Related Research Articles

Eswatini, officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and also known by its former official name Swaziland and formerly the Kingdom of Swaziland, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its north, west, south, and southeast. At no more than 200 km (120 mi) north to south and 130 km (81 mi) east to west, Eswatini is one of the smallest countries in Africa; despite this, its climate and topography are diverse, ranging from a cool and mountainous highveld to a hot and dry lowveld.

Demographic features of the population of Eswatini include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

Artifacts indicating human activity dating back to the early Stone Age have been found in the Kingdom of Eswatini. The earliest known inhabitants of the region were Khoisan hunter-gatherers. Later, the population became predominantly Nguni during and after the great Bantu migrations. People speaking languages ancestral to the current Sotho and Nguni languages began settling no later than the 11th century. The country now derives its name from a later king named Mswati II. Mswati II was the greatest of the fighting kings of Eswatini, and he greatly extended the area of the country to twice its current size. The people of Eswatini largely belong to a number of clans that can be categorized as Emakhandzambili, Bemdzabu, and Emafikamuva, depending on when and how they settled in Eswatini.
SothoSesotho, also known as Southern Sotho or Sesotho sa Borwa is a Southern Bantu language of the Sotho–Tswana ("S.30") group, spoken in Lesotho, and South Africa where it is an official language;

Swazi or siSwati is a Bantu language of the Nguni group spoken in Eswatini and South Africa by the Swati people. The number of speakers is estimated to be in the region of 4.7 million including first and second language speakers. The language is taught in Eswatini and some South African schools in Mpumalanga, particularly former KaNgwane areas. Siswati is an official language of Eswatini, and is also one of the twelve official languages of South Africa.

The lilangeni is the currency of Eswatini and is subdivided into 100 cents. It is issued by the Central Bank of Eswatini and is authorised by the king and his family. The South African rand is also accepted in Eswatini. Similar to the Lesotho loti, there are singular and plural abbreviations, namely L and E, so where one might have an amount L1, it would be E2, E3, or E4.

The Swazi or Swati are a Bantu ethnic group native to Southern Africa, inhabiting Eswatini, a sovereign kingdom in Southern Africa, and South Africa's Mpumalanga province. EmaSwati are part of the Nguni-language speaking peoples whose origins can be traced through archaeology to East Africa where similar traditions, beliefs and cultural practices are found.

At least thirty-five languages are spoken in South Africa, twelve of which are official languages of South Africa: Ndebele, Pedi, Sotho, South African Sign Language, Swazi, Tsonga, Tswana, Venda, Afrikaans, Xhosa, Zulu and English, which is the primary language used in parliamentary and state discourse, though all official languages are equal in legal status. In addition, South African Sign Language was recognised as the twelfth official language of South Africa by the National Assembly on 3 May 2023. Unofficial languages are protected under the Constitution of South Africa, though few are mentioned by any name.
Phuthi (Síphùthì) is a Nguni Bantu language spoken in southern Lesotho and areas in South Africa adjacent to the same border. The closest substantial living relative of Phuthi is Swati, spoken in Eswatini and the Mpumalanga province of South Africa. Although there is no contemporary sociocultural or political contact, Phuthi is linguistically part of a historic dialect continuum with Swati. Phuthi is heavily influenced by the surrounding Sesotho and Xhosa languages, but retains a distinct core of lexicon and grammar not found in either Xhosa or Sesotho, and found only partly in Swati to the north.

Lobamba is a city in Eswatini, and is one of the two capitals, serving as the legislative, traditional, spiritual, seat of government of the Parliament of Eswatini, and Ludzidzini Royal Village, the residence of Queen Ntfombi, the Queen Mother.

The House of Dlamini is the royal house of the Kingdom of Eswatini. Mswati III, as king and Ngwenyama of Eswatini, is the current head of the house of Dlamini. Swazi kings up to the present day are referred to as Ingwenyama and they rule together with the Queen Mother who is called Indlovukati. The Swazi kings, like other Nguni nations, practice polygamy and thus have many wives and children.
Lubuli is a town in southeastern Eswatini (Swaziland). It is located close to the South African border just to the northwest of the town of Nsoko on the road between there and Maloma.
Matsapha is a town in central Eswatini. The Matsapha urban boundary is defined in the Urban Government Act of 1969, as amended in 2012, and covers an area of approximately 2,000 hectares. Matsapha was established as an industrial park in 1965 and was officially gazetted as an urban area in 1969. Matsapha is located in the Upper Middleveld of Eswatini in the Manzini region, which is in the centre of the country. Matsapha is 11 km (7 mi) from the city of Manzini, the country's commercial capital, and 35 km (22 mi) from Mbabane, the administrative capital of the country. It is well located as it is on Eswatini's main east–west axis between South Africa and Mozambique, 16 km (10 mi) from the junction of the Lavumisa road that leads to Durban and KwaZulu Natal. It lies at an altitude of 625 m (2,051 ft) above sea level.
The Southern Bantu languages are a large group of Bantu languages, largely validated in Janson (1991/92). They are nearly synonymous with Guthrie's Bantu zone S, apart from the exclusion of Shona and the inclusion of Makhuwa. They include all of the major Bantu languages of South Africa, Botswana, Lesotho, Eswatini, and Mozambique, with outliers such as Lozi in Zambia and Namibia, and Ngoni in Zambia, Tanzania and Malawi.

