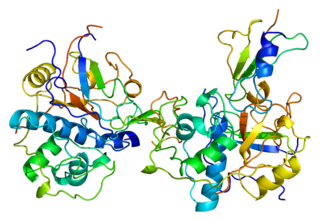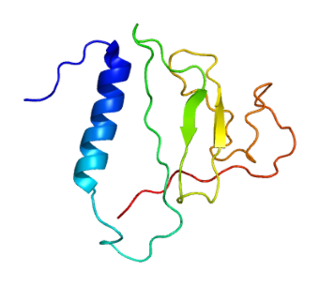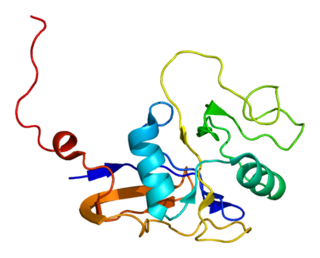
Thyroglobulin (Tg) is a 660 kDa, dimeric protein produced by the follicular cells of the thyroid and used entirely within the thyroid gland. Thyroglobulin protein accounts for approximately half of the protein content of the thyroid gland. Human TG (HTG) is a homodimer of subunits each containing 2768 amino acids as synthesized.

Cathepsins are proteases found in all animals as well as other organisms. There are approximately a dozen members of this family, which are distinguished by their structure, catalytic mechanism, and which proteins they cleave. Most of the members become activated at the low pH found in lysosomes. Thus, the activity of this family lies almost entirely within those organelles. There are, however, exceptions such as cathepsin K, which works extracellularly after secretion by osteoclasts in bone resorption. Cathepsins have a vital role in mammalian cellular turnover.

The low-density lipoprotein receptor gene family codes for a class of structurally related cell surface receptors that fulfill diverse biological functions in different organs, tissues, and cell types. The role that is most commonly associated with this evolutionarily ancient family is cholesterol homeostasis. In humans, excess cholesterol in the blood is captured by low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and removed by the liver via endocytosis of the LDL receptor. Recent evidence indicates that the members of the LDL receptor gene family are active in the cell signalling pathways between specialized cells in many, if not all, multicellular organisms.

Cathepsin S is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTSS gene. Transcript variants utilizing alternative polyadenylation signals exist for this gene.

Cathepsin C (CTSC) also known as dipeptidyl peptidase I (DPP-I) is a lysosomal exo-cysteine protease belonging to the peptidase C1 family. In humans, it is encoded by the CTSC gene.
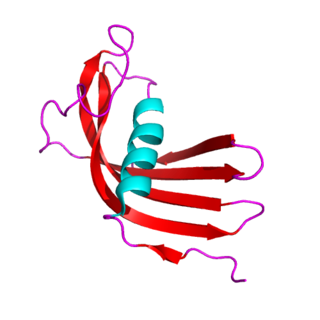
The cystatins are a family of cysteine protease inhibitors which share a sequence homology and a common tertiary structure of an alpha helix lying on top of an anti-parallel beta sheet. The family is subdivided as described below.

Cathepsin B is in humans encoded by the CTSB gene. Cathepsin B belongs to a family of lysosomal cysteine proteases and plays an important role in intracellular proteolysis. Upregulation of cathepsin B is found in premalignant lesions and various pathological conditions, as well as cancers.

Frizzled is a family of G protein-coupled receptor proteins that serves as receptors in the Wnt signaling pathway and other signaling pathways. When activated, Frizzled leads to activation of Dishevelled in the cytosol.
The mannose receptor is a C-type lectin primarily present on the surface of macrophages and immature dendritic cells, but is also expressed on the surface of skin cells such as human dermal fibroblasts and keratinocytes. It is the first member of a family of endocytic receptors that includes Endo180 (CD280), M-type PLA2R, and DEC-205 (CD205).

Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3, also known as IGFBP-3, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGFBP3 gene. IGFBP-3 is one of six IGF binding proteins that have highly conserved structures and bind the insulin-like growth factors IGF-1 and IGF-2 with high affinity. IGFBP-7, sometimes inappropriately included in this family, shares neither the conserved structural features nor the high IGF affinity.

Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGFBP4 gene.

Cathepsin D is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTSD gene. This gene encodes a lysosomal aspartyl protease composed of a protein dimer of disulfide-linked heavy and light chains, both produced from a single protein precursor. Cathepsin D is an aspartic endo-protease that is ubiquitously distributed in lysosomes. The main function of cathepsin D is to degrade proteins and activate precursors of bioactive proteins in pre-lysosomal compartments. This proteinase, which is a member of the peptidase A1 family, has a specificity similar to but narrower than that of pepsin A. Transcription of the CTSD gene is initiated from several sites, including one that is a start site for an estrogen-regulated transcript. Mutations in this gene are involved in the pathogenesis of several diseases, including breast cancer and possibly Alzheimer disease. Homozygous deletion of the CTSD gene leads to early lethality in the post-natal phase. Deficiency of CTSD gene has been reported an underlying cause of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (NCL).

Cathepsin L1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTSL1 gene.

Cystatin-B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CSTB gene.

Cathepsin H is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTSH gene.

Cathepsin Z, also called cathepsin X or cathepsin P, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTSZ gene. It is a member of the cysteine cathepsin protease family, which has 11 members. As one of the 11 cathepsins, cathepsin Z contains distinctive features from others. Cathepsin Z has been reported involved in cancer malignancy and inflammation.

Cathepsin F is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTSF gene.
CUB domain is an evolutionarily conserved protein domain.
CCN proteins are a family of extracellular matrix (ECM)-associated proteins involved in intercellular signaling. Due to their dynamic role within the ECM they are considered matricellular proteins.
The Kazal domain is an evolutionary conserved protein domain usually indicative of serine protease inhibitors. However, kazal-like domains are also seen in the extracellular part of agrins, which are not known to be protease inhibitors.

In computing, a Digital Object Identifier or DOI is a persistent identifier or handle used to uniquely identify objects, standardized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). An implementation of the Handle System, DOIs are in wide use mainly to identify academic, professional, and government information, such as journal articles, research reports and data sets, and official publications though they also have been used to identify other types of information resources, such as commercial videos.
PubMed Central (PMC) is a free digital repository that archives publicly accessible full-text scholarly articles that have been published within the biomedical and life sciences journal literature. As one of the major research databases within the suite of resources that have been developed by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), PubMed Central is much more than just a document repository. Submissions into PMC undergo an indexing and formatting procedure which results in enhanced metadata, medical ontology, and unique identifiers which all enrich the XML structured data for each article on deposit. Content within PMC can easily be interlinked to many other NCBI databases and accessed via Entrez search and retrieval systems, further enhancing the public's ability to freely discover, read and build upon this portfolio of biomedical knowledge.
The public domain consists of all the creative works to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable.

Pfam is a database of protein families that includes their annotations and multiple sequence alignments generated using hidden Markov models. The most recent version, Pfam 31.0, was released in March 2017 and contains 16,712 families.
InterPro is a database of protein families, domains and functional sites in which identifiable features found in known proteins can be applied to new protein sequences in order to functionally characterise them.