Coverage of Railway; Egremont - Beckermet - Sellafield.

Egremont is a market town, civil parish and two electoral wards in the Borough of Copeland in Cumbria, England, 5 miles (8.0 km) south of Whitehaven and on the River Ehen. Historically in Cumberland, the town, which lies at the foot of Uldale Valley and Dent Fell, has a long industrial heritage including dyeing, weaving and iron ore mining. It had a population of 7,444 in 2001, increasing to 8,194 at the 2011 Census.

Beckermet is a village and civil parish in the English county of Cumbria, located near the coast between Egremont and Seascale. Historically within Cumberland, it is served by Braystones railway station and is less than a mile west of the A595 road. It is around 2 miles (3 km) from the Sellafield nuclear plant which may be seen from the higher parts of the village.

Sellafield is a nuclear fuel reprocessing and nuclear decommissioning site, close to the village of Seascale on the coast of the Irish Sea in Cumbria, England. The site is served by Sellafield railway station.
In 1864 it was proposed to extend the Whitehaven, Cleator and Egremont Railway's line that ran from Moor Row to Egremont and by doing so extend it to Sellafield with a section of new railway. The Parlementary Act for this new railway was obtained in June 1864 and it was to be known as the Cleator and Furness Railway. When proposed the line would connect with the Whitehaven & Furness Junction Railway but soon afterwards, the W&FJR became part of the Furness Railway. The railway would open as the joint properties of the Furness Railway and the Whitehaven, Cleator and Egremont Railway.
The Whitehaven, Cleator and Egremont Railway was an English railway company which built and operated a standard gauge railway in Cumberland, England intended to open up the hematite orefield to the south-east of Whitehaven. It opened for goods traffic in 1855 and for passenger traffic in 1857.

Moor Row is a village situated in North West England. It is in Cumbria and is located on a minor road off the A595 road south of Whitehaven.

The Furness Railway (Furness) was a railway company operating in the Furness area of Lancashire in North West England.
It was worked by the WC&ER until the company sold out to the London & North Western Railway when the FR disputed the purchase. In 1866 the London & North Western Railway purchased two small railways in West Cumberland and the Furness Railway insisted the former company expanded no further in the Whitehaven area. An agreement was reached and it was this agreement that the Furness Railway maintained had been ignored when in 1878 the London & North Western Railway purchased the WC&ER lines. The following year an agreement was reached where the WC&ER would become the joint property of the Furness Railway and the London & North Western Railway after which the Cleator and Furness Railway became part of the LNWR & FR Joint Lines.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

The Cumbrian Coast line is a rail route in North West England, running from Carlisle to Barrow-in-Furness via Workington and Whitehaven. The line forms part of Network Rail route NW 4033, which continues via Ulverston and Grange-over-Sands to Carnforth, where it connects with the West Coast Main Line.

Cleator Moor or is a small town, civil parish and two electoral wards in the English county of Cumbria and within the boundaries of the historic county of Cumberland.
The Cockermouth & Workington Railway was an English railway company which built and operated a railway between the Cumbrian towns of Workington and Cockermouth. The railway opened for service in 1847, and ran from the Whitehaven Junction Railway station at Workington to a station at Cockermouth near the bridge over the Derwent. A single-tracked line of eight and a half miles length, its revenue came largely from the transport of coal from the pits of the lower Derwent valley to the port at Workington for shipment by sea. The Marron extension of the Whitehaven, Cleator and Egremont Railway and the Derwent Branch of the Maryport and Carlisle Railway were both constructed to link with the C&WR and together give an alternative route for the northward movement of haematite ore from the Cumberland ore-field. The completion of the Cockermouth, Keswick and Penrith Railway made the C&WR part of a continuous through route between South Durham and the Cumberland orefield. These developments both improved the potential profitability of the C&WR and made control of it important to bigger companies wishing to maximise the iron-ore traffic over their lines: the C&WR was absorbed by the London and North Western Railway in 1866.

Moor Row railway station was built by the Whitehaven, Cleator and Egremont Railway. It served the village of Moor Row, Cumbria, England.

Tracks were laid southwards from Whitehaven and Moor Row as far as Egremont by the Whitehaven, Cleator and Egremont Railway, opening to passengers on 1 July 1857.
Woodend railway station was planned by the Whitehaven, Cleator and Egremont Railway on its Sellafield to Moor Row branch, but by the time the station opened the company had been bought out by the LNWR and Furness Railway who operated the line jointly until grouping in 1923.
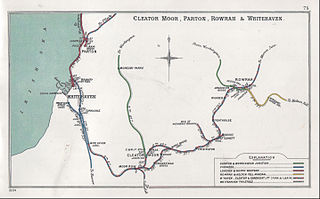
Cleator Moor has had three passenger stations:

Cleator Moor had three passenger stations:

Rowrah railway station was built by the Whitehaven, Cleator and Egremont Railway. It served the village of Rowrah, Cumbria, England.

Winder railway station was built by the Whitehaven, Cleator and Egremont Railway. It served the village of Winder, Frizington, Cumbria, England.

Yeathouse railway station was a later addition to the Whitehaven, Cleator and Egremont Railway. It served the communities of Yeathouse and Eskett, near Frizington, Cumbria, England.
Egremont railway station was built by the Whitehaven, Cleator and Egremont Railway as the first southern terminus of what would become the Moor Row to Sellafield branch. In 1878 the company was bought out by the LNWR and Furness Railway who operated the line jointly until grouping in 1923.
St Thomas Cross Platform was a railway station used by workmen's trains on the Moor Row to Sellafield line on what is now the southeastern, Cringlethwaite, edge of Egremont, Cumbria, England.
Beckermet Mines railway station was situated at Pit No.1 of the mine of the same name. It was used by workmen's trains which travelled along a branch which curved eastwards off the Moor Row to Sellafield line, primarily to handle the iron ore lifted at the site.

Distington railway station was opened jointly by the Cleator and Workington Junction Railway (C&WJR) and the LNWR and Furness Joint Railway on 1 October 1879. It was situated on the northern edge of the village of Distington, Cumbria, England where the C&WJR's north-south main line crossed the Joint Line's east-west Gilgarran Branch.
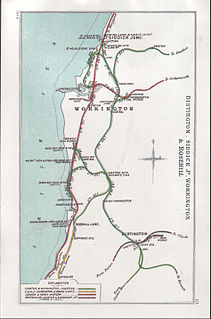
Siddick Junction railway station was opened by the Cleator and Workington Junction (C&WJR) and London and North Western Railways in 1880 to provide exchange platforms for passengers wishing to change trains from one company's line to the other. A passenger travelling from Maryport to Distington, for example, would change at Siddick Junction. As a purely exchange station - like Dovey Junction and Dukeries Junction elsewhere in the country - the owning companies would not need to provide road or footpath access or ticketing facilities as no passengers were invited to enter or leave the station except by train.

Linefoot railway station, sometimes referred to as Linefoot Junction and sometimes as Linefoot Goods, briefly served the scattered community around the crossroads at Linefoot, near Cockermouth in Cumbria, England.

Buckhill Colliery Halt railway station was an unadvertised halt for workers at Buckhill Colliery north east of Camerton, near Cockermouth in Cumbria, England.