Hlane Royal National Park is a national park in Eswatini, roughly 67 km northeast of Manzini along the MR3 road. Prior to being designated a public park, it was a private royal hunting ground. Hlane, meaning 'wilderness', was named by King Sobhuza II. It is now held in trust for the nation by His Majesty King Mswati III, and is managed by Big Game Parks, a privately owned body.

Lesotho, a country in Southern Africa, is home to several languages, including Phuthi, Sesotho, Xhosa, Zulu and English, — all, except for English, belong to the Niger–Congo language family.

Eswatini–South Africa relations refers to the current and historical relationship between Eswatini and South Africa. South Africa surrounds Eswatini on the north, west and south. The two states share strong historical and cultural ties. Mutual High Commissions were established in Pretoria and Mbabane at the end of the apartheid era in 1994. Eswatini's High Commission in Pretoria is also cross-accredited to Botswana, Lesotho, Namibia, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
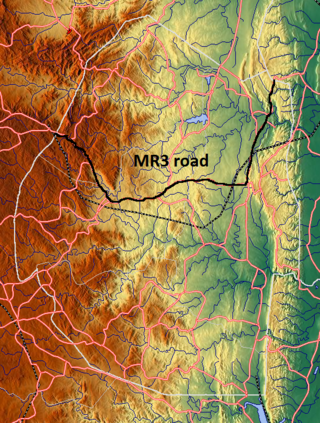
The MR3 road, also known as the Matsapha–Mbabane–Ngwenya road or Road No. MR3, is a major highway of Eswatini. It is one of the busiest roads in the country, crossing it from east to west. Along with the MR7 and MR8 roads, it forms the "backbone of Swaziland's internal transport system." It connects the EN5 road in Mozambique near Namaacha at 25°59′21″S31°59′53″E to the N17 road in South Africa at 26°12′45″S30°59′18″E, near Ngwenya. The road passes through Hlane Royal National Park and through the capital of Mbabane, about 110 kilometres (68 mi) further to the southwest. The highway descends into the Ezulwini Valley in four lanes. At Manzini, a bridge crosses the Mzimene River.
Ezulwini Valley is a valley of northwest Eswatini. Also known as "The Valley of Heaven", the valley lasts for about 30 kilometres, and is bounded to the east by the Mdzimba hills. The historical capital of Eswatini Lobamba is located in the valley, also known as the Royal Valley, a place of many legends of Swazi history. The main highway is the MR3 road; some parts have four lanes. The valley extends as far down as Kwaluseni. The valley contains a number of notable wildlife sanctuaries and features including the 4,500-hectare Mlilwane Wildlife Sanctuary and the Royal Swazi Sun Hotel. The valley is undergoing significant development with the growth of Tourism in Eswatini, with the building of casinos, bars, hotels, shops such as the Gables Shopping Centre and urbanization. Also of note is the Ezulwini Handicrafts Centre and Swazi National Museum in Lobamba. Despite the urban developments in the valley, the landscape still has some "soft green hills and plains-game grazing in the lush lands below."
Bhaca, or IsiBhaca (Baca) is a Bantu language of South Africa. Traditionally considered a dialect of Swati, it is closer to Xhosa, Phuthi and Zulu. It is spoken southeast of Lesotho, where Sotho, Xhosa and Zulu meet, mainly around Mount Frere, Mzimkhulu, and to a lesser extent in Mount Ayliff, Matatiele, Harding, Bulwer, Underberg, Highflats, Umzinto, Umzumbe and Ixopo.
References
- Austin, P., ed. (2008). One thousand languages: living, endangered, and lost. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 9780520255609.
- Dalby, A. (1998). Dictionary of Languages: The Definitive Reference to More Than 400 Languages. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 9780231115698.
- Fitzpatrick, M. (2004). South Africa, Lesotho & Swaziland. Lonely Planet Travel Guides Series. ISBN 9781741041620.
- Fitzpatrick, M. (2006). South Africa, Lesotho & Swaziland. Lonely Planet Travel Guides Series. ISBN 9781740599702.
- Kanduza, A. M.; et al., eds. (2003). Issues in the economy and politics of Swaziland since 1968. OSSREA.
- Simons, G. F.; et al., eds. (2018). Ethnologue: Languages of the World (21st ed.). Dallas: SIL International.
- Stokes, J., ed. (2009). Encyclopedia of the Peoples of Africa and the Middle East. New York: Infobase Publishing. ISBN 9780816071586.
