Transportation in Malaysia started to develop during British colonial rule, and the country's transport network is now diverse and developed. Malaysia's road network is extensive, covering 144,403 kilometres, including 1,821 km of expressways. The main highway of the country extends over 800 km, reaching the Thai border from Singapore. Peninsular Malaysia has an extensive road network, whilst the road system in East Malaysia is not as well-developed. The main modes of transport in Peninsular Malaysia include buses, trains, cars and to an extent, commercial travel on aeroplanes.
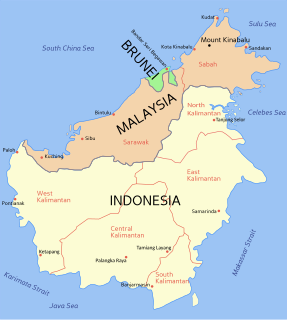
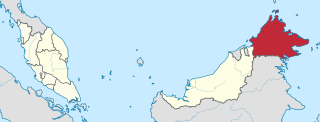
East Malaysia, also known as Sabah, Sarawak and Labuan or Malaysian Borneo, is the part of Malaysia on the island of Borneo, the world's third largest island. It consists of the Malaysian states of Sabah, closer to the Philippines than the west of the country, Sarawak in the west and the Federal Territory of Labuan. Labuan is an island in its small archipelago of the same name due north of Brunei; its closest land mass is with Sabah. It lies to the east of Peninsular Malaysia, the part of the country on the Malay Peninsula. The two are separated by the South China Sea.

Labuan, officially the Federal Territory of Labuan, is a federal territory of Malaysia. It is made up of the eponymous Labuan Island and six smaller islands, and is located off the coast of the state of Sabah in East Malaysia. Labuan's capital is Victoria and is best known as an offshore financial centre offering international financial and business services via Labuan IBFC since 1990 as well as being an offshore support hub for deepwater oil and gas activities in the region. It is also a tourist destination for people travelling through Sabah, nearby Bruneians and scuba divers. The name Labuan derives from the Malay word labuhan which means harbour. Labuan is often referred to as the pearl of Borneo.

Miri is a coastal city in northeastern Sarawak, Malaysia, located near the border of Brunei, on the island of Borneo. The city covers an area of 997.43 square kilometres (385.11 sq mi), located 798 kilometres (496 mi) northeast of Kuching and 329 kilometres (204 mi) southwest of Kota Kinabalu. Miri is the second largest city in Sarawak, with a population of 358,020 as of 2016. The city is also the capital of Miri District of the Miri Division.

PETRONAS, short for Petroliam Nasional Berhad, is a Malaysian oil and gas company that was founded on 17 August 1974. Wholly owned by the Government of Malaysia, the corporation is vested with the entire oil and gas resources in Malaysia and is entrusted with the responsibility of developing and adding value to these resources. Petronas is ranked among Fortune Global 500's largest corporations in the world. Fortune ranks Petronas as the 75th largest company in the world in 2013. Fortune also ranks Petronas as the 12th most profitable company in the world and the most profitable in Asia.
Pengerang is a mukim and a new municipal area in Kota Tinggi District, southeastern Johor, Malaysia. It is also known as a small custom cum immigration post. It is separated from Pulau Tekong and Changi Airport, Singapore by the Tebrau Straits.

Sultan Ismail Petra Airport is an airport that operates in Kota Bharu, a city in the state of Kelantan in Malaysia. The airport is named after Ismail Petra of Kelantan, the twenty eight Sultan of Kelantan, who ruled from 1979 to 2010. The present new terminal was officially opened in September 2002. The 12,000 m² airport terminal has three aircraft stands, three aerobridges and is able to handle maximum capacity 1.45 million passengers. The airport consists of 9 check-in counters and offers flights between a total of 7 domestic destinations from Malaysia Airlines, AirAsia, Firefly, and Malindo Air. In 2014, this made it the busiest airport in the East Coast.

Sabah Electricity Sdn. Bhd. (SESB) is an electrical company that generates, transmits and distributes electricity mainly in Sabah and Federal Territory of Labuan. It supplies electrical power to 413,983 customers distributed over a wide area of 74,000 km2. 82.8% of the customers are domestic customers consuming only 28.8% of the power generated. This company employs more than 2,300 employees and the main stakeholders of this company are Tenaga Nasional Berhad (TNB) (80%) and Sabah State Government (20%).

