Related Research Articles

The Northrop GrummanEA-6B Prowler is a twin-engine, four-seat, mid-wing electronic-warfare aircraft derived from the A-6 Intruder airframe. The EA-6A was the initial electronic warfare version of the A-6 used by the United States Marine Corps and United States Navy; it was used during the Vietnam War. Development on the more advanced EA-6B began in 1966. An EA-6B aircrew consisted of one pilot and three Electronic Countermeasures Officers, though it was not uncommon for only two ECMOs to be used on missions. It was capable of carrying and firing anti-radiation missiles (ARMs), such as the AGM-88 HARM.

The Raytheon Company was a major U.S. defense contractor and industrial corporation with manufacturing concentrations in weapons and military and commercial electronics. It was previously involved in corporate and special-mission aircraft until early 2007. Raytheon was the world's largest producer of guided missiles. In April 2020, the Raytheon Company merged with United Technologies Corporation to form Raytheon Technologies, which changed its name to RTX Corporation in July 2023.

An active electronically scanned array (AESA) is a type of phased array antenna, which is a computer-controlled antenna array in which the beam of radio waves can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antenna. In the AESA, each antenna element is connected to a small solid-state transmit/receive module (TRM) under the control of a computer, which performs the functions of a transmitter and/or receiver for the antenna. This contrasts with a passive electronically scanned array (PESA), in which all the antenna elements are connected to a single transmitter and/or receiver through phase shifters under the control of the computer. AESA's main use is in radar, and these are known as active phased array radar (APAR).

An electronic countermeasure (ECM) is an electrical or electronic device designed to trick or deceive radar, sonar, or other detection systems, like infrared (IR) or lasers. It may be used both offensively and defensively to deny targeting information to an enemy. The system may make many separate targets appear to the enemy, or make the real target appear to disappear or move about randomly. It is used effectively to protect aircraft from guided missiles. Most air forces use ECM to protect their aircraft from attack. It has also been deployed by military ships and recently on some advanced tanks to fool laser/IR guided missiles. It is frequently coupled with stealth advances so that the ECM systems have an easier job. Offensive ECM often takes the form of jamming. Self-protecting (defensive) ECM includes using blip enhancement and jamming of missile terminal homers.

Radar warning receiver (RWR) systems detect the radio emissions of radar systems. Their primary purpose is to issue a warning when a radar signal that might be a threat is detected, like a fighter aircraft's fire control radar. The warning can then be used, manually or automatically, to evade the detected threat. RWR systems can be installed in all kind of airborne, sea-based, and ground-based assets such as aircraft, ships, automobiles, military bases.
Northrop Grumman Electronic Systems (NGES) was a business segment of Northrop Grumman from 1996 to 2015 until a reorganization on January 1, 2016 merged other Northrop Grumman businesses into NGES to form a new segment called Mission Systems. NGES had originally been created by Northrop Grumman's acquisition of Westinghouse Electronic Systems Group in 1996. The Electronic Systems sector was a designer, developer, and manufacturer of a wide variety of advanced defense electronics and systems. The division had 120 locations worldwide, including 72 international offices, and approximately 24,000 employees; accounting for 20% of company sales in 2005.

The ADM-160 MALD is an air-launched, expendable decoy missile developed by the United States. Later variants (MALD-J) are additionally equipped with electronic countermeasures to actively jam early warning and target acquisition radars.

The AN/APG-63 and AN/APG-70 are a family of all-weather multimode radar systems designed by Hughes Aircraft for the F-15 Eagle air superiority fighter. These X band pulse-Doppler radar systems are designed for both air-air and air-ground missions; they are able to look up at high-flying targets and down at low-flying targets without being confused by ground clutter. The systems can detect and track aircraft and small high-speed targets at distances beyond visual range down to close range, and at altitudes down to treetop level. The radar feeds target information into the aircraft's central computer for effective weapons delivery. For close-in dogfights, the radar automatically acquires enemy aircraft and projects this information onto the cockpit head-up display. The name is assigned from the Army Navy Joint Electronics Type Designation System.

