Related Research Articles

Climate change mitigation (or decarbonisation) is action to limit the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that cause climate change. Climate change mitigation actions include conserving energy and replacing fossil fuels with clean energy sources. Secondary mitigation strategies include changes to land use and removing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. Current climate change mitigation policies are insufficient as they would still result in global warming of about 2.7 °C by 2100, significantly above the 2015 Paris Agreement's goal of limiting global warming to below 2 °C.

A carbon footprint (or greenhouse gas footprint) is a calculated value or index that makes it possible to compare the total amount of greenhouse gases that an activity, product, company or country adds to the atmosphere. Carbon footprints are usually reported in tonnes of emissions (CO2-equivalent) per unit of comparison. Such units can be for example tonnes CO2-eq per year, per kilogram of protein for consumption, per kilometer travelled, per piece of clothing and so forth. A product's carbon footprint includes the emissions for the entire life cycle. These run from the production along the supply chain to its final consumption and disposal.
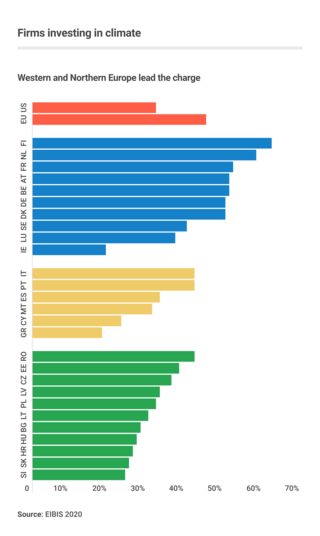
Business action on climate change is a topic which since 2000 includes a range of activities relating to climate change, and to influencing political decisions on climate change-related regulation, such as the Kyoto Protocol. Major multinationals have played and to some extent continue to play a significant role in the politics of climate change, especially in the United States, through lobbying of government and funding of climate change deniers. Business also plays a key role in the mitigation of climate change, through decisions to invest in researching and implementing new energy technologies and energy efficiency measures.
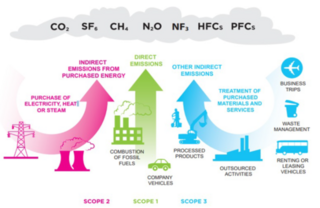
Carbon accounting is a framework of methods to measure and track how much greenhouse gas (GHG) an organization emits. It can also be used to track projects or actions to reduce emissions in sectors such as forestry or renewable energy. Corporations, cities and other groups use these techniques to help limit climate change. Organizations will often set an emissions baseline, create targets for reducing emissions, and track progress towards them. The accounting methods enable them to do this in a more consistent and transparent manner.

A low-carbon economy (LCE) is an economy which absorbs as much greenhouse gas as it emits. Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions due to human activity are the dominant cause of observed climate change since the mid-20th century. There are many proven approaches for moving to a low-carbon economy, such as encouraging renewable energy transition, energy conservation, and electrification of transportation. An example are zero-carbon cities.

Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide, from burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate change. The largest annual emissions are from China followed by the United States. The United States has higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 GtC, of which 484±20 GtC from fossil fuels and industry, and 219±60 GtC from land use change. Land-use change, such as deforestation, caused about 31% of cumulative emissions over 1870–2022, coal 32%, oil 24%, and gas 10%.

The United States produced 5.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2020, the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person. In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GHG, followed by the United States with 11%, then India with 6.6%. In total the United States has emitted a quarter of world GHG, more than any other country. Annual emissions are over 15 tons per person and, amongst the top eight emitters, is the highest country by greenhouse gas emissions per person.

