
An arch is a curved vertical structure spanning an open space underneath it. Arches may support the load above them, or they may perform a purely decorative role. As a decorative element, the arch dates back to the 4th millennium BC, but structural load-bearing arches became popular only after their adoption by the Ancient Romans in the 4th century BC.

Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of medieval Europe that was predominant in the 11th and 12th centuries. The style eventually developed into the Gothic style with the shape of the arches providing a simple distinction: the Romanesque is characterized by semicircular arches, while the Gothic is marked by the pointed arches. The Romanesque emerged nearly simultaneously in multiple countries ; its examples can be found across the continent, making it the first pan-European architectural style since Imperial Roman architecture. Similarly to Gothic, the name of the style was transferred onto the contemporary Romanesque art.

Gothic architecture is an architectural style that was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture. It originated in the Île-de-France and Picardy regions of northern France. The style at the time was sometimes known as opus Francigenum ; the term Gothic was first applied contemptuously during the later Renaissance, by those ambitious to revive the architecture of classical antiquity.

A dome is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a matter of controversy and there are a wide variety of forms and specialized terms to describe them.

An ogive is the roundly tapered end of a two-dimensional or three-dimensional object. Ogive curves and surfaces are used in engineering, architecture, woodworking, and munitions.
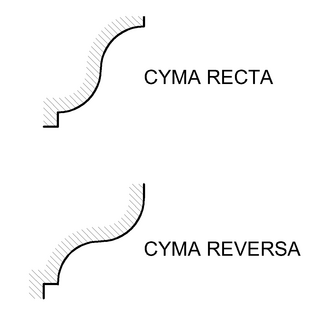
An ogee ( ) is an object, element, or curve—often seen in architecture and building trades—that has a serpentine- or extended S-shape (sigmoid). Ogees consist of a "double curve", the combination of two semicircular curves or arcs that, as a result of a point of inflection from concave to convex or vice versa, have ends of the overall curve that point in opposite directions.

The flying buttress is a specific form of buttress composed of an arch that extends from the upper portion of a wall to a pier of great mass, in order to convey to the ground the lateral forces that push a wall outwards, which are forces that arise from vaulted ceilings of stone and from wind-loading on roofs.

A rib vault or ribbed vault is an architectural feature for covering a wide space, such as a church nave, composed of a framework of crossed or diagonal arched ribs. Variations were used in Roman architecture, Byzantine architecture, Islamic architecture, Romanesque architecture, and especially Gothic architecture. Thin stone panels fill the space between the ribs. This greatly reduced the weight and thus the outward thrust of the vault. The ribs transmit the load downward and outward to specific points, usually rows of columns or piers. This feature allowed architects of Gothic cathedrals to make higher and thinner walls and much larger windows.

A barrel vault, also known as a tunnel vault, wagon vault or wagonhead vault, is an architectural element formed by the extrusion of a single curve along a given distance. The curves are typically circular in shape, lending a semi-cylindrical appearance to the total design. The barrel vault is the simplest form of a vault: effectively a series of arches placed side by side. It is a form of barrel roof.

Tracery is an architectural device by which windows are divided into sections of various proportions by stone bars or ribs of moulding. Most commonly, it refers to the stonework elements that support the glass in a window. The purpose of the device is practical as well as decorative, because the increasingly large windows of Gothic buildings needed maximum support against the wind. The term probably derives from the tracing floors on which the complex patterns of windows were laid out in late Gothic architecture. Tracery can be found on the exterior of buildings as well as the interior.
This page is a glossary of architecture.
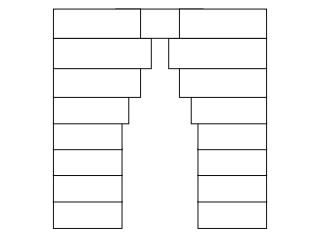
A corbel arch is an arch-like construction method that uses the architectural technique of corbeling to span a space or void in a structure, such as an entranceway in a wall or as the span of a bridge. A corbel vault uses this technique to support the superstructure of a building's roof.

In architecture, a vault is a self-supporting arched form, usually of stone or brick, serving to cover a space with a ceiling or roof. As in building an arch, a temporary support is needed while rings of voussoirs are constructed and the rings placed in position. Until the topmost voussoir, the keystone, is positioned, the vault is not self-supporting. Where timber is easily obtained, this temporary support is provided by centering consisting of a framed truss with a semicircular or segmental head, which supports the voussoirs until the ring of the whole arch is completed.

French architecture consists of architectural styles that either originated in France or elsewhere and were developed within the territories of France.

English Gothic is an architectural style that flourished from the late 12th until the mid-17th century. The style was most prominently used in the construction of cathedrals and churches. Gothic architecture's defining features are pointed arches, rib vaults, buttresses, and extensive use of stained glass. Combined, these features allowed the creation of buildings of unprecedented height and grandeur, filled with light from large stained glass windows. Important examples include Westminster Abbey, Canterbury Cathedral and Salisbury Cathedral. The Gothic style endured in England much longer than in Continental Europe.

The Plantagenet style or Angevine Gothic is an architectural style of western France, mainly of the second half of 12th and the 13th century. By Eugène Viollet-le-Duc it was called "Style ogivale Plantagenêt", something like "Plantagenet Ribs Style". It is named by the House of Anjou-Plantagenet. It is characterized by cross-ribbed vaults and extremely curved relatively domelike vaults.

Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of medieval Europe characterised by semi-circular arches. The term "Romanesque" is usually used for the period from the 10th to the 12th century with "Pre-Romanesque" and "First Romanesque" being applied to earlier buildings with Romanesque characteristics. Romanesque architecture can be found across the continent, diversified by regional materials and characteristics, but with an overall consistency that makes it the first pan-European architectural style since Imperial Roman Architecture. The Romanesque style in England is traditionally referred to as Norman architecture.

The Old Town Hall in Prague, the capital of the Czech Republic, is one of the city's most visited monuments. It is located in Old Town Square.

A pointed arch, ogival arch, or Gothic arch is an arch with a pointed crown meet at an angle at the top of the arch. Also known as a two-centred arch, its form is derived from the intersection of two circles. This architectural element was particularly important in Gothic architecture. The earliest use of a pointed arch dates back to bronze-age Nippur. As a structural feature, it was first used in eastern Christian architecture, Byzantine architecture and Sasanian architecture, but in the 12th century it came into use in France and England as an important structural element, in combination with other elements, such as the rib vault and later the flying buttress. These allowed the construction of cathedrals, palaces and other buildings with dramatically greater height and larger windows which filled them with light.

Perpendicular Gothic architecture was the third and final style of English Gothic architecture developed in the Kingdom of England during the Late Middle Ages, typified by large windows, four-centred arches, straight vertical and horizontal lines in the tracery, and regular arch-topped rectangular panelling. Perpendicular was the prevailing style of Late Gothic architecture in England from the 14th century to the 17th century. Perpendicular was unique to the country: no equivalent arose in Continental Europe or elsewhere in the British Isles. Of all the Gothic architectural styles, Perpendicular was the first to experience a second wave of popularity from the 18th century on in Gothic Revival architecture.




















