
Email is a method of transmitting and receiving messages using electronic devices. It was conceived in the late–20th century as the digital version of, or counterpart to, mail. Email is a ubiquitous and very widely used communication medium; in current use, an email address is often treated as a basic and necessary part of many processes in business, commerce, government, education, entertainment, and other spheres of daily life in most countries.
A mail exchanger record specifies the mail server responsible for accepting email messages on behalf of a domain name. It is a resource record in the Domain Name System (DNS). It is possible to configure several MX records, typically pointing to an array of mail servers for load balancing and redundancy.
An email address identifies an email box to which messages are delivered. While early messaging systems used a variety of formats for addressing, today, email addresses follow a set of specific rules originally standardized by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in the 1980s, and updated by RFC 5322 and 6854. The term email address in this article refers to just the addr-spec in Section 3.4 of RFC 5322. The RFC defines address more broadly as either a mailbox or group. A mailbox value can be either a name-addr, which contains a display-name and addr-spec, or the more common addr-spec alone.
Various anti-spam techniques are used to prevent email spam.

Email spam, also referred to as junk email, spam mail, or simply spam, is unsolicited messages sent in bulk by email (spamming). The name comes from a Monty Python sketch in which the name of the canned pork product Spam is ubiquitous, unavoidable, and repetitive. Email spam has steadily grown since the early 1990s, and by 2014 was estimated to account for around 90% of total email traffic.
Address munging is the practice of disguising an e-mail address to prevent it from being automatically collected by unsolicited bulk e-mail providers. Address munging is intended to disguise an e-mail address in a way that prevents computer software from seeing the real address, or even any address at all, but still allows a human reader to reconstruct the original and contact the author: an email address such as, "no-one@example.com", becomes "no-one at example dot com", for instance.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is an email authentication method which ensures the sending mail server is authorized to originate mail from the email sender's domain. This authentication only applies to the email sender listed in the "envelope from" field during the initial SMTP connection. If the email is bounced, a message is sent to this address, and for downstream transmission it typically appears in the "Return-Path" header. To authenticate the email address which is actually visible to recipients on the "From:" line, other technologies such as DMARC must be used. Forgery of this address is known as email spoofing, and is often used in phishing and email spam.
Hashcash is a proof-of-work system used to limit email spam and denial-of-service attacks. Hashcash was proposed in 1997 by Adam Back and described more formally in Back's 2002 paper "Hashcash – A Denial of Service Counter-Measure". In Hashcash the client has to concatenate a random number with a string several times and hash this new string. It then has to do so over and over until a hash beginning with a certain number of zeros is found.
A Joe job is a spamming technique that sends out unsolicited e-mails using spoofed sender data. Early Joe jobs aimed at tarnishing the reputation of the apparent sender or inducing the recipients to take action against them, but they are now typically used by commercial spammers to conceal the true origin of their messages and to trick recipients into opening emails apparently coming from a trusted source.
A bounce message or just "bounce" is an automated message from an email system, informing the sender of a previous message that the message has not been delivered. The original message is said to have "bounced".
Email authentication, or validation, is a collection of techniques aimed at providing verifiable information about the origin of email messages by validating the domain ownership of any message transfer agents (MTA) who participated in transferring and possibly modifying a message.
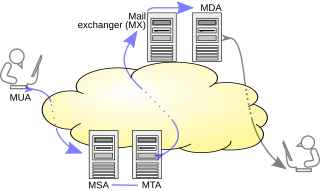
A message submission agent (MSA), or mail submission agent, is a computer program or software agent that receives electronic mail messages from a mail user agent (MUA) and cooperates with a mail transfer agent (MTA) for delivery of the mail. It uses ESMTP, a variant of the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), as specified in RFC 6409.
Disposable email addressing, also known as DEA, dark mail or masked email, refers to an approach that involves using a unique email address for each contact or entity, or using it for a limited number of times or uses. The benefit to the owner is that if anyone compromises the address or utilizes it in connection with email abuse, the address owner can easily cancel it without affecting any of their other contacts.
Email harvesting or scraping is the process of obtaining lists of email addresses using various methods. Typically these are then used for bulk email or spam.
Email spoofing is the creation of email messages with a forged sender address. The term applies to email purporting to be from an address which is not actually the sender's; mail sent in reply to that address may bounce or be delivered to an unrelated party whose identity has been faked. Disposable email address or "masked" email is a different topic, providing a masked email address that is not the user's normal address, which is not disclosed, but forwards mail sent to it to the user's real address.
A challenge–response system is a type of that automatically sends a reply with a challenge to the (alleged) sender of an incoming e-mail. It was originally designed in 1997 by Stan Weatherby, and was called Email Verification. In this reply, the purported sender is asked to perform some action to assure delivery of the original message, which would otherwise not be delivered. The action to perform typically takes relatively little effort to do once, but great effort to perform in large numbers. This effectively filters out spammers. Challenge–response systems only need to send challenges to unknown senders. Senders that have previously performed the challenging action, or who have previously been sent e-mail(s) to, would be automatically receive a challenge.
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is an email authentication method designed to detect forged sender addresses in email, a technique often used in phishing and email spam.
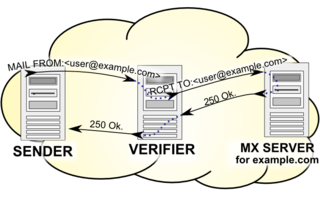
Callback verification, also known as callout verification or Sender Address Verification, is a technique used by SMTP software in order to validate e-mail addresses. The most common target of verification is the sender address from the message envelope. It is mostly used as an anti-spam measure.
Backscatter is incorrectly automated bounce messages sent by mail servers, typically as a side effect of incoming spam.
A cold email is an unsolicited e-mail that is sent to a receiver without prior contact. It could also be defined as the email equivalent of cold calling. Cold emailing is a subset of email marketing and differs from transactional and warm emailing.