China is both the world's largest energy consumer and the largest industrial country, and ensuring adequate energy supply to sustain economic growth has been a core concern of the Chinese Government since the founding of the People's Republic of China in 1949. Since the country's industrialization in the 1960s, China is currently the world's largest emitter of greenhouse gases, and coal in China is a major cause of global warming. China is also the world's largest renewable energy producer, and the largest producer of hydroelectricity, solar power and wind power in the world. The energy policy of China is connected to its industrial policy, where the goals of China's industrial production dictate its energy demand managements.
The climate policy of China has a massive impact on global climate change, as China is the largest emitter of greenhouse gases in the world. Chinese plans to abide by carbon emission reduction goals involves peaking greenhouse gas emissions before 2030, and achieving carbon neutrality before 2060. Due to the buildup of solar power and the burning of coal, Chinese energy policy is closely related to its climate policy. There is also policy to adapt to climate change. Ding Xuexiang represented China at the 2023 United Nations Climate Change Conference in 2023, and may be influential in setting climate policy.

Climate change has received significant scientific, public and political attention in Sweden. In 1896, Swedish chemist Svante Arrhenius was the first scientist to quantify global heating. Sweden has a high energy consumtion per capita, but reducing the dependency on fossil energy has been on the agenda of cabinets of the Governments of Sweden since the 1970s oil crises. In 2014 and 2016, Sweden was ranked #1 in the Global Green Economy Index (GGEI), because the Swedish economy produces relatively low emissions. Sweden has had one of the highest usages of biofuel in Europe and aims at prohibiting new sales of fossil-cars, including hybrid cars, by 2035, and for an energy supply system with zero net atmospheric greenhouse gas emissions by 2045.

Climate change has resulted in an increase in temperature of 2.3 °C (4.14 °F) (2022) in Europe compared to pre-industrial levels. Europe is the fastest warming continent in the world. Europe's climate is getting warmer due to anthropogenic activity. According to international climate experts, global temperature rise should not exceed 2 °C to prevent the most dangerous consequences of climate change; without reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, this could happen before 2050. Climate change has implications for all regions of Europe, with the extent and nature of impacts varying across the continent.

The Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI) is a scoring system designed by the German environmental and development organisation Germanwatch e.V. to enhance transparency in international climate politics. On the basis of standardised criteria, the index evaluates and compares the climate protection performance of 63 countries and the European Union (EU), which are together responsible for more than 90% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.

Climate change is expected to significantly impact Morocco on multiple dimensions, similar to other countries in the Middle East and North Africa region. As a coastal country with hot and arid climates, environmental impacts from climate change are likely to be wide and varied. Analysis of these environmental changes on the economy of Morocco are expected to create challenges at all levels of the economy. The main effects will be felt in the agricultural systems and fisheries which employ half of the population, and account for 14% of GDP. In addition, because 60% of the population and most of the industrial activity are on the coast, sea level rise is a major threat to key economic forces. Morocco’s average temperatures have increased by 0.2 °C per decade since the 1960s. Morocco is particularly susceptible to heat waves, droughts and floods.

Iran is among the most vulnerable countries to climate change in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA). Iran contributes to about 1.8% of global greenhouse gas emissions (GHG), and is ranked 8th in greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) world wide and is ranked first in the MENA region due to its reliance on oil and natural gas. Climate change has led to reduced precipitation as well as increased temperatures, with Iran holding the hottest temperature recorded in Asia.

Niklas Höhne is a German scientist in the field of national and international climate policy and mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions. He is founder of the NewClimate Institute in Cologne, Germany and professor at Wageningen University.

Climate-smart agriculture (CSA) is a set of farming methods that has three main objectives with regards to climate change. Firstly, they use adaptation methods to respond to the effects of climate change on agriculture. Secondly, they aim to increase agricultural productivity and to ensure food security for a growing world population. Thirdly, they try to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture as much as possible. Climate-smart agriculture works as an integrated approach to managing land. This approach helps farmers to adapt their agricultural methods to the effects of climate change.

India was ranked seventh among the list of countries most affected by climate change in 2019. India emits about 3 gigatonnes (Gt) CO2eq of greenhouse gases each year; about two and a half tons per person, which is less than the world average. The country emits 7% of global emissions, despite having 17% of the world population. The climate change performance index of India ranks eighth among 63 countries which account for 92% of all GHG emissions in the year 2021.
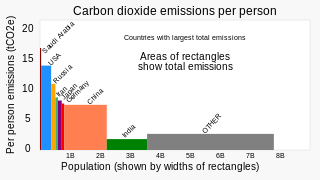
China's total greenhouse gas emissions are the world's highest, accounting for 35% of the world's total according to the International Energy Agency. The country's per capita greenhouse gas emissions are the 34th highest of any country, as of 2023.

