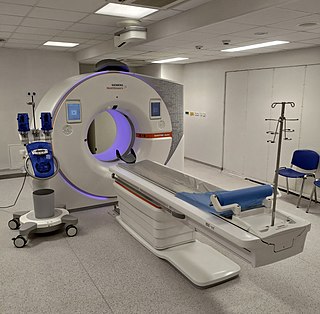
A computed tomography scan is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists.
Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) is a technical standard for the digital storage and transmission of medical images and related information. It includes a file format definition, which specifies the structure of a DICOM file, as well as a network communication protocol that uses TCP/IP to communicate between systems. The primary purpose of the standard is to facilitate communication between the software and hardware entities involved in medical imaging, especially those that are created by different manufacturers. Entities that utilize DICOM files include components of picture archiving and communication systems (PACS), such as imaging machines (modalities), radiological information systems (RIS), scanners, printers, computing servers, and networking hardware.
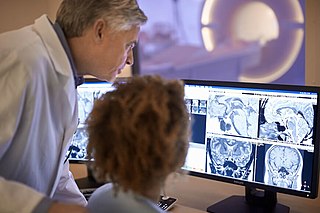
Radiology is the medical specialty that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography, but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no ionizing electromagnetic radiation, as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above.
Medical physics deals with the application of the concepts and methods of physics to the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of human diseases with a specific goal of improving human health and well-being. Since 2008, medical physics has been included as a health profession according to International Standard Classification of Occupation of the International Labour Organization.

Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging.

Health informatics is the study and implementation of computer structures and algorithms to improve communication, understanding, and management of medical information. It can be viewed as branch of engineering and applied science.

Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is performed by injecting a radio-opaque contrast agent into the blood vessel and imaging using X-ray based techniques such as fluoroscopy.

GE HealthCare Technologies, Inc. is an American multinational medical technology company headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. It was spun-off from General Electric on January 4, 2023, with GE retaining 10.24%. As of 2017, it is a manufacturer and distributor of diagnostic imaging agents and radiopharmaceuticals for imaging modalities used in medical imaging procedures. It offers dyes used in magnetic-resonance-imaging procedures; manufactures medical diagnostic equipment, including CT image machines; MRI, XRAY; Ultrasound; Cath Labs; Mammogram; Nuclear Medicine Cameras; and develops Health technology for medical imaging and information technologies, medical diagnostics, patient monitoring systems, disease research, drug discovery, and biopharmaceutical manufacturing. It was incorporated in 1994 and operates in more than 100 countries.

Radiographers, also known as radiologic technologists, diagnostic radiographers and medical radiation technologists are healthcare professionals who specialise in the imaging of human anatomy for the diagnosis and treatment of pathology. Radiographers are infrequently, and almost always erroneously, known as x-ray technicians. In countries that use the title radiologic technologist they are often informally referred to as techs in the clinical environment; this phrase has emerged in popular culture such as television programmes. The term radiographer can also refer to a therapeutic radiographer, also known as a radiation therapist.

Carestream Health, formerly Eastman Kodak Company's Health Group, is an independent subsidiary of Onex Corporation which is one of Canada's largest corporations.
Imaging informatics, also known as radiology informatics or medical imaging informatics, is a subspecialty of biomedical informatics that aims to improve the efficiency, accuracy, usability and reliability of medical imaging services within the healthcare enterprise. It is devoted to the study of how information about and contained within medical images is retrieved, analyzed, enhanced, and exchanged throughout the medical enterprise.
Health information technology (HIT) is health technology, particularly information technology, applied to health and health care. It supports health information management across computerized systems and the secure exchange of health information between consumers, providers, payers, and quality monitors. Based on a 2008 report on a small series of studies conducted at four sites that provide ambulatory care – three U.S. medical centers and one in the Netherlands, the use of electronic health records (EHRs) was viewed as the most promising tool for improving the overall quality, safety and efficiency of the health delivery system.

Medical image sharing is the electronic exchange of medical images between hospitals, physicians and patients. Rather than using traditional media, such as a CD or DVD, and either shipping it out or having patients carry it with them, technology now allows for the sharing of these images using the cloud. The primary format for images is DICOM. Typically, non-image data such as reports may be attached in standard formats like PDF during the sending process. Additionally, there are standards in the industry, such as IHE Cross Enterprise Document Sharing for Imaging (XDS-I), for managing the sharing of documents between healthcare enterprises. A typical architecture involved in setup is a locally installed server, which sits behind the firewall, allowing secure transmissions with outside facilities. In 2009, the Radiological Society of North America launched the "Image Share" project, with the goal of giving patients control of their imaging histories by allowing them to manage these records as they would online banking or shopping.
Harsh Mahajan is an Indian radiologist and one of the pioneers of imaging technology in India. He is the founder of Mahajan Imaging, a diagnostic imaging centre in the Indian capital of New Delhi. He is a former president of the Indian Radiological and Imaging Association (IRIA) and the director of the Department of Nuclear Medicine and Bone Densitometry at the Sir Ganga Ram Hospital. He has served as the honorary radiologist to the President of India and as the Honorary Consultant to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). He is on the Board of Advisors of Rishihood University. He has published several articles on clinical radiography and other medical topics. The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour of the Padma Shri in 2002.

Artificial intelligence in healthcare is a term used to describe the use of machine-learning algorithms and software, or artificial intelligence (AI), to copy human cognition in the analysis, presentation, and understanding of complex medical and health care data, or to exceed human capabilities by providing new ways to diagnose, treat, or prevent disease. Specifically, AI is the ability of computer algorithms to arrive at approximate conclusions based solely on input data.
Enterprise imaging has been defined as "a set of strategies, initiatives, and workflows implemented across a healthcare enterprise to consistently and optimally capture, index, manage, store, distribute, view, exchange, and analyze all clinical imaging and multimedia content to enhance the electronic health record". The concepts of enterprise imaging are elucidated in a series of papers by members of the HIMSS-SIIM Enterprise Imaging Workgroup.
Elizabeth Anne Krupinski is a Professor and Vice Chair for Research of Radiology & Imaging Sciences at Emory University. She works on the perception of medical images and decision-making. Dr. Krupinski is a Fellow of SPIE, Fellow of the Society Imaging Informatics in Medicine, Fellow of the American Telemedicine Association(ATA) and Fellow of the American Institute for Medical & Biological Engineering (AIMBE). She has previously served as Chair for the SPIE Medical Imaging Conference, Chair of SIIM, President of the American Telemedicine Association, President of the Medical Image Perception Society and Vice President of the Society for Education and the Advancement of Research in Connected Health.
Jose Morey is a Puerto Rican physician. He is the founder and chief executive officer of Ad Astra Media.
Sergey Pavlovich Morozov is a Russian radiologist and healthcare official.
Robert A. Greenes is a pioneer in the field of biomedical informatics (BMI). His work has focused on knowledge representation, decision support, and human-computer interaction for health and healthcare. He was co-developer of the MUMPS System and Language in the 1960s. He is an Emeritus Professor of Biomedical Informatics at Arizona State University.









