
Chrominance is the signal used in video systems to convey the color information of the picture, separately from the accompanying luma signal. Chrominance is usually represented as two color-difference components: U = B′ − Y′ (blue − luma) and V = R′ − Y′ (red − luma). Each of these difference components may have scale factors and offsets applied to it, as specified by the applicable video standard.
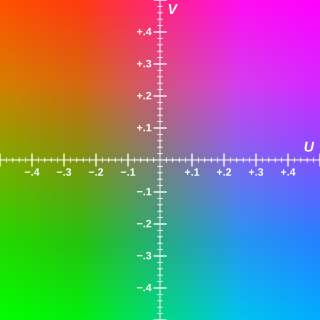
Y′UV, also written YUV, is the color model found in the PAL analogue color TV standard. A color is described as a Y′ component (luma) and two chroma components U and V. The prime symbol (') denotes that the luma is calculated from gamma-corrected RGB input and that it is different from true luminance. Today, the term YUV is commonly used in the computer industry to describe colorspaces that are encoded using YCbCr.

Composite video is an analog video format that typically carries a 525 or 625 line signal on a single channel, unlike the higher-quality S-Video and the even higher-quality component video.

S-Video is an analog video signal format that carries standard-definition video, typically at 525 lines or 625 lines. It encodes video luma and chrominance on two separate channels, achieving higher image quality than composite video which encodes all video information on one channel. It also eliminates several types of visual defects such as dot crawl which commonly occur with composite video. Although it improved over composite video, S-Video has lower color resolution than component video, which is encoded over three channels.

Chroma subsampling is the practice of encoding images by implementing less resolution for chroma information than for luma information, taking advantage of the human visual system's lower acuity for color differences than for luminance.
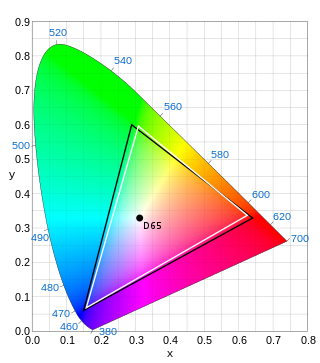
ITU-R Recommendation BT.601, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 601 or BT.601, is a standard originally issued in 1982 by the CCIR for encoding interlaced analog video signals in digital video form. It includes methods of encoding 525-line 60 Hz and 625-line 50 Hz signals, both with an active region covering 720 luminance samples and 360 chrominance samples per line. The color encoding system is known as YCbCr 4:2:2.

Component video is an analog video signal that has been split into two or more component channels. In popular use, it refers to a type of component analog video (CAV) information that is transmitted or stored as three separate signals. Component video can be contrasted with composite video in which all the video information is combined into a single signal that is used in analog television. Like composite, component cables do not carry audio and are often paired with audio cables.

D-1 or 4:2:2 Component Digital is an SMPTE digital recording video standard, introduced in 1986 through efforts by SMPTE engineering committees. It started as a Sony and Bosch - BTS product and was the first major professional digital video format. SMPTE standardized the format within ITU-R 601, also known as Rec. 601, which was derived from SMPTE 125M and EBU 3246-E standards.

Serial digital interface (SDI) is a family of digital video interfaces first standardized by SMPTE in 1989. For example, ITU-R BT.656 and SMPTE 259M define digital video interfaces used for broadcast-grade video. A related standard, known as high-definition serial digital interface (HD-SDI), is standardized in SMPTE 292M; this provides a nominal data rate of 1.485 Gbit/s.

SMPTE color bars are a television test pattern used where the NTSC video standard is utilized, including countries in North America. The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) refers to the pattern as Engineering Guideline (EG) 1-1990. Its components are a known standard, and created by test pattern generators. Comparing it as received to the known standard gives video engineers an indication of how an NTSC video signal has been altered by recording or transmission and what adjustments must be made to bring it back to specification. It is also used for setting a television monitor or receiver to reproduce NTSC chrominance and luminance information correctly.

YCbCr, Y′CbCr, or Y Pb/Cb Pr/Cr, also written as YCBCR or Y′CBCR, is a family of color spaces used as a part of the color image pipeline in video and digital photography systems. Y′ is the luma component and CB and CR are the blue-difference and red-difference chroma components. Y′ is distinguished from Y, which is luminance, meaning that light intensity is nonlinearly encoded based on gamma corrected RGB primaries.
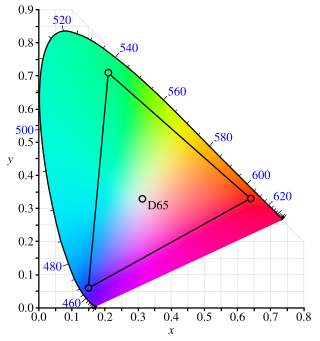
The Adobe RGB (1998) color space or opRGB is a color space developed by Adobe Inc. in 1998. It was designed to encompass most of the colors achievable on CMYK color printers, but by using RGB primary colors on a device such as a computer display. The Adobe RGB (1998) color space encompasses roughly 50% of the visible colors specified by the CIELAB color space – improving upon the gamut of the sRGB color space, primarily in cyan-green hues. It was subsequently standardized by the IEC as IEC 61966-2-5:1999 with a name opRGB and is used in HDMI.

Dot crawl is a visual defect of color analog video standards when signals are transmitted as composite video, as in terrestrial broadcast television. It consists of moving checkerboard patterns which appear along horizontal color transitions. It results from intermodulation or crosstalk between chrominance and luminance components of the signal, which are imperfectly multiplexed in the frequency domain.
In video, luma represents the brightness in an image. Luma is typically paired with chrominance. Luma represents the achromatic image, while the chroma components represent the color information. Converting R′G′B′ sources into luma and chroma allows for chroma subsampling: because human vision has finer spatial sensitivity to luminance differences than chromatic differences, video systems can store and transmit chromatic information at lower resolution, optimizing perceived detail at a particular bandwidth.
MUSE, commercially known as Hi-Vision was a Japanese analog high-definition television system, with design efforts going back to 1979.

A video decoder is an electronic circuit, often contained within a single integrated circuit chip, that converts base-band analog video signals to digital video. Video decoders commonly allow programmable control over video characteristics such as hue, contrast, and saturation. A video decoder performs the inverse function of a video encoder, which converts raw (uncompressed) digital video to analog video. Video decoders are commonly used in video capture devices and frame grabbers.

Rec. 709, also known as Rec.709, BT.709, and ITU 709, is a standard developed by ITU-R for image encoding and signal characteristics of high-definition television.
Various accessories for the PlayStation 2 video game console have been produced by Sony, as well as third parties. These include controllers, audio and video input devices like microphones and video cameras, and cables for better sound and picture quality.
ITU-R Recommendation BT.2100, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 2100 or BT.2100, introduced high-dynamic-range television (HDR-TV) by recommending the use of the perceptual quantizer (PQ) or hybrid log–gamma (HLG) transfer functions instead of the traditional "gamma" previously used for SDR-TV.
















