Linnaean taxonomy can mean either of two related concepts:
- The particular form of biological classification (taxonomy) set up by Carl Linnaeus, as set forth in his Systema Naturae (1735) and subsequent works. In the taxonomy of Linnaeus there are three kingdoms, divided into classes, and they, in turn, into lower ranks in a hierarchical order.
- A term for rank-based classification of organisms, in general. That is, taxonomy in the traditional sense of the word: rank-based scientific classification. This term is especially used as opposed to cladistic systematics, which groups organisms into clades. It is attributed to Linnaeus, although he neither invented the concept of ranked classification nor gave it its present form. In fact, it does not have an exact present form, as "Linnaean taxonomy" as such does not really exist: it is a collective (abstracting) term for what actually are several separate fields, which use similar approaches.
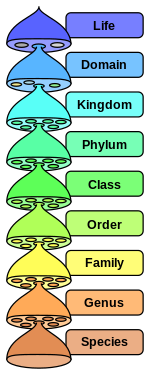
In biology, taxonomy is the scientific study of naming, defining (circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms.
Genus is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.
Order is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families.

In biology, a taxon is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based ("Linnaean") nomenclature. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping.

The International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants is the set of rules and recommendations dealing with the formal botanical names that are given to plants, fungi and a few other groups of organisms, all those "traditionally treated as algae, fungi, or plants". It was formerly called the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN); the name was changed at the International Botanical Congress in Melbourne in July 2011 as part of the Melbourne Code which replaced the Vienna Code of 2005.

A botanical name is a formal scientific name conforming to the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and, if it concerns a plant cultigen, the additional cultivar or Group epithets must conform to the International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants (ICNCP). The code of nomenclature covers "all organisms traditionally treated as algae, fungi, or plants, whether fossil or non-fossil, including blue-green algae (Cyanobacteria), chytrids, oomycetes, slime moulds and photosynthetic protists with their taxonomically related non-photosynthetic groups ."

Pierre Magnol was a French botanist. He was born in the city of Montpellier, where he lived and worked for most of his life. He became Professor of Botany and Director of the Royal Botanic Garden of Montpellier and held a seat in the Académie Royale des Sciences de Paris for a short while. He was one of the innovators who devised the botanical scheme of classification. He was the first to publish the concept of plant families as they are understood today, a natural classification of groups of plants that have features in common.

The International Association for Plant Taxonomy (IAPT) is an organization established to promote an understanding of plant biodiversity, facilitate international communication of research between botanists, and oversee matters of uniformity and stability in plant names. The IAPT was founded on July 18, 1950, at the Seventh International Botanical Congress in Stockholm, Sweden. The IAPT headquarters is located in Bratislava, Slovakia. Its president, since 2017, is Patrick S. Herendeen of the Chicago Botanic Garden; vice-president is Gonzalo Nieto Feliner of the Real Jardín Botánico, Madrid; and secretary-general is Karol Marhold of the Plant Science and Biodiversity Centre, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Bratislava.
Botanical nomenclature is the formal, scientific naming of plants. It is related to, but distinct from taxonomy. Plant taxonomy is concerned with grouping and classifying plants; botanical nomenclature then provides names for the results of this process. The starting point for modern botanical nomenclature is Linnaeus' Species Plantarum of 1753. Botanical nomenclature is governed by the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), which replaces the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN). Fossil plants are also covered by the code of nomenclature.
Nomenclature codes or codes of nomenclature are the various rulebooks that govern the naming of living organisms. Standardizing the scientific names of biological organisms allows researchers to discuss findings.
In botany, the correct name according to the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) is the one and only botanical name that is to be used for a particular taxon, when that taxon has a particular circumscription, position and rank. Determining whether a name is correct is a complex procedure. The name must be validly published, a process which is defined in no less than 16 Articles of the ICN. It must also be "legitimate", which imposes some further requirements. If there are two or more legitimate names for the same taxon, then the correct name is the one which has priority, i.e. it was published earliest, although names may be conserved if they have been very widely used. Validly published names other than the correct name are called synonyms. Since taxonomists may disagree as to the circumscription, position or rank of a taxon, there can be more than one correct name for a particular plant. These may also be called synonyms.
In botanical nomenclature, author citation is the way of citing the person or group of people who validly published a botanical name, i.e. who first published the name while fulfilling the formal requirements as specified by the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN). In cases where a species is no longer in its original generic placement, both the authority for the original genus placement and that for the new combination are given.
In botany, the phrase ordo naturalis, 'natural order', was once used for what today is a family. Its origins lie with Carl Linnaeus who used the phrase when he referred to natural groups of plants in his lesser-known work, particularly Philosophia Botanica. In his more famous works the Systema Naturae and the Species Plantarum, plants were arranged according to his artificial "Sexual system", and Linnaeus used the word ordo for an artificial unit. In those works, only genera and species were "real" taxa.

Lilianae is a botanical name for a superorder of flowering plants. Such a superorder of necessity includes the type family Liliaceae. Terminations at the rank of superorder are not standardized by the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), although the suffix -anae has been proposed.

James Lauritz Reveal was a U.S. botanist best known for his contributions to the genus Eriogonum and for his work on suprageneric names. His website, at PlantSystematics.org, also presents material on plant taxonomy including the Reveal system. He published extensively on North American flora, was a member of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group, and was one of the authors of the APG II and APG III classifications.

In biology, taxonomic rank is the relative level of a group of organisms in an ancestral or hereditary hierarchy. A common system of biological classification (taxonomy) consists of species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, and domain. While older approaches to taxonomic classification were phenomenological, forming groups on the basis of similarities in appearance, organic structure and behaviour, methods based on genetic analysis have opened the road to cladistics.

Critica Botanica was written by Swedish botanist, physician, zoologist and naturalist Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778). The book was published in Germany when Linnaeus was 29 with a discursus by the botanist Johannes Browallius (1707–1755), bishop of Åbo. The first edition was published in July 1737 under the full title Critica botanica in qua nomina plantarum generica, specifica & variantia examini subjiciuntur, selectoria confirmantur, indigna rejiciuntur; simulque doctrina circa denominationem plantarum traditur. Seu Fundamentorum botanicorum pars IV Accedit Johannis Browallii De necessitate historiae naturalis discursus.

This is a list of terms and symbols used in scientific names for organisms, and in describing the names. For proper parts of the names themselves, see List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names. Note that many of the abbreviations are used with or without a stop.

BurmannialesMart. was an order of monocotyledons, subsequently discontinued.