Related Research Articles
Information retrieval (IR) in computing and information science is the task of identifying and retrieving information system resources that are relevant to an information need. The information need can be specified in the form of a search query. In the case of document retrieval, queries can be based on full-text or other content-based indexing. Information retrieval is the science of searching for information in a document, searching for documents themselves, and also searching for the metadata that describes data, and for databases of texts, images or sounds.

Memex [memory expansion] is a hypothetical electromechanical device for interacting with microform documents and described in Vannevar Bush's 1945 article "As We May Think". Bush envisioned the memex as a device in which individuals would compress and store all of their books, records, and communications, "mechanized so that it may be consulted with exceeding speed and flexibility". The individual was supposed to use the memex as an automatic personal filing system, making the memex "an enlarged intimate supplement to his memory".
In computing, a search engine is an information retrieval software system designed to help find information stored on one or more computer systems. Search engines discover, crawl, transform, and store information for retrieval and presentation in response to user queries. The search results are usually presented in a list and are commonly called hits. The most widely used type of search engine is a web search engine, which searches for information on the World Wide Web.
Wide Area Information Server (WAIS) is a client–server text searching system that uses the ANSI Standard Z39.50 Information Retrieval Service Definition and Protocol Specifications for Library Applications" (Z39.50:1988) to search index databases on remote computers. It was developed in 1990 as a project of Thinking Machines, Apple Computer, Dow Jones, and KPMG Peat Marwick.

In mass communication, digital media is any communication media that operates in conjunction with various encoded machine-readable data formats. Digital content can be created, viewed, distributed, modified, listened to, and preserved on a digital electronic device, including digital data storage media and digital broadcasting. Digital is defined as any data represented by a series of digits, and media refers to methods of broadcasting or communicating this information. Together, digital media refers to mediums of digitized information broadcast through a screen and/or a speaker. This also includes text, audio, video, and graphics that are transmitted over the internet for viewing or listening to on the internet.
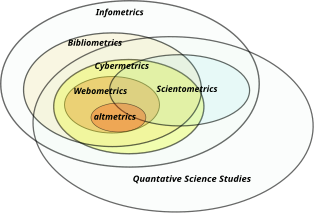
Information science, documentology or informatology is an academic field which is primarily concerned with analysis, collection, classification, manipulation, storage, retrieval, movement, dissemination, and protection of information. Practitioners within and outside the field study the application and the usage of knowledge in organizations in addition to the interaction between people, organizations, and any existing information systems with the aim of creating, replacing, improving, or understanding the information systems.
Social software, also known as social apps or social platform includes communications and interactive tools that are often based on the Internet. Communication tools typically handle capturing, storing and presenting communication, usually written but increasingly including audio and video as well. Interactive tools handle mediated interactions between a pair or group of users. They focus on establishing and maintaining a connection among users, facilitating the mechanics of conversation and talk. Social software generally refers to software that makes collaborative behaviour, the organisation and moulding of communities, self-expression, social interaction and feedback possible for individuals. Another element of the existing definition of social software is that it allows for the structured mediation of opinion between people, in a centralized or self-regulating manner. The most improved area for social software is that Web 2.0 applications can all promote co-operation between people and the creation of online communities more than ever before. The opportunities offered by social software are instant connections and opportunities to learn. An additional defining feature of social software is that apart from interaction and collaboration, it aggregates the collective behaviour of its users, allowing not only crowds to learn from an individual but individuals to learn from the crowds as well. Hence, the interactions enabled by social software can be one-to-one, one-to-many, or many-to-many.
The deep web, invisible web, or hidden web are parts of the World Wide Web whose contents are not indexed by standard web search-engine programs. This is in contrast to the "surface web", which is accessible to anyone using the Internet. Computer scientist Michael K. Bergman is credited with inventing the term in 2001 as a search-indexing term.

A9.com was a former subsidiary of Amazon that developed search engine and search advertising technology. A9 was based in Palo Alto, California, with teams in Seattle, Bangalore, Beijing, Dublin, Iași, Munich and Tokyo. A9 has development efforts in areas of product search, cloud search, visual search, augmented reality, advertising technology and community question answering.
Internet privacy involves the right or mandate of personal privacy concerning the storage, re-purposing, provision to third parties, and display of information pertaining to oneself via the Internet. Internet privacy is a subset of data privacy. Privacy concerns have been articulated from the beginnings of large-scale computer sharing and especially relate to mass surveillance.
Social bookmarking is an online service which allows users to add, annotate, edit, and share bookmarks of web documents. Many online bookmark management services have launched since 1996; Delicious, founded in 2003, popularized the terms "social bookmarking" and "tagging". Tagging is a significant feature of social bookmarking systems, allowing users to organize their bookmarks and develop shared vocabularies known as folksonomies.

