This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

An ionic crystal is a crystal consisting of ions bound together by their electrostatic attraction. Examples of such crystals are the alkali halides, including potassium fluoride, potassium chloride, potassium bromide, potassium iodide, sodium fluoride, and other combinations of sodium, caesium, rubidium, or lithium ions with fluoride, bromide, chloride or iodide ions.
NaCl has a 6:6 co-ordination.
The properties of NaCl reflect the strong interactions that exist between the ions. It is a good conductor of electricity when molten, but very poor in the solid state. When fused the mobile ions carry charge through the liquid.
They are characterized by strong absorption of infrared radiation and have planes along which they cleave easily.
The exact arrangement of ions in an ionic lattice varies according to the size of the ions in the solid.
A halide is a binary phase, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative than the halogen, to make a fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide, astatide, or theoretically tennesside compound. The alkali metals combine directly with halogens under appropriate conditions forming halides of the general formula, MX. Many salts are halides; the hal- syllable in halide and halite reflects this correlation. All Group 1 metals form halides that are white solids at room temperature.
Calcium fluoride is the inorganic compound of the elements calcium and fluorine with the formula CaF2. It is a white insoluble solid. It occurs as the mineral fluorite (also called fluorspar), which is often deeply coloured owing to impurities.
Molybdenum trioxide is chemical compound with the formula MoO3. This compound is produced on the largest scale of any molybdenum compound. It occurs as the rare mineral molybdite. Its chief application is as an oxidation catalyst and as a raw material for the production of molybdenum metal.

Molybdic acid refers to hydrated forms of molybdenum trioxide and related species. The monohydrate is MoO3·H2O and the dihydrate (MoO3·2H2O) are well characterized. They are yellow diamagnetic solids.
Molybdenum dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula MoO2. It is a violet-colored solid and is a metallic conductor. It crystallizes in a monoclinic cell, and has a distorted rutile, (TiO2) crystal structure. In TiO2 the oxide anions are close packed and titanium atoms occupy half of the octahedral interstices (holes). In MoO2 the octahedra are distorted, the Mo atoms are off-centre, leading to alternating short and long Mo – Mo distances and Mo-Mo bonding. The short Mo – Mo distance is 251 pm which is less than the Mo – Mo distance in the metal, 272.5 pm. The bond length is shorter than would be expected for a single bond. The bonding is complex and involves a delocalisation of some of the Mo electrons in a conductance band accounting for the metallic conductivity.
MoO2 can be prepared :
Ionic conduction is the movement of an ion from one site to another through defects in the crystal lattice of a solid or aqueous solution.
Dry lubricants or solid lubricants are materials that, despite being in the solid phase, are able to reduce friction between two surfaces sliding against each other without the need for a liquid oil medium.
Arsenic trifluoride is a chemical compound of arsenic and fluorine with the chemical formula AsF3. It is a colorless liquid which reacts readily with water.

FLiBe is a molten salt made from a mixture of lithium fluoride (LiF) and beryllium fluoride (BeF2). It is both a nuclear reactor coolant and solvent for fertile or fissile material. It served both purposes in the Molten-Salt Reactor Experiment (MSRE).

In chemistry a molybdate is a compound containing an oxoanion with molybdenum in its highest oxidation state of 6. Molybdenum can form a very large range of such oxoanions which can be discrete structures or polymeric extended structures, although the latter are only found in the solid state.The larger oxoanions are members of group of compounds termed polyoxometalates, and because they contain only one type of metal atom are often called isopolymetalates. The discrete molybdenum oxoanions range in size from the simplest MoO2−
4, found in potassium molybdate up to extremely large structures found in isopoly-molybdenum blues that contain for example 154 Mo atoms. The behaviour of molybdenum is different from the other elements in group 6. Chromium only forms the chromates, CrO2−
4, Cr
2O2−
7, Cr
3O2−
10 and Cr
4O2−
13 ions which are all based on tetrahedral chromium. Tungsten is similar to molybdenum and forms many tungstates containing 6 coordinate tungsten.
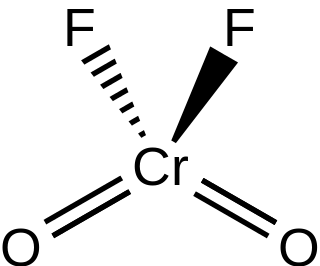
Chromyl fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO2F2. It is a violet-red colored crystalline solid that melts to an orange-red liquid.
Fluorine forms a great variety of chemical compounds, within which it always adopts an oxidation state of −1. With other atoms, fluorine forms either polar covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Most frequently, covalent bonds involving fluorine atoms are single bonds, although at least two examples of a higher order bond exist. Fluoride may act as a bridging ligand between two metals in some complex molecules. Molecules containing fluorine may also exhibit hydrogen bonding. Fluorine's chemistry includes inorganic compounds formed with hydrogen, metals, nonmetals, and even noble gases; as well as a diverse set of organic compounds.
For many elements the highest known oxidation state can be achieved in a fluoride. For some elements this is achieved exclusively in a fluoride, for others exclusively in an oxide; and for still others the highest oxidation states of oxides and fluorides are always equal.

Molybdenum(III) bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula MoBr3. It is a black solid that is insoluble in most solvents but dissolves in donor solvents such as pyridine.
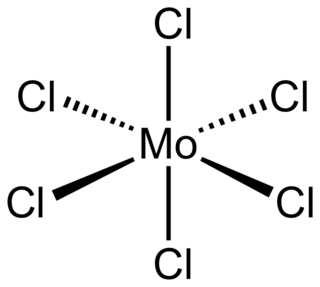
Molybdenum(VI) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula MoCl6. It is a black diamagnetic solid. The molecules adopt an octahedral structure as seen in tungsten(VI) chloride.







