The Ottonian dynasty was a Saxon dynasty of German monarchs (919–1024), named after three of its kings and Holy Roman Emperors named Otto, especially its first Emperor Otto I. It is also known as the Saxon dynasty after the family's origin in the German stem duchy of Saxony. The family itself is also sometimes known as the Liudolfings, after its earliest known member Count Liudolf and one of its primary leading-names. The Ottonian rulers were successors of the Germanic king Conrad I who was the only Germanic king to rule in East Francia after the Carolingian dynasty and before this dynasty.

The Duchy of Lorraine, originally Upper Lorraine, was a duchy now included in the larger present-day region of Lorraine in northeastern France. Its capital was Nancy.

Eastphalian, or Eastfalian, is a West Low German dialect spoken in southeastern parts of Lower Saxony and western parts of Saxony-Anhalt in Germany.

Rudolf of Rheinfelden was Duke of Swabia from 1057 to 1079. Initially a follower of his brother-in-law, the Salian emperor Henry IV, his election as German anti-king in 1077 marked the outbreak of the Great Saxon Revolt and the first phase of open conflict in the Investiture Controversy between Emperor and Papacy. After a series of armed conflicts, Rudolf succumbed to his injuries after his forces defeated Henry's in the Battle on the Elster.
Otto of Nordheim was Duke of Bavaria from 1061 until 1070. He was one of the leaders of the Saxon Rebellion in 1073-75 and the Great Saxon Revolt of 1077-88 against King Henry IV of Germany.

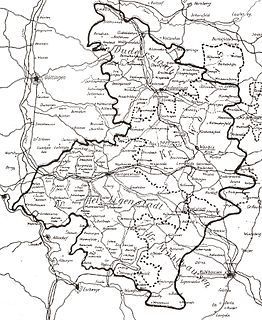
Eastphalia is a historical region in northern Germany, encompassing the eastern Gaue (shires) of the historic stem duchy of Saxony, roughly confined by the River Leine in the west and the Elbe and Saale in the east. The territory corresponds with the southeastern part of the present-day states of Lower Saxony, western Saxony-Anhalt and northern Thuringia. Together with Westphalia, central Angria and Nordalbingia it was one of the four main Saxon administrative regions. It should not be confused with East Westphalia (Ostwestfalen).

The Margravate of Meissen was a medieval principality in the area of the modern German state of Saxony. It originally was a frontier march of the Holy Roman Empire, created out of the vast Marca Geronis in 965. Under the rule of the Wettin dynasty, the margravate finally merged with the former Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg into the Saxon Electorate by 1423.

Bovenden is a municipality in the district of Göttingen, in Lower Saxony, Germany. In 2010 the population in the eight villages belonging to the municipality was 13,350.
Henry Berengar (1136/7–1150), sometimes numbered Henry (VI), was the eldest legitimate son of Conrad III of Germany and his second wife, Gertrude von Sulzbach. He was named after his father's maternal grandfather, the Emperor Henry IV, and his mother's father, Count Berengar II of Sulzbach. He was groomed for the succession, but predeceased his father.

The Duchy of Franconia was one of the five stem duchies of East Francia and the medieval Kingdom of Germany emerging in the early 10th century. The word Franconia, first used in a Latin charter of 1053, was applied like the words Francia, France, and Franken, to a portion of the land occupied by the Franks.
Ulric Manfred II or Manfred Ulric was the count of Turin and marquis of Susa in the early 11th century. He was the last male margrave from the Arduinid dynasty. Ulric Manfred's daughter, Adelaide, inherited the majority of his property. Through marriage to Adelaide (c.1045), Otto of Savoy, a younger son of Count Humbert I of Savoy became margrave of Turin. Their descendants would later comprise the House of Savoy who ruled Sardinia and Italy.

The Saxon Eastern March was a march of the Holy Roman Empire from the 10th until the 12th century. The term "eastern march" stems from the Latin term marchia Orientalis and originally could refer to either a march created on the eastern frontier of the East Frankish duchy of Saxony or another on the eastern border of the Duchy of Bavaria: the Bavarian marchia Orientalis, corresponding to later Austria.

The March or Margraviate of Lusatia was as an eastern border march of the Holy Roman Empire in the lands settled by Polabian Slavs. It arose in 965 in the course of the partition of the vast Marca Geronis. Ruled by several Saxon margravial dynasties, among them the House of Wettin, the lordship was contested by the Polish kings as well as by the Ascanian margraves of Brandenburg. The remaining territory was finally incorporated into the Lands of the Bohemian Crown in 1367.
Arnulf II was Archbishop of Milan from 998 to 1018.

Theodor von Sickel was a German-Austrian historian born in Aken, Province of Saxony, Kingdom of Prussia. He specialized in early European medieval history, and is considered to be the founder of modern diplomatics.

Adelaide I, a member of the royal Ottonian dynasty was the second Princess-abbess of Quedlinburg from 999, and Abbess of Gernrode from 1014, and Abbess of Gandersheim from 1039 until her death, as well as a highly influential kingmaker of medieval Germany.

Scharzfeld is a village in the borough of Herzberg am Harz in the district of Göttingen in South Lower Saxony, Germany.

The Battle of Flochberg was a victory for the royal forces of Henry (VI) of Germany over the House of Welf, led by Welf VI and his son, Welf VII. Henry's father, Conrad III, and Welf VI had gone on the Second Crusade together. On his return journey in 1148 Welf had entered into an alliance with Roger II of Sicily, Conrad's enemy. Having agreed to foment discord in Germany, he revived the Welf claim to the Duchy of Bavaria for his nephew, Henry the Lion.

Arnulf of Carinthia was the duke of Carinthia who overthrew his uncle, Emperor Charles the Fat, became the Carolingian king of East Francia from 887, the disputed King of Italy from 894 and the disputed Holy Roman Emperor from February 22, 896 until his death at Regensburg, Bavaria.

The Monumenta Germaniae Historica is a comprehensive series of carefully edited and published primary sources, both chronicle and archival, for the study of Northwestern and Central European history from the end of the Roman Empire to 1500. Despite the name, the series covers important sources for the history of many countries besides Germany, since the Society for the Publication of Sources on Germanic Affairs of the Middle Ages has included documents from many other areas subjected to the influence of Germanic tribes or rulers. The editor from 1826 until 1874 was Georg Heinrich Pertz (1795–1876); in 1875 he was succeeded by Georg Waitz (1813-1886).