
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery to end users or its storage.
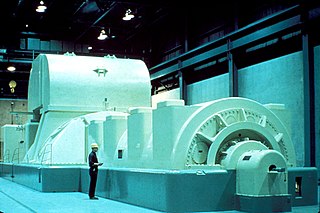
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motion-based power or fuel-based power into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines, wind turbines and even hand cranks. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. Generators provide nearly all the power for electrical grids.

Alstom is a French multinational rolling stock manufacturer which operates worldwide in rail transport markets. It is active in the fields of passenger transportation, signaling, and locomotives, producing high-speed, suburban, regional and urban trains along with trams.

Siemens AG is a German multinational technology conglomerate. Its operations encompass automation and digitalization in the process and manufacturing industries, intelligent infrastructure for buildings and distributed energy systems, rail transport solutions, as well as health technology and digital healthcare services. Siemens is the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe, and holds the position of global market leader in industrial automation and industrial software.

A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electrical grid.

The Westinghouse Electric Corporation was an American manufacturing company founded in 1886 by George Westinghouse. It was originally named "Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company" and was renamed "Westinghouse Electric Corporation" in 1945. The company acquired the CBS television network in 1995 and was renamed "CBS Corporation" until being acquired by Viacom in 1999, a merger completed in April 2000. The CBS Corporation name was later reused for one of the two companies resulting from the split of Viacom in 2005.
Distributed generation, also distributed energy, on-site generation (OSG), or district/decentralized energy, is electrical generation and storage performed by a variety of small, grid-connected or distribution system-connected devices referred to as distributed energy resources (DER).

The Electricity Supply Board is a state owned electricity company operating in the Republic of Ireland. While historically a monopoly, the ESB now operates as a commercial semi-state concern in a "liberalised" and competitive market. It is a statutory corporation whose members are appointed by the government of Ireland.

Ansaldo Energia S.p.A. is an Italian power engineering company. It is based in Genoa, Italy. The absorbed parent company, Gio. Ansaldo & C., was started in 1853. It was taken over by Leonardo S.p.A. In 2011, Leonardo S.p.A. sold a 45% stake in Ansaldo Energia to First Reserve Corporation. In 2013, Fondo Strategico Italiano acquired an 85% share of the company. It then sold a 40% share to Shanghai Electric Corporation.
Subsea technology involves fully submerged ocean equipment, operations, or applications, especially when some distance offshore, in deep ocean waters, or on the seabed. The term subsea is frequently used in connection with oceanography, marine or ocean engineering, ocean exploration, remotely operated vehicle (ROVs) autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), submarine communications or power cables, seafloor mineral mining, oil and gas, and offshore wind power.

Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy S.A., formerly Gamesa Corporación Tecnológica S.A. and Grupo Auxiliar Metalúrgico S.A., is a Spanish-German wind engineering company based in Zamudio, Biscay, Spain. In Spain, the company has two other main sites one in Madrid and the other one in Sarriguren (Navarre). The Services Commercial Office is located in the Parque de la Innovación de Navarra in Sarriguren. It manufactures wind turbines and provides onshore and offshore wind services. It is the world's second largest wind turbine manufacturer.

MAPNA Group is a group of Iranian companies involved in development and execution of thermal and renewable power plants, oil & gas, railway transportation and other industrial projects as well as manufacturing main equipment including gas and steam turbines, electrical generator, turbine blade and vane, HRSG and conventional boilers, electric and control systems, gas compressor, locomotive and other pertinent equipment.
The electricity sector in Argentina constitutes the third largest power market in Latin America. It relies mostly on thermal generation and hydropower generation (36%). The prevailing natural gas-fired thermal generation is at risk due to the uncertainty about future gas supply.
Shanghai Electric is a Chinese multinational power generation and electrical equipment manufacturing company headquartered in Shanghai. The company traces its roots to 1880.

The Burbo Bank Offshore Wind Farm is a 348 MW offshore wind farm located on the Burbo Flats in Liverpool Bay on the west coast of the UK in the Irish Sea. It consists of an original 90 MW wind farm commissioned in 2007 and a 258 MW extension completed in 2017.

GE Power is an American energy technology company, owned by General Electric.

Electricity sector in Hong Kong ranges from generation, transmission, distribution and sales of electricity covering Hong Kong. The combustion of coal, natural gas and oil are the main sources of electricity in Hong Kong. The electricity sector contributes 60.4% of Hong Kong's total greenhouse gas emissions.

EuroAfrica Interconnector is a planned HVDC interconnector and submarine power cable between the Greek, Cypriot, and Egypt power grids. The Interconnector is an energy highway bridging Africa and Europe. It will have a capacity to transmit 2,000 megawatts of electricity in either direction. Annual transmission capacity will be rated at 17.5 TWh, much more than the annual production at the Aswan Dam power stations. President of Egypt Abdel Fattah el-Sisi, President of Cyprus Nicos Anastasiades and Prime Minister of Greece Kyriakos Mitsotakis, issued a joint declaration at the conclusion of the 7th Trilateral Summit, held in Cairo on October 8, 2019, in which they expressed their desire to continue strengthening their cooperation in matters of energy. In particular, the joint declaration by the three leaders stated they recognised the importance of establishing an electrical grid between Egypt, Cyprus and Greece, building on the framework agreement between the Egyptian Electricity Holding Company and the Euro Africa Interconnector Company on 22 May 2019.

GE Renewable Energy is a manufacturing and services division of the American company General Electric. It is headquartered in Boulogne-Billancourt, France and focuses on the production of energy systems that use renewable sources. Its products include wind, hydroelectric and solar power generating facilities. It is the world’s largest wind turbine manufacturer.

Siemens Energy AG is an energy company formed through the spin-off of the former Gas and Power division of Siemens, and it includes full ownership of Siemens Gamesa.