A climate target, climate goal or climate pledge is a measurable long-term commitment for climate policy and energy policy with the aim of limiting the climate change. Researchers within, among others, the UN climate panel have identified probable consequences of global warming for people and nature at different levels of warming. Based on this, politicians in a large number of countries have agreed on temperature targets for warming, which is the basis for scientifically calculated carbon budgets and ways to achieve these targets. This in turn forms the basis for politically decided global and national emission targets for greenhouse gases, targets for fossil-free energy production and efficient energy use, and for the extent of planned measures for climate change mitigation and adaptation.

Climate change in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) refers to changes in the climate of the MENA region and the subsequent response, adaption and mitigation strategies of countries in the region. In 2018, the MENA region emitted 3.2 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide and produced 8.7% of global greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) despite making up only 6% of the global population. These emissions are mostly from the energy sector, an integral component of many Middle Eastern and North African economies due to the extensive oil and natural gas reserves that are found within the region. The region of Middle East is one of the most vulnerable to climate change. The impacts include increase in drought conditions, aridity, heatwaves and sea level rise.
References
- ↑ "India seventh on index of countries impacted by climate change in 2019". The Indian Express. 26 January 2021. Retrieved 15 September 2022.
- ↑ "Unser Leitbild | Germanwatch e.V." www.germanwatch.org (in German). 7 July 2006. Retrieved 2022-04-28.
- ↑ Dahmer, Laura (23 September 2021). "Christoph Bals". Tagesspiegel Background Sustainable Finance.
- ↑ Hellman, Rachel. "U.S. Lags in Latest Climate Protection Rankings" . Retrieved 7 September 2022.
Developed by Germanwatch, NewClimate Institute and the Climate Action Network, the CCPI is an independent monitoring tool for tracking countries' climate protection performance.
- ↑ Martin, Sarah (11 December 2019). "Australia ranked worst of 57 countries on climate change policy". The Guardian. Retrieved 2 September 2022.
- ↑ "Egypt advances 20 places in Climate Policy category at Climate Change Performance Index 2022". Egypt Independent . 6 December 2021. Retrieved 15 September 2022.
- ↑ Doyle, Michael (9 November 2021). "Australia's climate policy dead last in latest Climate Change Performance Index". ABC News . Retrieved 2 September 2022.
- 1 2 "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-05-08. Retrieved 2019-05-08.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ Qayyah, Moynihan; Chisato, Goya. "These are the 17 countries that have done the most to limit global warming since 2017". Business Insider. Retrieved 4 September 2022.
The total scores took into account respective countries' efforts in terms of greenhouse gas emissions (40% of the final score), renewable energy (20%), energy consumption (20%) and climate policies implemented (20%).
- ↑ "Methodology". Climate Change Performance Index. 2017-10-16. Retrieved 2019-05-08.
- ↑ "About". Climate Change Performance Index. 2017-10-16. Retrieved 2019-05-08.
- ↑ "Climate Change Performance Index". Climate Change Performance Index. Retrieved 2019-05-08.
- ↑ "Pakistan over-punished for climate change: Joudat Ayaz". Latest News - The Nation. Retrieved 31 August 2022.
- ↑ "Global Climate Risk Index". germanwatch.org. Retrieved 2020-09-07.
- ↑ Footer, Mark (24 October 2021). "COP26: how climate crisis affects tourism – Asian destinations at risk". South China Morning Post . Retrieved 7 September 2022.
- ↑ "Haiti Tops Index of Nations Worst-hit by Extreme Weather in 2016". VOA . Retrieved 7 September 2022.
The index does not take into account slow-onset climate risks such as rising sea levels or melting glaciers.
- ↑ Zimmermann, Nils (9 November 2016). "Strong German climate policy needed in wake of Trump victory". Deutsche Welle. Bonn and Berlin, Germany. Retrieved 2016-11-10.