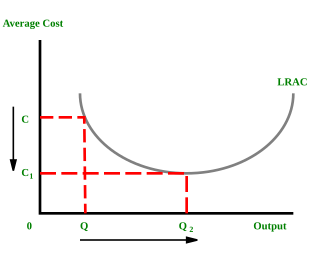
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, with cost per unit of output decreasing with increasing scale. At the basis of economies of scale there may be technical, statistical, organizational or related factors to the degree of market control.

In economics, the Gini coefficient, sometimes called Gini index, or Gini ratio, is a measure of statistical dispersion intended to represent the income or wealth distribution of a nation's residents, and is the most commonly used measurement of inequality. It was developed by the Italian statistician and sociologist Corrado Gini and published in his 1912 paper Variability and Mutability.

An industry is a sector that produces goods or related services within an economy. The major source of revenue of a group or company is an indicator of what industry it should be classified in. When a large corporate group has multiple sources of revenue generation, it is considered to be working in different industries. The manufacturing industry became a key sector of production and labour in European and North American countries during the Industrial Revolution, upsetting previous mercantile and feudal economies. This came through many successive rapid advances in technology, such as the development of steam power and the production of steel and coal.

Political economy is the study of production and trade and their relations with law, custom and government; and with the distribution of national income and wealth. As a discipline, political economy originated in moral philosophy, in the 18th century, to explore the administration of states' wealth, with "political" signifying the Greek word polity and "economy" signifying the Greek word "okonomie". The earliest works of political economy are usually attributed to the British scholars Adam Smith, Thomas Malthus, and David Ricardo, although they were preceded by the work of the French physiocrats, such as François Quesnay (1694–1774) and Anne-Robert-Jacques Turgot (1727–1781).

A developing country is a country with a less developed industrial base and a low Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreement on which countries fit this category. A nation's GDP per capita compared with other nations can also be a reference point. In general, the United Nations accepts any country's claim of itself being "developing".
Economic geography is the subfield of geography which studies the influence of geography on economic activity. It can also be considered a subfield or method in economics.
The knowledge economy is the use of knowledge to create goods and services. In particular, it refers to a high portion of skilled workers in the economy of a locality, country, or the world, and the idea that most jobs require specialized skills. In particular, the main personal capital of knowledge workers is knowledge, and many knowledge worker jobs require a lot of thinking and manipulating information as opposed to moving or crafting physical objects. It stands in contrast to an agrarian economy or an industrialized economy. Knowledge economy emphasizes the importance of skills in a service economy, the third phase of economic development, also called a post-industrial economy. It is related to the terms information economy, which emphasizes the importance of information as non-physical capital, and digital economy, which emphasize the degree to which information technology facilitates trade. For companies, intellectual property such as trade secrets, copyrighted material, and patented processes become more valuable in a knowledge economy than in earlier eras.
Socioeconomics is the social science that studies how economic activity affects and is shaped by social processes. In general it analyzes how societies progress, stagnate, or regress because of their local or regional economy, or the global economy. Societies are divided into 3 groups: social, cultural and economic.
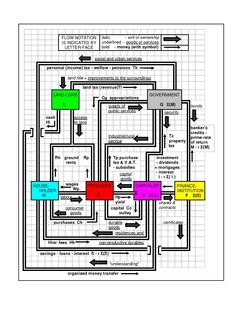
An economic system, or economic order, is a system of production, resource allocation and distribution of goods and services within a society or a given geographic area. It includes the combination of the various institutions, agencies, entities, decision-making processes and patterns of consumption that comprise the economic structure of a given community. As such, an economic system is a type of social system. The mode of production is a related concept. All economic systems have three basic questions to ask: what to produce, how to produce and in what quantities and who receives the output of production.
The post–World War I recession was an economic recession that hit much of the world in the aftermath of World War I. In many nations, especially in North America, economic growth continued and even accelerated during World War I as nations mobilized their economies to fight the war in Europe. After the war ended, the global economy began to decline. In the United States, 1918–1919 saw a modest economic retreat, but the second part of 1919 saw a mild recovery. A more severe recession hit the United States in 1920 and 1921, when the global economy fell very sharply.

The economy of India is characterised as a developing market economy. It is the world's fifth-largest economy by nominal GDP and the third-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP). According to the IMF, on a per capita income basis, India ranked 142nd by GDP (nominal) and 119th by GDP (PPP) per capita in 2018. From independence in 1947 until 1991, successive governments promoted protectionist economic policies with extensive state intervention and regulation; the end of the Cold War and an acute balance of payments crisis in 1991 led to the adoption of a broad program of economic liberalisation. Since the start of the 21st century, annual average GDP growth has been 6% to 7%, and from 2014 to 2018, India was the world's fastest growing major economy, surpassing China. Historically India was one of the largest economy in the world for most of the two millennia from 1st until 19th century.

World-systems theory is a multidisciplinary, macro-scale approach to world history and social change which emphasizes the world-system as the primary unit of social analysis.

During the Roman Republic, the Roman economy was largely agrarian, centered on the trading of commodities such as grain and wine. Financial markets were established through such trade, and financial institutions which extended credit for personal use and public infrastructure, were established primarily through inter-family wealth. In times of agricultural and cash shortfall, Roman officials and moneyers tended to respond by coining money; this happened during the prolonged crisis of the First Punic War, and created economic distortion and difficulties. Beginning in the early Roman Empire, the economy became monetized to a near-universal extent, in the sense of using money to express prices and debts, and a basic banking system was formed. Emperors issued coinage stamped with their portraits to disseminate propaganda, to create public goodwill, and to symbolise their wealth and power. The Roman Imperial economy was often unstable, inflated in part by Emperors who issued money to fund high-profile imperial projects such as public building works, or costly wars that offered opportunities for propaganda, but little or no material gain.
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services by different agents. Understood in its broadest sense, 'The economy is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the production, use, and management of resources'. Economic agents can be individuals, businesses, organizations, or governments. Economic transactions occur when two groups or parties agree to the value or price of the transacted good or service, commonly expressed in a certain currency. However, monetary transactions only account for a small part of the economic domain. Economic activity is spurred by production which uses natural resources, labor and capital. It has changed over time due to technology, innovation such as, that which produces intellectual property and changes in industrial relations. A given economy is the result of a set of processes that involves its culture, values, education, technological evolution, history, social organization, political structure and legal systems, as well as its geography, natural resource endowment, and ecology, as main factors. These factors give context, content, and set the conditions and parameters in which an economy functions. In other words, the economic domain is a social domain of human practices and transactions. It does not stand alone.

Christopher K. Chase-Dunn is an American sociologist best known for his contributions to world-systems theory.

A black market, underground economy or shadow economy, is a clandestine market or series of transactions that has some aspect of illegality or is characterized by some form of noncompliant behavior with an institutional set of rules. If the rule defines the set of goods and services whose production and distribution is prohibited by law, non-compliance with the rule constitutes a black market trade since the transaction itself is illegal. Parties engaging in the production or distribution of prohibited goods and services are members of the illegal economy. Examples include the drug trade, prostitution, illegal currency transactions and human trafficking. Violations of the tax code involving income tax evasion constitute membership in the unreported economy.

The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression that took place mostly during the 1930s, beginning in the United States. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations; in most countries, it started in 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s. It was the longest, deepest, and most widespread depression of the 20th century. In the 21st century, the Great Depression is commonly used as an example of how intensely the world's economy can decline.











