See also
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Sloughing. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Sloughing may refer to:
Sloughing in biology refers to the act of shedding or casting off dead tissue, such as cells of the endometrium, shed during menstruation, or the shedding of skin in amphibians.
Skin sloughing is the process of shedding dead surface cells from the skin. It is most associated with cosmetic skin maintenance via exfoliation, but can also occur biologically or for medical reasons.
Soil sloughing is soil falling off banks and slopes due to a loss in cohesion. Soil sloughs off for the same reasons as landslides in general, with very wet soil being among the leading factors. Sloughing is a relatively shallow phenomenon involving the uppermost layers of the soil. Bare soils are more likely to slough than soils with plant cover in part because the roots help hold the surface against gravity. Unabated soil sloughing can end in massive bank or slope failure.
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Sloughing. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
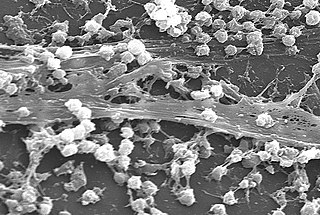
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric conglomeration of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes".

In biology, moulting, or molting, also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body, either at specific times of the year, or at specific points in its life cycle.

Ailuronyx is a small genus of geckos from Seychelles, commonly known as skin-sloughing geckos. They have a reputation for delicacy and especially for shedding strips of skin if handled.

Pressure ulcers, also known as bedsores, are localized damage to the skin and/or underlying tissue that usually occur over a bony prominence as a result of usually long-term pressure, or pressure in combination with shear or friction. The most common sites are the skin overlying the sacrum, coccyx, heels, and hips, though other sites can be affected, such as the elbows, knees, ankles, back of shoulders, or the back of the cranium.

An eschar is a slough or piece of dead tissue that is cast off from the surface of the skin, particularly after a burn injury, but also seen in gangrene, ulcer, fungal infections, necrotizing spider bite wounds, tick bites associated with spotted fevers, and exposure to cutaneous anthrax. The term "eschar" is not interchangeable with "scab". An eschar contains necrotic tissue, whereas a scab is composed of dried blood and exudate.
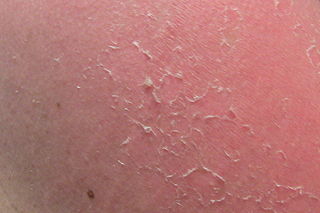
Desquamation, commonly called skin peeling, is the shedding of the outermost membrane or layer of a tissue, such as the skin. The term is from Latin desquamare, meaning 'to scrape the scales off a fish'.
Dander is material shed from the body of humans and animals that have fur, hair, or feathers. The term is similar to dandruff, when an excess of flakes becomes visible. Skin flakes that come off the main body of an animal are dander, while the flakes of skin called dandruff come from the scalp and are composed of epithelial skin cells. The surface layer of mammalian skin is called the stratum corneum, which is shed as part of normal skin replacement.

Staphylococcus epidermidis is a Gram-positive bacterium, and one of over 40 species belonging to the genus Staphylococcus. It is part of the normal human flora, typically the skin flora, and less commonly the mucosal flora. It is a facultative anaerobic bacteria. Although S. epidermidis is not usually pathogenic, patients with compromised immune systems are at risk of developing infection. These infections are generally hospital-acquired. S. epidermidis is a particular concern for people with catheters or other surgical implants because it is known to form biofilms that grow on these devices. Being part of the normal skin flora, S. epidermidis is a frequent contaminant of specimens sent to the diagnostic laboratory.
The Slough–Windsor & Eton line is a branch railway line 2 miles 63 chains (4.5 km) long, in Berkshire, England. Trains run between the line's only two stations, Slough and Windsor & Eton Central. At its northern end, the branch line joins the Great Western Main Line, but passenger trains from Windsor rarely use the connection, usually terminating at Slough.
Water stagnation occurs when water stops flowing. Stagnant water can be a major environmental hazard.

A subfossil is a part of a dead organism that is partially, rather than fully, fossilized, as is a fossil. Partial fossilization may be present because not enough time has elapsed since the animal died for full fossilization, or because the conditions in which the remains were deposited were not optimal for fossilization.

Trichophyton is a genus of fungi, which includes the parasitic varieties that cause tinea, including athlete's foot, ringworm, jock itch, and similar infections of the nail, beard, skin and scalp. Trichophyton fungi are molds characterized by the development of both smooth-walled macro- and microconidia. Macroconidia are mostly borne laterally directly on the hyphae or on short pedicels, and are thin- or thick-walled, clavate to fusiform, and range from 4 to 8 by 8 to 50 μm in size. Macroconidia are few or absent in many species. Microconidia are spherical, pyriform to clavate or of irregular shape, and range from 2 to 3 by 2 to 4 μm in size.

A trickling filter is a type of wastewater treatment system. It consists of a fixed bed of rocks, coke, gravel, slag, polyurethane foam, sphagnum peat moss, ceramic, or plastic media over which sewage or other wastewater flows downward and causes a layer of microbial slime (biofilm) to grow, covering the bed of media. Aerobic conditions are maintained by splashing, diffusion, and either by forced-air flowing through the bed or natural convection of air if the filter medium is porous.

Reptile skin is covered with scutes or scales which, along with many other characteristics, distinguish reptiles from animals of other classes. Scales are made of alpha and beta-keratin and are formed from the epidermis. They may be ossified or tubercular, as in the case of lizards, or modified elaborately, as in the case of snakes.
Slough is a town in Berkshire, England.

The Scitalis or Scytale is a serpent from Medieval bestiaries, such as the Aberdeen Bestiary, supposed to have such marvelous markings on its back that its appearance would stun the viewer, slowing the person down so that they could be caught. Its bodily heat was so great that it shed its skin even in the winter.

A pimple is a kind of comedo that results from excess sebum and dead skin cells getting trapped in the pores of the skin. In its aggravated state, it may evolve into a pustule or papules. Pimples can be treated by acne medications, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatories prescribed by a physician, or various over the counter remedies purchased at a pharmacy.