Related Research Articles
A pidgin, or pidgin language, is a grammatically simplified means of communication that develops between two or more groups of people that do not have a language in common: typically, its vocabulary and grammar are limited and often drawn from several languages. It is most commonly employed in situations such as trade, or where both groups speak languages different from the language of the country in which they reside. Linguists do not typically consider pidgins as full or complete languages.

A creole language, or simply creole, is a stable natural language that develops from the simplifying and mixing of different languages into a new one within a fairly brief period of time: often, a pidgin evolved into a full-fledged language. While the concept is similar to that of a mixed or hybrid language, creoles are often characterized by a tendency to systematize their inherited grammar. Like any language, creoles are characterized by a consistent system of grammar, possess large stable vocabularies, and are acquired by children as their native language. These three features distinguish a creole language from a pidgin. Creolistics, or creology, is the study of creole languages and, as such, is a subfield of linguistics. Someone who engages in this study is called a creolist.
The Middle English creole hypothesis is the concept that the English language is a creole, which is typically a language that developed from a pidgin. The vast differences between Old English and Middle English have led some historical linguists to claim that the language underwent creolisation at around the 11th century, during the Norman conquest of England.

Portuguese creoles are creole languages which have Portuguese as their substantial lexifier. The most widely-spoken creoles influenced by Portuguese are Cape Verdean Creole, Guinea-Bissau Creole and Papiamento.
In linguistics, a stratum or strate is a language that influences or is influenced by another through contact. A substratum or substrate is a language that has lower power or prestige than another, while a superstratum or superstrate is the language that has higher power or prestige. Both substratum and superstratum languages influence each other, but in different ways. An adstratum or adstrate is a language that is in contact with another language in a neighbor population without having identifiably higher or lower prestige. The notion of "strata" was first developed by the Italian linguist Graziadio Isaia Ascoli (1829–1907), and became known in the English-speaking world through the work of two different authors in 1932.
In the field of dialectology, a diasystem or polylectal grammar is a linguistic analysis set up to encode or represent a range of related varieties in a way that displays their structural differences.
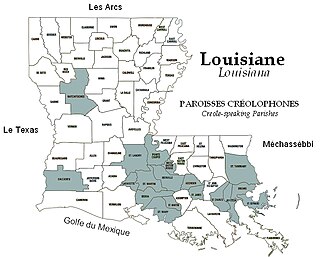
Louisiana Creole is a French-based creole language spoken by fewer than 10,000 people, mostly in the state of Louisiana. It is spoken today by people who racially identify as White, Black, mixed, and Native American, as well as Cajun and Louisiana Creole. It should not be confused with its sister language, Louisiana French, a dialect of the French language. Many Louisiana Creole people do not speak the Louisiana Creole language and may instead use French or English as everyday languages.
Language contact occurs when speakers of two or more languages or varieties interact and influence each other. The study of language contact is called contact linguistics. When speakers of different languages interact closely, it is typical for their languages to influence each other. Language contact can occur at language borders, between adstratum languages, or as the result of migration, with an intrusive language acting as either a superstratum or a substratum.
In sociolinguistics, prestige is the level of regard normally accorded a specific language or dialect within a speech community, relative to other languages or dialects. Prestige varieties are language or dialect families which are generally considered by a society to be the most "correct" or otherwise superior. In many cases, they are the standard form of the language, though there are exceptions, particularly in situations of covert prestige. In addition to dialects and languages, prestige is also applied to smaller linguistic features, such as the pronunciation or usage of words or grammatical constructs, which may not be distinctive enough to constitute a separate dialect. The concept of prestige provides one explanation for the phenomenon of variation in form among speakers of a language or languages.
A mixed language is a language that arises among a bilingual group combining aspects of two or more languages but not clearly deriving primarily from any single language. It differs from a creole or pidgin language in that, whereas creoles/pidgins arise where speakers of many languages acquire a common language, a mixed language typically arises in a population that is fluent in both of the source languages.
In linguistics, relexification is a mechanism of language change by which one language changes much or all of its lexicon, including basic vocabulary, with the lexicon of another language, without drastically changing the relexified language's grammar. The term is principally used to describe pidgins, creoles, and mixed languages.
A diaphoneme is an abstract phonological unit that identifies a correspondence between related sounds of two or more varieties of a language or language cluster. For example, some English varieties contrast the vowel of late with that of wait or eight. Other English varieties contrast the vowel of late or wait with that of eight. This non-overlapping pair of phonemes from two different varieties can be reconciled by positing three different diaphonemes: A first diaphoneme for words like late, a second diaphoneme for words like wait, and a third diaphoneme for words like eight.
A post-creole continuum is a dialect continuum of varieties of a creole language between those most and least similar to the superstrate language. Due to social, political, and economic factors, a creole language can decreolize towards one of the languages from which it is descended, aligning its morphology, phonology, and syntax to the local standard of the dominant language but to different degrees depending on a speaker's status.

