
The Canon d'Infanterie de 37 modèle 1916 TRP was a French infantry support gun, first used during World War I. TRP stands for tir rapide, Puteaux. The tactical purpose of this gun was the destruction of machine gun nests.
The MG 34 is a German recoil-operated air-cooled general-purpose machine gun, first tested in 1929, introduced in 1934, and issued to units in 1936. It introduced an entirely new concept in automatic firepower – the Einheitsmaschinengewehr – and is generally considered the world's first general-purpose machine gun (GPMG). Both the MG 34 and MG 42 were erroneously nicknamed "Spandau" by Allied troops, a carryover from the World War I nickname for the MG 08, which was produced at the Spandau Arsenal.
The MG 42 is a German recoil-operated air-cooled general-purpose machine gun used extensively by the Wehrmacht and the Waffen-SS during the second half of World War II. Entering production in 1942, it was intended to supplement and replace the earlier MG 34, which was more expensive and took much longer to produce, but both weapons were produced until the end of World War II.

The StG 44 is a German assault rifle developed during World War II by Hugo Schmeisser. It is also known by its early designations as the MP 43 and MP 44. The StG 44 was an improvement of an earlier design, the Maschinenkarabiner 42(H).
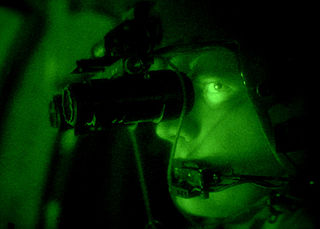
A night-vision device (NVD), also known as a night optical/observation device (NOD), night-vision goggle (NVG), is an optoelectronic device that allows visualization of images in low levels of light, improving the user's night vision. The device enhances ambient visible light and converts near-infrared light into visible light which can be seen by the user; this is known as I2 (image intensification). By comparison, viewing of infrared thermal radiation is referred to as thermal imaging and operates in a different section of the infrared spectrum. A night vision device usually consists of an image intensifier tube, a protective housing, and may have some type of mounting system. Many NVDs also include a protective sacrificial lens, mounted over the front lens (ie. objective lens) on NVDs to protect the latter from damage by environmental hazards and some can incorporate telescopic lenses. The image produced by an NVD is typically monochrome green, as green was considered to be the easiest color to look at for prolonged periods in the dark. Night vision devices may be passive, relying solely on ambient light, or may be active, using an IR (infrared) illuminator to visualize the environment better.

The Gewehr 43 or Karabiner 43 is a 7.92×57mm Mauser caliber semi-automatic rifle developed by Germany during World War II. The design was based on that of the earlier G41(W) but incorporated an improved short-stroke piston gas system similar to that of the Soviet SVT-40.

A telescopic sight, commonly called a scope informally, is an optical sighting device based on a refracting telescope. It is equipped with some form of a referencing pattern – known as a reticle – mounted in a focally appropriate position in its optical system to provide an accurate point of aim. Telescopic sights are used with all types of systems that require magnification in addition to reliable visual aiming, as opposed to non-magnifying iron sights, reflector (reflex) sights, holographic sights or laser sights, and are most commonly found on long-barrel firearms, particularly rifles, usually via a scope mount. Similar devices are also found on other platforms such as Artillery, Tanks and even Aircraft. The optical components may be combined with optoelectronics to add night vision or smart device features.

The PK is a belt-fed general-purpose machine gun, chambered for the 7.62×54mmR rimmed cartridge.

A tactical light or weapon light is a flashlight used in conjunction with a firearm to aid low-light target identification, allowing the user to simultaneously aim a weapon and illuminate the target. Tactical lights can be handheld or mounted to the weapon with the light beam parallel to the bore. Tactical lights can also serve as a non-lethal weapon, used to temporarily blind and disorient targets or, in the case of a large handheld flashlight, to be used as a blunt weapon.
Hugo Schmeisser was a German developer of 20th century infantry weapons.

A heavy machine gun (HMG) is significantly larger than light, medium or general-purpose machine guns. HMGs are typically too heavy to be man-portable and require mounting onto a weapons platform to be operably stable or tactically mobile, have more formidable firepower, and generally require a team of personnel for operation and maintenance.
The Heckler & Koch MG4 is a belt-fed 5.56 mm light machine gun designed and developed by German firearm manufacturer Heckler & Koch. It was developed in the late 1990s and first seen publicly in September 2001. It has been selected to replace the 7.62 mm MG3 general-purpose machine gun in the Bundeswehr at the squad support level; it will complement the MG3 in other roles. It will also be the secondary armament of the new Puma infantry fighting vehicle. Overall, it is designed to be light, provide maximum safety to the user and function reliably under adverse conditions using a wide range of ammunition from different manufacturers, without the need to adjust the gas system. It was known as the MG43 prior to its adoption by the Bundeswehr.

The AN/PEQ-2 Infrared Target Pointer/Illuminator/Aiming Light (ITPIAL) is a laser sight for use on rifles fitted with a Picatinny rail. It was manufactured by Insight Technology.

The major components of sniper equipment are the precision sniper rifle, various optical scopes and field glasses, specialized ammunition and camouflage materials for the sniper’s body and equipment. A sniper’s spotter typically also wears camouflage. In the 2010s, a spotter uses various optical gear and in some cases a laser rangefinder. Snipers may also use monopods, bipods or tripods to steady their aim.
The evolution of German military rifles is a history of common and diverse paths followed by the separate German states, until the mid-19th century when Prussia emerged as the dominant state within Germany and the nation was unified. This article discusses rifled shoulder arms developed in or for the military of the states that later became Germany; it excludes firearms of the Austrian Empire, except where they were used substantially by German troops.

The AN/PAS-13B Thermal Weapon Sight (TWS) is an infrared sight developed for the United States military by Raytheon. The sight is designed for use on small arms in the U.S. military's inventory, but it can also be used as a standalone observation device. The AN/PAS-13B uses thermal imaging so that it can be used day or night. Thermal imaging also allows the sight to see through smoke or fog, things that may normally obscure other night vision devices. The AN/PAS-13 first became operationally capable with the U.S. Army in 1998 and has reached a total production of 33,400 units.

Battlefield illumination is technology that improves visibility for military forces operating in difficult low-light conditions. The risks and dangers to armies fighting in poor light have been known since Ancient Chinese times. Prior to the advent of the electrical age, fire was used to improve visibility on the battlefield.

1PN58 is the GRAU index for a Soviet designed passive night scope for a range of Soviet designed small arms and grenade launchers. 1PN is the GRAU index of night vision devices, where PN stands for Nochnoy Pritsel meaning night sight. It is also called NSPUM. or NSPU-1. The 1PN58 was introduced into Soviet service in the early 1970s and is still used by many of the Soviet Union's successor states, and has been used in numerous conflicts around the world.

The CLE Canister, or CLE Container was a standardized cylindrical container used by the British during World War II to airdrop supplies to troops on the ground. The name initially derived from the Central Landing Establishment that developed them, although this was later backronymed to Container Light Equipment.

A laser sight is a device attached or integral to a firearm to aid target acquisition. Unlike optical and iron sights where the user looks through the device to aim at the target, laser sights project a beam onto the target, providing a visual reference point.
















