Related Research Articles
This aims to be a complete list of the articles on real estate.
Market value or OMV is the price at which an asset would trade in a competitive auction setting. Market value is often used interchangeably with open market value, fair value or fair market value, although these terms have distinct definitions in different standards, and may or may not differ in some circumstances.
Comparables is a real estate appraisal term referring to properties with characteristics that are similar to a subject property whose value is being sought. This can be accomplished either by a real estate agent who attempts to establish the value of a potential client's home or property through market analysis or, by a licensed or certified appraiser or surveyor using more defined methods, when performing a real estate appraisal.
Business valuation is a process and a set of procedures used to estimate the economic value of an owner's interest in a business. Valuation is used by financial market participants to determine the price they are willing to pay or receive to effect a sale of a business. In addition to estimating the selling price of a business, the same valuation tools are often used by business appraisers to resolve disputes related to estate and gift taxation, divorce litigation, allocate business purchase price among business assets, establish a formula for estimating the value of partners' ownership interest for buy-sell agreements, and many other business and legal purposes such as in shareholders deadlock, divorce litigation and estate contest. In some cases, the court would appoint a forensic accountant as the joint expert doing the business valuation.
Capitalization rate is a real estate valuation measure used to compare different real estate investments. Although there are many variations, a cap rate is often calculated as the ratio between the net operating income produced by an asset and the original capital cost or alternatively its current market value.
Highest and best use, or highest or best use (HBU), is a concept that originated with early economists such as Irving Fisher (1867-1947), who conceptualized the idea of maximum productivity. One of the earliest citations of the term is found in the Minutes of the Maine Legislature as early as 1831 in speaking about the assessment and valuation of real estate: "...the land was classified preceding such change of use, had such real estate been assessed at its highest and best use..." It is the concept in real estate appraisal that shows how the highest value for a property is arrived at. In any case where the market value of real property is sought, that value must be based on its highest and best use. Highest and best use is always that use that would produce the highest value for a property, regardless of its actual current use.
Farmland development rights in Suffolk County, New York began in 1975 in Suffolk County as the state of New York began a program to purchase development rights for farmland to insure they remained as farms and open space rather than being developed for housing.
A Comp Check is a request made to a State Licensed or Certified real estate appraiser, sometimes to assure a minimum opinion of value before an order, is placed. Because providing an opinion of value is the definition of an appraisal in the United States, the practice of the look-up, when excess care is not taken, runs a greater risk of being in violation of the Uniform Standards of Professional Appraisal Practice (USPAP) than an assignment with a more thorough Scope of Work.
Valuation is considered as one of the most critical areas in finance; it plays a key role in many areas of finance such as buy/sell, solvency, merger and acquisition.
The German income approach is the standard approach used in Germany for the valuing of property that produces a stream of future cash flows.
Automated valuation model (AVM) is the name given to a service that can provide real estate property valuations using mathematical modelling combined with a database. Most AVMs calculate a property’s value at a specific point in time by analyzing values of comparable properties. Some also take into account previous surveyor valuations, historical house price movements and user inputs.
The American Measurement Standard is an authoritative measurement standard for use with single-family dwellings. The AMS C42129-2009 is a voluntary guide developed for the measurement, calculation, and communication of square footage in residential dwellings.
In the field of real estate appraisal, extraordinary assumptions and hypothetical conditions are two closely related types of assumptions which are made as predicating conditions of an appraisal problem. Under the Uniform Standards of Professional Appraisal Practice (USPAP), they are two of the assignment conditions on which an appraisal assignment is predicated, the others being general assumptions, laws & regulations, supplemental standards, jurisdictional exceptions, and other conditions affecting scope of work. Making the distinction between the two is important when compiling or reporting appraisals in the United States or other jurisdictions where USPAP is considered the professional standard because USPAP has different specific disclosure requirements for each in an appraisal report and specifies different conditions under which each can be made.
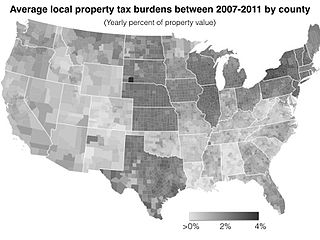
Most local governments in the United States impose a property tax, also known as a millage rate, as a principal source of revenue. This tax may be imposed on real estate or personal property. The tax is nearly always computed as the fair market value of the property times an assessment ratio times a tax rate, and is generally an obligation of the owner of the property. Values are determined by local officials, and may be disputed by property owners. For the taxing authority, one advantage of the property tax over the sales tax or income tax is that the revenue always equals the tax levy, unlike the other taxes. The property tax typically produces the required revenue for municipalities' tax levies. A disadvantage to the taxpayer is that the tax liability is fixed, while the taxpayer's income is not.
A broker price opinion is a report that is performed by a licensed real estate agent, broker or appraiser. It is similar to doing a CMA but most times the real estate professional gets paid to do a BPO. A BPO can be either an Exterior Drive-By or a Full Interior report. When doing a BPO, the real estate pro researches the ‘subject property,’ they take pictures of it, they also scope out the neighborhood as well as pull 6 comparable properties in their MLS. They then take all of this information, the pictures they took of the subject and their knowledge of the local real estate market and they input it into a BPO form. The final BPO is used to support their professional opinion that will help determine the potential selling price or estimated value of a real estate property.
The Gallagher Amendment was an amendment to the Colorado Constitution enacted in 1982 concerning property tax. It set forth the guidelines in the Colorado Constitution for determining the actual value of property and the valuation for assessment of such property. The Gallagher Amendment was a legislative referendum drafted by Dennis J. Gallagher, then a state legislator.