A search engine is a software system that provides hyperlinks to web pages and other relevant information on the Web in response to a user's query. The user inputs a query within a web browser or a mobile app, and the search results are often a list of hyperlinks, accompanied by textual summaries and images. Users also have the option of limiting the search to a specific type of results, such as images, videos, or news.
Google Personalized Search is a personalized search feature of Google Search, introduced in 2004. All searches on Google Search are associated with a browser cookie record. When a user performs a search, the search results are not only based on the relevance of each web page to the search term, but also on which websites the user visited through previous search results. This provides a more personalized experience that can increase the relevance of the search results for the particular user. Such filtering may also have side effects, such as the creation of a filter bubble.
A vertical search engine is distinct from a general web search engine, in that it focuses on a specific segment of online content. They are also called specialty or topical search engines. The vertical content area may be based on topicality, media type, or genre of content. Common verticals include shopping, the automotive industry, legal information, medical information, scholarly literature, job search and travel. Examples of vertical search engines include the Library of Congress, Mocavo, Nuroa, Trulia, and Yelp.
In computer science, the semantic desktop is a collective term for ideas related to changing a computer's user interface and data handling capabilities so that data are more easily shared between different applications or tasks and so that data that once could not be automatically processed by a computer could be. It also encompasses some ideas about being able to share information automatically between different people. This concept is very much related to the Semantic Web, but is distinct insofar as its main concern is the personal use of information.
In computing, logging is the act of keeping a log of events that occur in a computer system, such as problems, errors or just information on current operations. These events may occur in the operating system or in other software. A message or log entry is recorded for each such event. These log messages can then be used to monitor and understand the operation of the system, to debug problems, or during an audit. Logging is particularly important in multi-user software, to have a central overview of the operation of the system.
Amit Sheth is a computer scientist at University of South Carolina in Columbia, South Carolina. He is the founding Director of the Artificial Intelligence Institute, and a Professor of Computer Science and Engineering. From 2007 to June 2019, he was the Lexis Nexis Ohio Eminent Scholar, director of the Ohio Center of Excellence in Knowledge-enabled Computing, and a Professor of Computer Science at Wright State University. Sheth's work has been cited by over 48,800 publications. He has an h-index of 117, which puts him among the top 100 computer scientists with the highest h-index. Prior to founding the Kno.e.sis Center, he served as the director of the Large Scale Distributed Information Systems Lab at the University of Georgia in Athens, Georgia.
Natural-language user interface is a type of computer human interface where linguistic phenomena such as verbs, phrases and clauses act as UI controls for creating, selecting and modifying data in software applications.

"As We May Think" is a 1945 essay by Vannevar Bush which has been described as visionary and influential, anticipating many aspects of information society. It was first published in The Atlantic in July 1945 and republished in an abridged version in September 1945—before and after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Bush expresses his concern for the direction of scientific efforts toward destruction, rather than understanding, and explicates a desire for a sort of collective memory machine with his concept of the memex that would make knowledge more accessible, believing that it would help fix these problems. Through this machine, Bush hoped to transform an information explosion into a knowledge explosion.

A digital library is an online database of digital objects that can include text, still images, audio, video, digital documents, or other digital media formats or a library accessible through the internet. Objects can consist of digitized content like print or photographs, as well as originally produced digital content like word processor files or social media posts. In addition to storing content, digital libraries provide means for organizing, searching, and retrieving the content contained in the collection. Digital libraries can vary immensely in size and scope, and can be maintained by individuals or organizations. The digital content may be stored locally, or accessed remotely via computer networks. These information retrieval systems are able to exchange information with each other through interoperability and sustainability.
References
- ↑ "Trexy Blazes the Search Trail". Brian Solis. September 12, 2006. Archived from the original on December 23, 2010.
- ↑ Macoustra, Jane (2009). Global Research Without Leaving Your Desk. Elsevier Science. p. 14. ISBN 978-1-78063-021-2.
- ↑ "Medallists of the Technology Awards 2006". British Computer Society . Archived from the original on December 20, 2006.