NAPE-PLD may refer to:
NAPE-PLD may refer to:

A phospholipase is an enzyme that hydrolyzes phospholipids into fatty acids and other lipophilic substances. There are four major classes, termed A, B, C, and D, which are distinguished by the type of reaction which they catalyze:
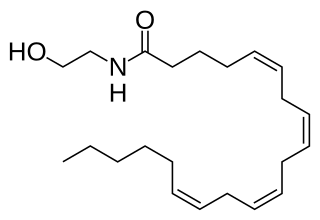
Anandamide (ANA), also referred to as N-arachidonoylethanolamine (AEA) is a fatty acid neurotransmitter belonging to the fatty acid derivative group known as N-Acylethanolamine (NAE). Anandamide takes its name from the Sanskrit word ananda, meaning "joy, bliss, delight," plus amide. Anandamide, the first discovered endocannabinoid, engages with the body's endocannabinoid system by binding to the same cannabinoid receptors that THC found in cannabis acts on. Anandamide can be found within tissues in a wide range of animals. It has also been found in plants, such as the cacao tree.

Phosphatidylinositol or inositol phospholipid is a biomolecule. It was initially called "inosite" when it was discovered by Léon Maquenne and Johann Joseph von Scherer in the late 19th century. It was discovered in bacteria but later also found in eukaryotes, and was found to be a signaling molecule.
Phosphatidic acids are anionic phospholipids important to cell signaling and direct activation of lipid-gated ion channels. Hydrolysis of phosphatidic acid gives rise to one molecule each of glycerol and phosphoric acid and two molecules of fatty acids. They constitute about 0.25% of phospholipids in the bilayer.
Phospholipase D (EC 3.1.4.4, lipophosphodiesterase II, lecithinase D, choline phosphatase, PLD; systematic name phosphatidylcholine phosphatidohydrolase) is an enzyme of the phospholipase superfamily that catalyses the following reaction

Phospholipase B, also known as lysophospholipase, is an enzyme with a combination of both PLA1 and PLA2 activities; that is, it can cleave acyl chains from both the sn-1 and sn-2 positions of a phospholipid. In general, it acts on lysolecithin.

Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) is a class of phospholipids found in biological membranes. They are synthesized by the addition of cytidine diphosphate-ethanolamine to diglycerides, releasing cytidine monophosphate. S-Adenosyl methionine can subsequently methylate the amine of phosphatidylethanolamines to yield phosphatidylcholines.

Phospholipase A1 (EC 3.1.1.32; systematic name: phosphatidylcholine 1-acylhydrolase) encoded by the PLA1A gene is a phospholipase enzyme which removes the 1-acyl group:

Phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase is a transferase enzyme which converts phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) to phosphatidylcholine (PC) in the liver. In humans it is encoded by the PEMT gene within the Smith–Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17.
The enzyme lysophospholipase (EC 3.1.1.5) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a 3-propylmalate synthase (EC 2.3.3.12) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a sulfoacetaldehyde acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Oleoylethanolamide (OEA) is an endogenous peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α) agonist. It is a naturally occurring ethanolamide lipid that regulates feeding and body weight in vertebrates ranging from mice to pythons.
N-Acylphosphatidylethanolamines (NAPEs) are hormones released by the small intestine into the bloodstream when it processes fat. NAPEs travel to the hypothalamus in the brain and suppress appetite. This mechanism could be relevant for treating obesity.
N-acyl phosphatidylethanolamine phospholipase D (NAPE-PLD) is an enzyme that catalyzes the release of N-acylethanolamine (NAE) from N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamine (NAPE). This is a major part of the process that converts ordinary lipids into chemical signals like anandamide and oleoylethanolamine. In humans, the NAPE-PLD protein is encoded by the NAPEPLD gene.
A lysophosphatidylethanolamine (LPE) is a chemical compound derived from a phosphatidylethanolamine, which is typical of cell membranes. LPE results from partial hydrolysis of phosphatidylethanolamine, which removes one of the fatty acid groups. The hydrolysis is generally the result of the enzymatic action of phospholipase A2. LPE can be used in agricultural use to regulate plant growth such as color increase, sugar content increase, plant health increase, and storability increase without side effect.

1-Lysophosphatidylcholines are a class of phospholipids that are intermediates in the metabolism of lipids. They result from the hydrolysis of an acyl group from the sn-1 position of phosphatidylcholine. They are also called 2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholines. The synthesis of phosphatidylcholines with specific fatty acids occurs through the synthesis of 1-lysoPC. The formation of various other lipids generates 1-lysoPC as a by-product.
N-acetylphosphatidylethanolamine-hydrolysing phospholipase D (EC 3.1.4.54, NAPE-PLD, anandamide-generating phospholipase D, N-acyl phosphatidylethanolamine phospholipase D, NAPE-hydrolyzing phospholipase D) is an enzyme with systematic name 'N-acetylphosphatidylethanolamine phosphatidohydrolase. It catalyses the following chemical reaction
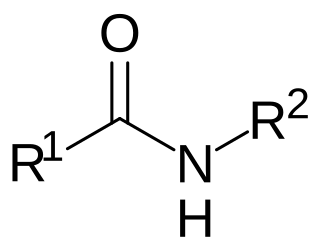
N-acyl amides are a general class of endogenous fatty acid compounds characterized by a fatty acyl group linked to a primary amine metabolite by an amide bond. Broadly speaking, N-acyl amides fall into several categories: amino acid conjugates, neurotransmitter conjugates, ethanolamine conjugates, and taurine conjugates. N-acyl amides have pleiotropic signaling functions in physiology, including in cardiovascular function, metabolic homeostasis, memory, cognition, pain, motor control and others. Initial attention focused on N-acyl amides present in mammalian organisms, however recently lipid signaling systems consisting of N-acyl amides have also been found to be present in invertebrates, such as Drosophila melanogaster. N-acyl amides play important roles in many biochemical pathways involved in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, as well as the metabolic enzymes, transporters, and receptors that regulate their signaling.