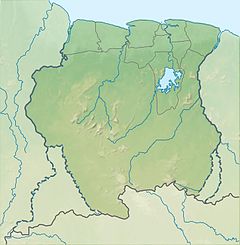
The Geography of Guyana comprises the physical characteristics of the country in Northern South America and part of Caribbean South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Suriname and Venezuela, with a land area of approximately 214,969 square km. The country is situated between 1 and 9 north latitude and between 56 and 62 west longitude. With a 459 km (285 mi)-long Atlantic coastline on the northeast, Guyana is bounded by Venezuela on the west, Brazil on the west and south, and Suriname on the east.

British Guiana was a British colony, part of the mainland British West Indies, which resides on the northern coast of South America. Since 1966 it has been known as the independent nation of Guyana.

Nickerie is a district of Suriname, on the north-west coast. Nickerie's capital city is Nieuw-Nickerie. Another town is Wageningen. The district borders the Atlantic Ocean to the north, the Surinamese district of Coronie to the east, the Surinamese district of Sipaliwini to the south and the region of East Berbice-Corentyne in Guyana to the west.

East Berbice-Corentyne is one of ten regions in Guyana covering the whole of the east of the country. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the north, the Nickerie District and Sipaliwini District of Suriname to the east, Brazil to the south and the regions of Mahaica-Berbice, Upper Demerara-Berbice, Potaro-Siparuni and Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo to the west.
Orealla is an Indigenous community in the East Berbice-Corentyne Region of Guyana, on the Courantyne River, approximately 33 miles (53 km) south of Crabwood Creek and 11 miles (18 km) north of Epira, located at 5°17′50″N57°20′50″W, altitude 11 metres. 15 miles (24 km) south-east on the other side of the Courantyne River lies the Surinamese village of Apoera. Orealla is an indigenous village.

Caribbean Hindustani is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by Indo-Caribbeans and the Indo-Caribbean diaspora. It is a koiné language mainly based on the Bhojpuri and Awadhi dialects. These Hindustani dialects were the most spoken dialects by the Indians who came as immigrants to the Caribbean from Colonial India as indentured laborers. It is closely related to Fiji Hindi and the Bhojpuri-Hindustani spoken in Mauritius and South Africa.

Apoera, also Apura, is a town in western Suriname. The village has a population of 777 people as of 2020. It is the final destination of the Southern East-West Link. 24 kilometres (15 mi) north-west on the other side of the Courantyne River lies the Guyanese village of Orealla. The village is home to the Lokono tribe, but has been westernized. Due to the influx of people of Guyana, the languages used are English, and Sranan Tongo. Dutch is rarely spoken and the native language has all but disappeared. According to the oral tradition, Apoera was founded around 1920 by the Gordon family.
Moleson Creek is a community on the Corentyne River in the East Berbice-Corentyne region of Guyana, and home to the Guyana-Suriname ferry stelling. It is north of Orealla Mission, 10 km (6.2 mi) south of Corriverton, and approximately 90 km (56 mi) from New Amsterdam.

Guyana, officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern coast of South America, part of the historic mainland British West Indies. Guyana is an indigenous word which means "Land of Many Waters". Georgetown is the capital of Guyana and is also the country's largest city. Guyana is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, Brazil to the south and southwest, Venezuela to the west, and Suriname to the east. With a land area of 214,969 km2 (83,000 sq mi), Guyana is the third-smallest sovereign state by area in mainland South America after Uruguay and Suriname, and is the second-least populous sovereign state in South America after Suriname; it is also one of the least densely populated countries on Earth. It has a wide variety of natural habitats and very high biodiversity. The country also hosts a part of the Amazon rainforest, the largest tropical rainforest in the world.
The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to the Co-operative Republic of Guyana.
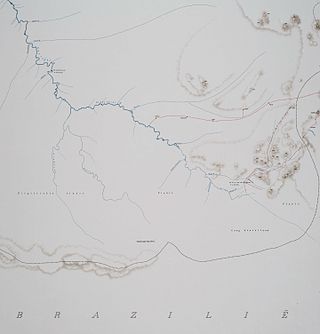
Kutari River, also called Cutari Rivier, Kutari Creek or Cutari Creek, is a small river on the southeastern border of Guyana and the southwestern region of Suriname. The location of the river is part of the disputed Tigri Area in the extreme South East region of Suriname.
The New River is a river of South America located in the southeastern region of Guyana. It forms the Western border of the Tigri Area or New River Triangle, a disputed territory that is claimed by both Guyana and Suriname. In 1965, to bolster this territorial claim, the Surinamese government issued a decree to begin referring to the river as the Upper Corantyne River in Suriname.

The Coeroeni River is a river in South America. It arises in the Tumuc-Humac Mountains, which forms the drainage divide between Pará, Brazil, and Suriname; from there it flows northward. The river is fed by the Aramatau, Kutari and Sipaliwini River. The Coeroeni goes on to form the border of the disputed Tigri Area by Guyana and Suriname. It eventually flows into the Courantyne River, which forms the international boundary between Guyana–Suriname.

South Drain, also Zuiddrain, is a town in western Suriname. Since the pavement of 32 kilometres (20 mi) road section to Nieuw Nickerie, it is the final destination of the northern East-West Link. The European Union funded the reconstruction, which started in 2007, with 13.2 million euro. The section was opened on 30 April 2010. There is a jeep trail between South Drain and Apoera, connecting the Northern East-West Link with the Southern East-West Link. Contrary to earlier plans, the pavement of this road is not imminent.

The borders of Suriname consist of land borders with three countries: Guyana, Brazil, and France. The borders with Guyana and France are in dispute, but the border with Brazil has been uncontroversial since 1906.

The Tigri Area is a wooded area that has been disputed by Guyana and Suriname since around 1840. It involves the area between the Upper Corentyne River, the Coeroeni River, and the Kutari River. This triangular area is known as the New River Triangle in Guyana. In 1969 the conflict ran high on, and since then it has been controlled by Guyana and claimed by Suriname. In 1971, both governments agreed that they would continue talks over the border issue and withdraw their military forces from the disputed triangle. Guyana has never held upon this agreement.
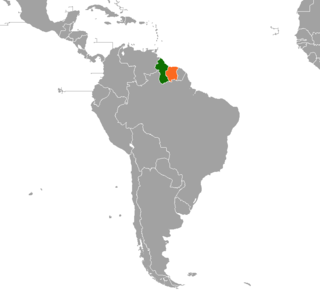
Guyana – Suriname relations are the bilateral relations between Guyana and Suriname. Suriname has an embassy in Georgetown. Guyana has an embassy in Paramaribo. The Courentyne River makes up most of the border between the two countries.
Kasuela is an indigenous village of the Tiriyó people in the East Berbice-Corentyne region of Guyana. The village has a population of about 80 people. The inhabitants are of the subgroup Mawayana or the Frog people.
Camp Tigri or Camp Jaguar is a military camp and airstrip located in the Tigri Area. The area is disputed between Suriname and Guyana.

The Taruma are an indigenous people found in the northern Brazil, southern Guyana, and southern Suriname. They used to speak Taruma which is considered critically endangered. The Taruma in Suriname have merged with the Tiriyó, in Brazil they merged with the Wai-wai. The Wapishana village of Maruranau in Guyana still recognises the tribe.