The General Dynamics–Grumman EF-111A Raven is a retired electronic-warfare aircraft designed to replace the EB-66 Destroyer in the United States Air Force. Its crews and maintainers often called it the "Spark-Vark", a play on the F-111's "Aardvark" nickname.

An infrared countermeasure (IRCM) is a device designed to protect aircraft from infrared homing missiles by confusing the missiles' infrared guidance system so that they miss their target. Heat-seeking missiles were responsible for about 80% of air losses in Operation Desert Storm. The most common method of infrared countermeasure is deploying flares, as the heat produced by the flares creates hundreds of targets for the missile.

Hughes AN/TPQ-36 Firefinder weapon locating system is a mobile radar system developed in the mid-late 1970s by Hughes Aircraft Company and manufactured by Northrop Grumman and ThalesRaytheonSystems, achieving initial operational capability in May 1982. The system is a "weapon-locating radar", designed to detect and track incoming mortar, artillery and rocket fire to determine the point of origin for counter-battery fire. It is currently in service at battalion and higher levels in the United States Army, United States Marine Corps, Australian Army, Portuguese Army, Turkish Army, and the Armed Forces of Ukraine.

In the U.S. Air Force, an electronic warfare officer (EWO) is a trained aerial navigator who has received training in enemy threat systems, electronic warfare principles and overcoming enemy air defense systems. These officers are specialists in finding, identifying and countering air defense systems and also radar-, infrared- and optically guided surface-to-air missiles, anti-aircraft artillery as well as enemy fighter planes. In aircraft that could penetrate enemy airspace EWOs protect their aircraft using radar jamming, chaff and flares to deceive potential threats. In other aircraft EWOs work to gather intelligence information on potential enemy air defense systems and communication systems.

The Boeing E-767 is an Airborne Warning and Control System (AWACS) aircraft that was designed in response to the Japan Air Self-Defense Force's requirements. It is essentially the Boeing E-3 Sentry's surveillance radar and air control system installed on a Boeing 767-200.

The AN/APG-81 is an active electronically scanned array (AESA) fire-control radar system designed by Northrop Grumman Electronic Systems for the Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II.

A missile approach warningsystem (MAW) is part of the avionics package on some military aircraft. A sensor detects attacking missiles. Its automatic warning cues the pilot to make a defensive maneuver and deploy the available countermeasures to disrupt missile tracking.

The AN/SPY-6 is an active electronically scanned array 3D radar under development for the United States Navy (USN). It will provide integrated air and missile defense for Flight III Arleigh Burke-class destroyers. Variants are under development for retrofitting Flight IIA Arleigh Burkes and for installation aboard Constellation-class frigates, Gerald R. Ford-class aircraft carriers, America-class amphibious assault ships, and San Antonio-class amphibious transport docks.
The Next Generation Jammer is a program to develop an airborne electronic warfare system, as a replacement for the AN/ALQ-99 found on the EA-18G military aircraft. It reached Initial Operating Capability in 2021.
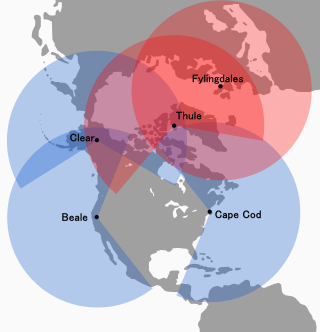
The Solid State Phased Array Radar System is a United States Space Force radar, computer, and communications system for missile warning and space surveillance. There are SSPARS systems at five sites: Beale Air Force Base, CA, Cape Cod Space Force Station, MA, Clear Space Force Station, AK, RAF Fylingdales, UK, and Pituffik Space Base, Greenland. The system completed replacement of the RCA 474L Ballistic Missile Early Warning System when the last SSPAR was operational at then-Clear Air Force Station in 2001.
References
- ↑ "$400m Hornet radar contract 'dumped' – Breaking News – National – Breaking News". The Age. Australia. 13 September 2006. Retrieved 15 February 2012.