DAF Trucks is a Dutch truck manufacturing company and a division of Paccar. DAF originally stood for van Doorne's Aanhangwagen Fabriek. Its headquarters and main plant are in Eindhoven. Cabs and axle assemblies are produced at its Westerlo plant in Belgium. Some of the truck models sold with the DAF brand are designed and built by Leyland Trucks at its Leyland plant in the United Kingdom.

Robert Bosch GmbH, commonly known as Bosch, is a German multinational engineering and technology company headquartered in Gerlingen, Germany. The company was founded by Robert Bosch in Stuttgart in 1886. Bosch is 94% owned by the Robert Bosch Stiftung, a charitable institution. Although the charity is funded by owning the vast majority of shares, it has no voting rights and is involved in health and social causes unrelated to Bosch's business.

Electronic stability control (ESC), also referred to as electronic stability program (ESP) or dynamic stability control (DSC), is a computerized technology that improves a vehicle's stability by detecting and reducing loss of traction (skidding). When ESC detects loss of steering control, it automatically applies the brakes to help steer the vehicle where the driver intends to go. Braking is automatically applied to wheels individually, such as the outer front wheel to counter oversteer, or the inner rear wheel to counter understeer. Some ESC systems also reduce engine power until control is regained. ESC does not improve a vehicle's cornering performance; instead, it helps reduce the chance of the driver losing control of the vehicle.

A four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 or 4WD, is a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer case providing an additional output drive shaft and, in many instances, additional gear ranges.
Tata Motors Limited is an Indian multinational automotive company, headquartered in Mumbai and part of the Tata Group. The company produces cars, trucks, vans, and busses.

The BMW E39 is the fourth generation of the BMW 5 Series range of executive cars, which was manufactured from 1995 to 2004. It was launched in the sedan body style, with the station wagon body style introduced in 1996. The E39 was replaced by the E60 5 Series in 2003, however E39 Touring models remained in production until May 2004.

ZF Sachs AG, also known as Fichtel & Sachs, was founded in Schweinfurt in 1895 and was a well-known German family business. At its last point as an independent company, the company name was Fichtel & Sachs AG.

The Audi RS 6 is a high-performance variant of the Audi A6 range, produced by the high-performance subsidiary company Audi Sport GmbH, for its parent company Audi AG, a subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group, from 2002 onwards.

The Westinghouse Air Brake Technologies Corporation was founded on September 28, 1869 by George Westinghouse in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Earlier in the year he had invented the railway air brake in New York state.
BorgWarner Inc. is an American automotive and e-mobility supplier headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan. As of 2022, the company maintains production facilities and sites at 92 locations in 24 countries, and generates revenues of US$15.8 billion, while employing around 52,000 people. The company is one of the 25 largest automotive suppliers in the world.

The PACE Award is an annual award from Automotive News. The focus of the award is an innovation (i) developed primarily by a supplier, (ii) that is new to the automotive industry, (iii) that is in use, and (iv) that "changes the rules of the game". Awards have been given for products, materials, processes, capital equipment, software and services. A panel of independent judges from industry, finance, research, and academia choose finalists from the initial applicants, make site visits to evaluate the innovation, and then gather to select winners, independent of the sponsors. Winners to date include suppliers from Japan, Korea, China, the US, Canada, Brazil, Germany, France, Italy, Poland and other European countries. Among the most awarded companies over the years are BorgWarner, Delphi Automotive, Federal-Mogul, Valeo and PPG Industries as well as Robert Bosch GmbH, Gentex Corporation, and Siemens.

TRW Automotive Holdings Corp. was an American global supplier of automotive systems, modules, and components to automotive original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and related aftermarkets. Tracing its roots from TRW Inc. it was originally headquartered in Livonia, Michigan. It was created in 2002 when the aerospace company Northrop Grumman purchased TRW and sold its automotive division to Blackstone Group.

The Land Rover Range Rover Evoque, also known as the Range Rover Evoque, is a subcompact luxury crossover SUV developed and produced by Jaguar Land Rover under their Land Rover marque. The original Evoque was a development of the Land Rover LRX concept vehicle, which was unveiled at the North American International Auto Show in January 2008. The first generation Evoque was produced from July 2011 until 2018 in three and five-door versions, with both two-wheel and four-wheel drive. The second generation of the car went into production in 2018.
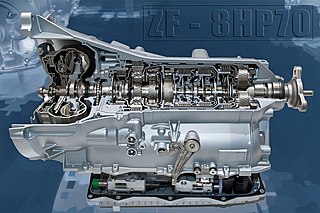
The ZF 8HP transmission is ZF Friedrichshafen AG's trademark name for its 8-speed automatic transmission models for longitudinal engine applications. The name is short for 8-speed transmission with hydraulic converter and planetary gearsets. Designed and first built by ZF's subsidiary in Saarbrücken, Germany, it debuted in 2008 on the BMW 7 Series (F01) 760Li sedan fitted with the V12 engine. BMW remains a major customer for the transmission.
The ZF Ecomat automotive transmission was specifically designed by ZF Friedrichshafen AG primarily for city-buses and motorcoaches. It has several generations – all of the automatic transmission type, and many variants. The latest variants use a lock-up torque converter along with a retarder. Some variants are listed below.
Koreatomy Automobile Parts Industries Company is a Korean automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Munrae-dong Yeongdeungpo-gu Seoul, South Korea. It was established in 1988 as Koreatomy Automobile Industries Co., Ltd. The company is a supplier of air suspension based in truck and bus driveline and chassis to pusher axle in automobile parts technology. It provides components and systems to the commercial vehicle, off-highway/construction and logistic industries. licensed by Daehan Logistics and manufactures commercial vehicle use air suspension products in joint ventures.
WABCO Holdings, Inc. was a U.S.-based provider of electronic braking, stability, suspension and transmission automation systems for heavy-duty commercial vehicles. In 2007, the Vehicle Control Systems was spun off as WABCO Holdings, Inc., an American provider of electronic braking, stability, suspension and transmission automation systems for heavy duty commercial vehicles. Their products are present in many commercial vehicles such as trucks, buses, trailers and off-highway vehicles but to only fill the niche roles. WABCO was acquired by ZF Friedrichshafen in May 2020.

A dual-clutch transmission (DCT) is a type of multi-speed vehicle transmission system, that uses two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets. The design is often similar to two separate manual transmissions with their respective clutches contained within one housing, and working as one unit. In car and truck applications, the DCT functions as an automatic transmission, requiring no driver input to change gears.

A drivetrain or Transmission System, is the group of components that deliver mechanical power from the prime mover to the driven components. In automotive engineering, the drivetrain is the components of a motor vehicle that deliver power to the drive wheels. This excludes the engine or motor that generates the power. In marine applications, the drive shaft will drive a propeller, thruster, or waterjet rather than a drive axle, while the actual engine might be similar to an automotive engine. Other machinery, equipment and vehicles may also use a drivetrain to deliver power from the engine(s) to the driven components.