, as well as Eleanor as First Lady, a modern democratic state of equal opportunity was begun in the United States. The series begins with the birth of Theodore in 1858 and ends with the death of Eleanor in 1962.
Alonzo L. Hamby is an American historian and academic. He is distinguished professor of history emeritus at Ohio University and the recipient of two National Endowment for the Humanities Fellowships, a Harry S. Truman Library Institute Senior Fellowship, a Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars Fellowship, and the Ohio Academy of History Distinguished Service Award.

The 1936 United States presidential election in Arkansas took place on November 3, 1936, as part of the 1936 United States presidential election. State voters chose nine representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
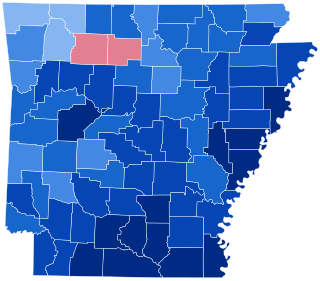
The 1940 United States presidential election in Arkansas took place on November 5, 1940, as part of the 1940 United States presidential election. State voters chose nine representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The first term of the presidency of Franklin D. Roosevelt began on March 4, 1933, when he was inaugurated as the 32nd president of the United States, and the second term of his presidency ended on January 20, 1941, with his inauguration to a third term. Roosevelt, the Democratic governor of the largest state, New York, took office after defeating incumbent President Herbert Hoover, his Republican opponent in the 1932 presidential election. Roosevelt led the implementation of the New Deal, a series of programs designed to provide relief, recovery, and reform to Americans and the American economy during the Great Depression. He also presided over a realignment that made his New Deal Coalition of labor unions, big city machines, white ethnics, African Americans, and rural white Southerners dominant in national politics until the 1960s and defined modern American liberalism.

The third presidential term of Franklin D. Roosevelt began on January 20, 1941, when he was once again inaugurated as the 32nd president of the United States, and the fourth term of his presidency ended with his death on April 12, 1945. Roosevelt won a third term by defeating Republican nominee Wendell Willkie in the 1940 United States presidential election. He remains the only president to serve for more than two terms. Unlike his first two terms, Roosevelt's third and fourth terms were dominated by foreign policy concerns, as the United States became involved in World War II in December 1941.
References
- ↑ Mattson, Kevin (2003). "The Historian as a Social Critic: Christopher Lasch and the Uses of History". The History Teacher. 36 (3): 378. doi:10.2307/1555694. ISSN 1945-2292. JSTOR 1555694.
- ↑ Mattson, Kevin (March 31, 2017). "An Oracle for Trump's America?". The Chronicle of Higher Education. Vol. 63, no. 30. Washington. ISSN 0009-5982 . Retrieved November 19, 2019.
- ↑ "unctv.org".
- ↑ "Contemporary Authors: First revision". Gale Research Company. August 29, 1969 – via Google Books.
- ↑ Prohibition: A film by Ken Burns & Lynn Novick, Episode 3: A Nation of Hypocrites, PBS, 2011
- ↑ "William E. Leuchtenburg Papers". University of North Carolina Archives.
- ↑ "Four with College ties win state's highest civilian honor — College of Arts & Sciences". college.unc.edu. Archived from the original on December 1, 2007.
- ↑ "Film & Website Credits". Prohibition: A film by Ken Burns & Lynn Novick. PBS. Retrieved January 9, 2019.
- ↑ "Professor Emeritus William Leuchtenburg celebrates 100th Birthday!". University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill . Retrieved September 28, 2022.
- ↑ "UNC-CH's William Leuchtenburg helped with Roosevelt dedication". www.unc.edu. Archived from the original on October 15, 2004.