This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
Flux is a rate of flow through a surface or substance in physics, or has a related meaning in applied mathematics.

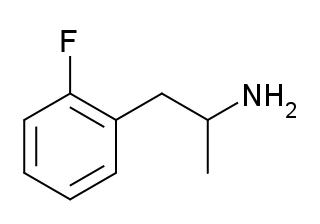
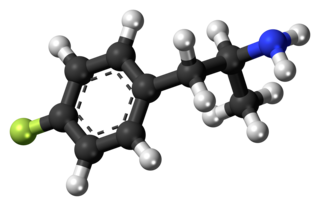
4-Fluoromethamphetamine (4-FMA) is a stimulant drug related to methamphetamine and 4-fluoroamphetamine. It has been reported to be sold as a designer drug, but little is known about its pharmacology or toxicology. It was first detected from legal highs sold in Japan in 2006 and became illegal to sell or to possess for the purpose of distribution in Japan in 2008. It was initially reported to be contained as an ingredient in some of the range of party pills sold internationally by the Israeli company Neorganics from around 2006 onwards, but this was later shown to be incorrect and this ingredient was eventually identified as the closely related compound 2-fluoromethamphetamine.

para-Chloroamphetamine (PCA), also known as 4-chloroamphetamine (4-CA), is a substituted amphetamine and monoamine releaser similar to MDMA, but with substantially higher neurotoxicity, thought to be due to the unrestrained release of both serotonin and dopamine by a metabolite. It is used as a neurotoxin by neurobiologists to selectively kill serotonergic neurons for research purposes, in the same way that 6-hydroxydopamine is used to kill dopaminergic neurons.

Ortetamine (INN), also known as 2-methylamphetamine, is a stimulant drug of the amphetamine class. In animal drug discrimination tests it substituted for dextroamphetamine more closely than either 3- or 4-methylamphetamine, although with only around 1/10 the potency of dextroamphetamine itself.

4-Methylamphetamine is a stimulant and anorectic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes.

para-Bromoamphetamine (PBA), also known as 4-bromoamphetamine (4-BA), is an amphetamine derivative which acts as a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA) and produces stimulant effects.

para-Iodoamphetamine (PIA), also known as 4-iodoamphetamine (4-IA), is a research chemical of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes.
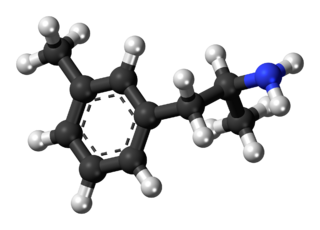
3-Methylamphetamine is a stimulant drug from the amphetamine family. It is self-administered by mice to a similar extent to 4-fluoroamphetamine and has comparable properties as a monoamine releaser, although with a more balanced release of all three monoamines, as opposed to the more dopamine/noradrenaline selective fluoro analogues.

meta-Methoxyamphetamine (MMA), also known as 3-methoxyamphetamine (3-MA), is a stimulant drug from the amphetamine family. It has similar effects in animal drug discrimination tests to the more widely known derivative 4-methoxyamphetamine (PMA), although with a slightly different ratio of monoamine release, being a combined serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine releasing agent rather than a fairly selective serotonin releaser like PMA. 3-Methoxyamphetamine has similarly appeared on the illicit market as a designer drug alternative to MDMA, although far more rarely than its infamous positional isomer. It produces gepefrine, a cardiac stimulant, as one of its major metabolites.

2,5-Dimethoxy-4-fluoroamphetamine (DOF) is a psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine classes. Alexander Shulgin briefly describes DOF in his book PiHKAL:
Animal studies that have compared DOF to the highly potent DOI and DOB imply that the human activity will be some four to six times less than these two heavier halide analogues. As of the present time, no human trials of DOF have been made.

3-Fluoromethcathinone is a chemical compound of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and cathinone classes that has been sold online as a designer drug. It is a structural isomer of flephedrone (4-fluoromethcathinone).

2-Fluoromethamphetamine (2-FMA) is a stimulant drug of the methamphetamine family which has been used as a designer drug. It is purported to possess little recreational value because less euphoria is produced than other amphetamines. It is said to be a functional stimulant with properties similar to Adderall.

3-Fluoroethamphetamine (3-FEA) is a stimulant drug of the amphetamine class which acts as a releasing agent of the monoamine neurotransmitters norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin.
6-APB is an empathogenic psychoactive compound of the substituted benzofuran, substituted amphetamine and substituted phenethylamine classes. 6-APB and other compounds are sometimes informally called "Benzofury" in newspaper reports. It is similar in structure to MDA, but differs in that the 3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl ring system has been replaced with a benzofuran ring. 6-APB is also the unsaturated benzofuran derivative of 6-APDB. It may appear as a tan grainy powder.
While the drug never became particularly popular, it briefly entered the rave and underground clubbing scene in the UK before its sale and import were banned. It falls under the category of research chemicals, sometimes called "legal highs." Because 6-APB and other substituted benzofurans have not been explicitly outlawed in some countries, they are often technically legal, contributing to their popularity.

3-Fluoromethamphetamine (3-FMA) is a stimulant drug from the amphetamine class that has been sold online as a designer drug.

para-Chloromethamphetamine is a stimulant that is the N-methyl derivative and prodrug of the neurotoxic drug para-chloroamphetamine (4-CA). It has been found to decrease serotonin in rats. Further investigation into the long-term effects of chloroamphetamines discovered that administration of 4-CMA caused a prolonged reduction in the levels of serotonin and the activity of tryptophan hydroxylase in the brain one month after injection of a single dose of the drug.