MMC Corporation Berhad is a leading utilities and infrastructure group of Malaysia, with diversified businesses under three divisions: energy and utilities, ports and logistics, and engineering and construction.
Malaysia LNG (MLNG) is a liquefied natural gas manufacturer in Malaysia. In 2007, it was the largest LNG manufacturing complex.
The border between Brunei and Malaysia consist of a 481.3 km land border and substantial lengths of maritime borders stretching from the coastline of the two countries to the edge of the continental shelf in the South China Sea.
The energy policy of Malaysia is determined by the Malaysian Government, which address issues of energy production, distribution, and consumption. The Department of Electricity and Gas Supply acts as the regulator while other players in the energy sector include energy supply and service companies, research and development institutions and consumers. Government-linked companies Petronas and Tenaga Nasional Berhad are major players in Malaysia's energy sector.
Sabah Gas Industries Sdn Bhd was a state owned holding company based in Labuan, Malaysia. It was established in 1982 by the Government of Sabah for the downstream operations of Sabah natural gas resources. The company owned and operated a 660,000-tonne per year methanol plant, a 600,000-tonne per year sponge iron factory, and a 79 MW natural gas-fired power station, all commissioned in 1984 after the gas pipeline from the offshore gas fields became operational. The industries were supplied by natural gas from the Erb West and Samarang offshore fields. In the beginning of the 1990s, due to financial difficulties, the company was put for privatisation. In 1992, the methanol plant was sold to Petronas and operates today as Petronas Methanol (Labuan) Sdn Bhd. The power station was sold to Sabah Electricity. The sponge iron factory was bought by the affiliated companies of the today's Lion Group. The plant operates today as Antara Steel Mills Sdn Bhd.
Floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) refers to water-based liquefied natural gas (LNG) operations employing technologies designed to enable the development of offshore natural gas resources. Floating above an offshore natural gas field, the FLNG facility produces, liquefies, stores and transfers LNG at sea before carriers ship it directly to markets. The world's first completed FLNG production facility is the PFLNG Satu located in Kanowit gas field off the shore of Sarawak in Malaysia. Petronas is the owner of the platform and first cargo was loaded onto the 150,200-cbm Seri Camellia LNG carrier on 03 April 2017. Multiple other FLNG facilities are in development. Another FLNG facility, developed by Exmar NV using Black & Veatch PRICO(R) technology, passed performance test in October 2016 in Nantong, China. Fortuna FLNG, to be commissioned in 2020, owned by a joint-venture between Ophir Energy and Golar LNG is still under development in Equatorial Guinea, the US$2 billion vessel would be the first to produce its gas in Africa. The agreement between Equatorial Guinea and state-owned GEPetrol, Ophir and OneLNG reconfirms GEPetrol’s participation rights as partners in 20 per cent of the FLNG project.

Sarawak Energy Berhad (SEB) is the Malaysian energy company based in Kuching, Sarawak. The company responsible for the generation, transmission and distribution of electricity for the state of Sarawak in Malaysia. It is wholly owned by the State Government of Sarawak.
Koreans in Malaysia numbered 12,690 individuals as of 2015, making them the 22nd-largest community of overseas Koreans, and the 5th-largest in Southeast Asia.
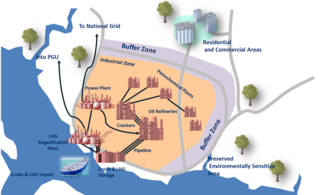
Pengerang Integrated Petroleum Complex (PIPC) is a megaproject development in Pengerang, Kota Tinggi District, Johor, Malaysia. It spans over an area of 80 km2 and will house oil refineries, naphtha crackers, petrochemical plants, liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminals and a regasification plant upon completion.
Sabah–Sarawak Gas Pipeline (SSGP) is a 500 kilometre Malaysian natural gas pipeline that linked Kimanis in Sabah to Bintulu in Sarawak. The pipeline is part of the Petronas development project of "Sabah–Sarawak Integrated Oil and Gas Project", and has start operating since early 2014.
Petroleum Sarawak Berhad (PETROS) is a state-owned oil and gas exploration firm established and owned by the State Government of Sarawak.