In linguistics, a koiné language, koiné dialect, or simply koiné is a standard or common language or dialect that has arisen as a result of the contact, mixing, and often simplification of two or more mutually intelligible varieties of the same language.
Linguistic insecurity comprises feelings of anxiety, self-consciousness, or lack of confidence in the mind of a speaker surrounding their use of language. Often, this anxiety comes from speakers' belief that their speech does not conform to the perceived standard and/or the style of language expected by the speakers' interlocutor(s). Linguistic insecurity is situationally induced and is often based on a feeling of inadequacy regarding personal performance in certain contexts, rather than a fixed attribute of an individual. This insecurity can lead to stylistic, and phonetic shifts away from an affected speaker's default speech variety; these shifts may be performed consciously on the part of the speaker, or may be reflective of an unconscious effort to conform to a more prestigious or context-appropriate variety or style of speech. Linguistic insecurity is linked to the perception of speech varieties in any community, and so may vary based on socioeconomic class and gender. It is also especially pertinent in multilingual societies.
A lexifier is the language that provides the basis for the majority of a pidgin or creole language's vocabulary (lexicon). Often this language is also the dominant, or superstrate language, though this is not always the case, as can be seen in the historical Mediterranean Lingua Franca. In mixed languages, there are no superstrates or substrates, but instead two or more adstrates. One adstrate still contributes the majority of the lexicon in most cases, and would be considered the lexifier. However, it is not the dominant language, as there are none in the development of mixed languages, such as in Michif.
Nativization is the process through which in the virtual absence of native speakers, a language undergoes new phonological, morphological, syntactical, semantic and stylistic changes, and gains new native speakers. This happens necessarily when a second language used by adult parents becomes the native language of their children. Nativization has been of particular interest to linguists, and to creolists more specifically, where the second language concerned is a pidgin.
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science, or part of the humanities.
Language complexity is a topic in linguistics which can be divided into several sub-topics such as phonological, morphological, syntactic, and semantic complexity. The subject also carries importance for language evolution.
Dialect levelling or leveling is the process of an overall reduction in the variation or diversity of features between two or more dialects. Typically, this comes about through assimilation, mixture, and merging of certain dialects, often by language standardization. It has been observed in most languages with large numbers of speakers after industrialisation and modernisation of the areas in which they are spoken.
References
- 1 2 Aitchison, Jean, 1938- (2013). Language change : progress or decay? (4th ed.). Oxford: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-107-02362-8. OCLC 799025044.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - 1 2 Trudgill, Peter. (2000). Sociolinguistics : an introduction to language and society (4th ed.). London: Penguin. ISBN 0-14-028921-6. OCLC 43880055.
- 1 2 Siegel, Jason (2010). "Decreolization: A critical review". IULC Working Papers. 10 (3). ISSN 1524-2110.
- ↑ Degraff, Michel (2005). "Linguists' most dangerous myth: The fallacy of Creole Exceptionalism". Language in Society. 34 (4). doi:10.1017/S0047404505050207. ISSN 0047-4045.
- ↑ Russell, Eric (2015). "Competences in contact: Phonology and lexifier targeted change". Journal of Pidgin and Creole Languages. 30 (1): 116–141. doi:10.1075/jpcl.30.1.04rus. ISSN 0920-9034.
- ↑ Mayeux, Oliver (2019-07-19). Rethinking decreolization: Language contact and change in Louisiana Creole (PhD thesis). University of Cambridge. doi:10.17863/cam.41629.