
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring and recording information about the members of a given population. The term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses include agriculture, business, and traffic censuses. The United Nations defines the essential features of population and housing censuses as "individual enumeration, universality within a defined territory, simultaneity and defined periodicity", and recommends that population censuses be taken at least every 10 years. United Nations recommendations also cover census topics to be collected, official definitions, classifications and other useful information to co-ordinate international practice.

Genealogy, also known as family history, is the study of families and the tracing of their lineages and history. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kinship and pedigrees of its members. The results are often displayed in charts or written as narratives.

Demography is the statistical study of populations, especially human beings. As a very general science, it can analyze any kind of dynamic living population, i.e., one that changes over time or space. Demography encompasses the study of the size, structure, and distribution of these populations, and spatial or temporal changes in them in response to birth, migration, aging, and death. Based on the demographic research of the earth, earth's population up to the year 2050 and 2100 can be estimated by demographers. Demographics are quantifiable characteristics of a given population.
A patronymic, or patronym, is a component of a personal name based on the given name of one's father, grandfather, or an earlier male ancestor. A component of a name based on the name of one's mother or a female ancestor is a matronymic. Each is a means of conveying lineage.
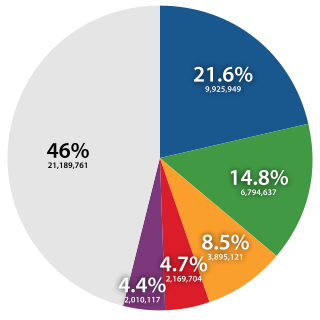
Chinese surnames are used by Han Chinese and Sinicized ethnic groups in Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Malaysia, Brunei, Taiwan, Korea, Singapore, Indonesia, Philippines, Vietnam and among overseas Chinese communities. In ancient times two types of surnames existed, namely xing or clan names, and shi or lineage names.
A surname, family name, or last name is the portion of a personal name that indicates a person's family. Depending on the culture, all members of a family unit may have identical surnames or there may be variations based on the cultural rules.
A Korean name consists of a family name followed by a given name, as used by the Korean people in both South Korea and North Korea. In the Korean language, ireum or seongmyeong usually refers to the family name (seong) and given name together.
Chinese personal names are names used by those from mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, and the Chinese diaspora overseas. Due to China's historical dominance of East Asian culture, many names used in Korea and Vietnam are adaptations of Chinese names, or have historical roots in Chinese, with appropriate adaptation to accommodate linguistic differences.
Japanese names in modern times usually consist of a family name (surname), followed by a given name. More than one given name is not generally used. Japanese names are usually written in kanji, which are characters usually Chinese in origin but Japanese in pronunciation. The kanji for a name may have a variety of possible Japanese pronunciations, hence parents might use hiragana or katakana when giving a birth name to their newborn child. Names written in hiragana or katakana are phonetic renderings, and so lack the visual meaning of names expressed in the logographic kanji.

In biology, a taxon is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is not uncommon, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping.

A given name is a part of a person's personal name. It identifies a person, and differentiates that person from the other members of a group who have a common surname. The term given name refers to the fact that the name usually is bestowed upon a person, normally to a child by their parents at or close to the time of birth. A Christian name, a first name which historically was given at baptism, is now also typically given by the parents at birth.
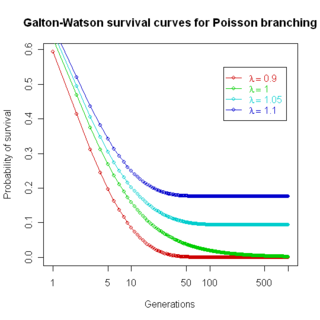
The Galton–Watson process is a branching stochastic process arising from Francis Galton's statistical investigation of the extinction of family names. The process models family names as patrilineal, while offspring are randomly either male or female, and names become extinct if the family name line dies out. This is an accurate description of Y chromosome transmission in genetics, and the model is thus useful for understanding human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroups, and is also of use in understanding other processes ; but its application to actual extinction of family names is fraught. In practice, family names change for many other reasons, and dying out of name line is only one factor, as discussed in examples, below; the Galton–Watson process is thus of limited applicability in understanding actual family name distributions.
In several cultures, a middle name is a portion of a personal name that is written between the person's given name and their surname. A person may be given a middle name regardless of whether it's necessary to distinguish them from other people with the same given name and surname. In cultures where a given name is expected to precede the surname, additional names are likely to be placed after the given name and before the surname, and thus called middle names. In English-speaking American culture, that term is often applied to names occupying that position even if the bearer would insist that that name is being mistakenly called a "middle name", and is actually :
A statistical parameter or population parameter is a quantity entering into the probability distribution of a statistic or a random variable. It can be regarded as a numerical characteristic of a statistical population or a statistical model.

A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent. However, there are other uses of this term. First, it is used to mean a collection of specific alleles in a cluster of tightly linked genes on a chromosome that are likely to be inherited together—that is, they are likely to be conserved as a sequence that survives the descent of many generations of reproduction. A second use is to mean a set of linked single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) alleles that tend to always occur together. It is thought that identifying these statistical associations and few alleles of a specific haplotype sequence can facilitate identifying all other such polymorphic sites that are nearby on the chromosome. Such information is critical for investigating the genetics of common diseases; which in fact have been investigated in humans by the International HapMap Project. Thirdly, many human genetic testing companies use the term in a third way: to refer to an individual collection of specific mutations within a given genetic segment;.

Eastern Slavic naming customs are the traditional way of identifying a person's given name and patronymic name in countries influenced by rule of the Russian Empire and more significantly the Soviet Union which enacted widespread Russification in culture, lingua franca, alphabet and customs.

Absheron Rayon, also spelled as Apsheron, is a rayon of Azerbaijan demarcated in 1963. Although it shares the same name as the Absheron Peninsula, the area covered by the rayon is not conterminous, being further west and mostly inland.
Vietnamese personal names generally consist of three parts: one patrilineal family name, one or more middle name(s), and one given name, used in that order. The "family name first" order follows the system of Chinese names and is common throughout the Chinese cultural sphere. However, it is different from Chinese, Korean, and Japanese names in the usage of "middle names", as they are less common in China and Korea and do not exist in Japan. Persons can be referred to by the whole name, the given name or a hierarchic pronoun, which usually connotes a degree of family relationship or kinship, in normal usage.

The Thirteenth United States Census, conducted by the Census Bureau on April 15, 1910, determined the resident population of the United States to be 92,228,496, an increase of 21.0 percent over the 76,212,168 persons enumerated during the 1900 Census. The 1910 Census switched from a portrait page orientation to a landscape orientation.
United States senators are conventionally ranked by the length of their tenure in the Senate. The senator in each U.S. state with the longer time in office is known as the senior senator; the other is the junior senator. This convention has no official standing, though seniority confers several benefits, including preference in the choice of committee assignments and physical offices. When senators have been in office for the same length of time, a number of tiebreakers, including previous offices held, are used to determine seniority.










